Abstract
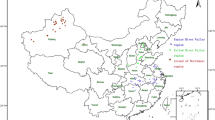
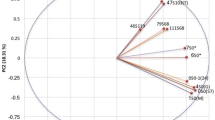
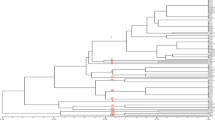
Twenty five isolates of Acidovorax avenae subsp. avenae causing bacterial leaf streak collected from infected maize crop grown in different geographical regions of Punjab, northern India were characterized for their molecular diversity using twenty five random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers. All the primers showed amplification with a total of 1769 amplified fragments. Among RAPD primers, S112 was found to be highly polymorphic with PIC value of 0.95 while OPT-4 was least polymorphic. The size of amplified DNA fragments ranged from 59 bp to 3.9 kbp. Dendrogram based on molecular data generated by 25 RAPD collectively divided all 25 isolates into four groups. From 25 isolates, 20 were used for their pathological characterization and based on the multivar cluster analysis of pathogenicity data, these were divided into three groups, each producing a distinct range of disease score on particular maize inbred/hybrid used in this study. Isolate Aaa2 was found to be the most virulent with an average disease score of 8.6, whereas Aaa17 was found least virulent with average disease score of 5.1. The most virulent isolates of this pathogen were present in central Punjab. This was the first attempt to study the genetic diversity and pathogenic variation in Punjab populations of A. avenae subsp. avenae.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Botstein D, White RL, Skolnick M, Davis RW (1980) Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet 32:314–331
Chen W, Wu J, Yuan H (2002) Identification of resistance on maize germplasm to maize ear rot. J Maize Sci 10:59–60
Chen J, Ding J, Li H, Li Z, Sun X, Li J, Wang R, Dai X, Dong H, Song W, Chen W, Xia Z, Wu J (2012) Detection and verification of quantitative trait loci for resistance to fusarium ear rot in maize. Mol Breed 30:1649–1656
Dange S. R. S., (1972). Studies on bacterial stripe disease of maize caused by Pseudomonas rubrilineans. Ph.D. Thesis. Postgraduate school. Indian Agriculture Research Institute, New Delhi, India
Dhkal M, Hunjan MS, Kaur H (2015) Phenotypic diversity in Acidovorax avenae subsp. avenae causing bacterial leaf streak of maize. Plant Disease Research 30:150–155
Dhkal M, Hunjan MS, Kaur H (2016a) Molecular identification of the pathogen causing bacterial leaf streak disease of maize and standardization of inoculation technique. Plant Disease Research 31:79–85
Dhkal M, Hunjan MS, Kaur H, Kaur R (2016b) Biochemical basis of bacterial leaf streak resistance in maize. Indian Phytopathol 69:373–380
FAOSTAT, (2014). Statistical databases and data-sets of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data
Fontana DP, Rago AM, Fontana CA, Vignolo GM, Cocconcelli PS, Mariotti JA (2013) Isolation and genetic characterization of Acidovorax avenae from red stripe infected sugarcane in northwestern Argentina. Eur J Plant Pathol 137:525–534
Hunjan M. S., (2012). Pathogenic and molecular characterization of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae [(Ishiyama) Swings et al.] causing bacterial blight of rice. PhD Thesis, Punjab Agricultural University, India
Johnson AG, Robert AL, Cash L (1945) Further studies of bacterial leaf blight and stalk rot of corn. Phytopathology 35:486 (Abstract)
Kaur H, Mohan C, Vikal Y, Singh M (2014) Pathogenic and molecular characterization of Fusarium moniliforme Sheld, the incitant of fusarium maize stalk rot in the Punjab state of India. Maydica 59:290–297
Kumar A., (2015). Genetic diversity of Erwinia chrysanthemi pv. zeae causing bacterial stalk rot of maize and its management. PhD Thesis, Punjab Agricultural University, India
Kumar A, Hunjan MS, Kaur H, Dhillon HK, Singh PP (2017) Biochemical responses associated with resistance to bacterial stalk rot caused by Dickeya zeae in maize. J Phytopathol 165:822–832
Lakshmi DL, Rabindran R (2012) Molecular variability in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae isolates of Tamil Nadu. Indian J Plant Protect 40:123–128
Lore JS, Vikal Y, Hunjan MS, Goel RK, Bharaj TS, Raina GL (2011) Genotypic and pathotypic diversity of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae, the cause of bacterial blight of rice in Punjab state of India. J Phytopathol 159:479–487
Mäki-Valkam T, Karjalainen R (1994) Differentiation of Erwinia carotovora subsp. atroseptica and carotovora by RAPD-PCR. Ann Appl Biol 125:301–309
Maschietto V, Colombi C, Pirona R, Pea G, Strozzi F, Marocco A, Rossini L, Lanubile A (2017) QTL mapping and candidate genes for resistance to fusarium ear rot and fumonisin contamination in maize. BMC Plant Biol 17:20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-017-0970-1
Mir ZR, Singh PK, Zaidi PH, Vinayan MT, Sharma SS, Krishna MK, Vemula AK, Rathore A, Nair SK (2018) Genetic analysis of resistance to post flowering stalk rot in tropical germplasm of maize (Zea mays L.). Crop Prot 106:42–49
Parent JG, Lacroix M, Page D, Vezina L (1996) Identification of Erwinia carotovora from soft rot diseased plants by random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) analysis. Plant Dis 80:494–499
Pataky JK, Toit du LJ, Kerns MR (1997) Bacterial leaf blight on shrunken-2 sweet corn. Plant Dis 81:1293–1298
Saiki RK, Gelfand DH, Stoffel S, Scharf SJ, Higuchi R, Horn GT, Mullis KB, Erlich HA (1988) Primer directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science 239:487–491
Shahrestani AT, Kazempour MN, Ebadie AA, Elahinia SA (2012) Genetic diversity of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in rice fields of Guilan Province (Iran) using RAPD markers. Agric Trop Subtrop 45:60–65
Sharma RC, Rai SN (2005) Evaluation of maize inbred lines for resistance to maydis leaf blight. Indian Phytopathol 58:339–340
Shrestha RK, Rosenberg T, Makarovsky D, Eckshtain-Levi N, Zelinger E, Kopelowits J, Sikorski J, Burdman S (2013) Phenotypic variation in the plant pathogenic bacterium Acidovorax citrulli. PLoS One 8:e73189. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0073189
Silva KMM, Xavier AS, Gama MAS, Lima NB, Lyra MCCP, Mariano RLR, Souza EB (2016) Polyphasic analysis of Acidovorax citrulli strains from northeastern Brazil. Sci Agric 73:252–259
Sinha SK, Prasad M (1975) Varietal screening of maize germplasm against stalk rot pathogen Erwinia carotovora f. Sp. zeae. Labdev J Sci Technol 13:128–133
Smith DR, White DG (1988) Diseases of corn. In: Sprague GF, Dudley JW (eds) Corn and corn improvement. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, pp 687–766
Techati N (2008) Identification and genetic diversity of bacterial leaf streak of corn. Kasetasrt University, Thailand, MSc Thesis
Thind BS (2012) Phytopathogenic Procaryotes and plant diseases. Scientific Publishers, Jodhpur, India
Ullasa BA, Mehta YR, Payak MM (1967) Xanthomonas rubrilineans on Zea mays in India. Indian Phytopathol 20:77–78
Willems A, Goor M, Thielemans S, Gillis M, Kersters K, De Ley J (1992) Transfer of several phytopathogenic Pseudomonas species to Acidovorax as Acidovorax avenae subsp. avenae subsp. nov., Comb.nov., Acidovorax avenae subsp. citrulli, Acidovorax avenae subsp. cattleyae, and Acidovorax konjaci. Int J Syst Bacteriol 42:107–119
Zivanovic M, Walcott RR (2017) Further characterization of genetically distinct groups of Acidovorax citrulli strains. Phytopathology 107:29–35
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dhkal, M., Hunjan, M.S., Kaur, H. et al. Characterization of Acidovorax avenae subsp. avenae causing bacterial leaf streak of maize in Punjab state of India. J Plant Pathol 101, 71–79 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42161-018-0138-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42161-018-0138-3