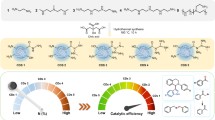
Abstract
Volatile organic compounds including toluene have high carcinogenicity and are very harmful to human health. In this work, an efficient nanocomposite photocatalyst of TiO2@MIL-101(Cr) were synthesized by hydrothermal method. The photocatalytic performances of catalysts were analyzed by the degradation of toluene. The toluene removal efficiency of TiO2@MIL-101(Cr) was 23.28% higher than that of MIL-101(Cr), and 26.88% higher than that of bare TiO2. X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscope results confirmed the successful synthesis of nanocomposite photocatalyst constructed of TiO2 nanoparticles and regular octahedral MIL-101(Cr). Compared with bare TiO2 nanoparticles, the specific surface area of TiO2@MIL-101(Cr) was improved from 49.4 to 136.08 m2 g−1. The reduced photoluminescence intensity of nanocomposite indicates the effective charge separation, which can increase the lifetime of charge carriers and improve the efficiency of interfacial charge transfer to the surface. The enhanced removal efficiency of the composites are mainly owing to the expansion of light response range, the suppress of electron (e−) and holes (h+) recombination, the promotion of the electron transfer and the improved toluene adsorption ability of TiO2@MIL-101(Cr).
Graphical abstract
In this work, an efficient nanocomposite photocatalyst of TiO2@MIL-101(Cr) were synthesized by hydrothermal method. The toluene removal efficiency of TiO2@MIL-101(Cr) was 23.28% higher than that of MIL-101(Cr), and 26.88% higher than that of bare TiO2.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang H, Chen C, Yang R, Yu Y, Albilali R, He C (2020) Remarkable promotion effect of lauric acid on Mn-MIL-100 for non-thermal plasma-catalytic decomposition of toluene. Appl Surf Sci 503:144290
Wang Q, Rhimi B, Wang H, Wang CY (2020) Efficient photocatalytic degradation of gaseous toluene over F-doped TiO2/exfoliated bentonite. Appl Surf Sci 530:147286
Zhang YG, Wu MY, Wang YF, Kwok YH, Pan WD, Szeto W, Huang HB, Leung DY (2021) Fluorinated TiO2 coupling with α-MnO2 nanowires supported on different substrates for photocatalytic VOCs abatement under vacuum ultraviolet irradiation. Appl Catal B Environ 140:117–134
Zhang Z, Jiang Z, Shang GW (2016) Low-temperature catalysis for VOCs removal in technology and application: a state-of-the-art review. Catal Today 264:270–278
Huang Y, Ho SSH, Niu R, Xu L, Lu Y, Cao J, Lee SC (2016) Removal of indoor volatile organic compounds via photocatalytic oxidation: a short review and prospect. Molecules 21:56
Luengas A, Barona A, Hort C, Gallastegui G, Platel V, Elias A (2015) A review of indoor air treatment technologies. Rev Environ Sci Bio/Technol 14:499–522
Huang ZH, Chen H, Zhao L, He X, Fang W, Du YY, Li WX, Wang GH, Zhang FQ (2018) CdSe QDs sensitized MIL-125/TiO2@SiO2 biogenic hierarchical composites with enhanced photocatalytic properties via two-level heterostructure. J Mater Sci 29:12045–12054
Feizpoor S, Habibi-Yangjeh A, Yubuta K (2018) Integration of carbon dots and polyaniline with TiO2 nanoparticles:substantially enhanced photocatalytic activity to removal various pollutants under visible light. J Photochem Photobiol A 367:94–104
Basavarajappa PS, Patil SB, Ganganagappa N, Reddy KR, Raghu AV, Reddy CV (2019) Recent progress in metal-doped TiO2, non-metal doped/codoped TiO2 and TiO2 nanostructured hybrids for enhanced photocatalysis. Polyhedron 45:7764–7778
Sheng HB, Chen DY, Li NJ, Xu QF, Li H, He JH, Lu JM (2017) Urchin-inspired TiO2@MIL-101 double-shell hollow particles: adsorption and highly efficient photocatalytic degradation of hydrogen sulfide. Chem Mater 29:5612–5616
Ma YJ, Tang Q, Sun WY, Yao ZY, Zhu WH, Li T, Wang JY (2020) Assembling ultrafine TiO2 nanoparticles on UiO-66 octahedrons to promote selective photocatalytic conversion of CO2 to CH4 at a low concentration. App Catal B Environ 270:118856
Ge M, Cao C, Huang J, Li S, Chen Z, Zhang KQ, Al-Deyab SS, Lai Y (2016) A review of one-dimensional TiO2 nanostructured materials for environmental and energy applications. J Mater Chem A 4:6772–6801
Tilgner D, Klarner M, Hammon S, Friedrich M, Verch A, Jonge ND, Kümmel ES, Kempe R (2019) H2-generation from alcohols by the MOF-based noble metal-free photocatalyst Ni/CdS/TiO2@MIL-101. Aust J Chem 72:842–847
Zheng X, Xu S, Wang Y, Sun X, Gao Y, Gao B (2018) Enhanced degradation of ciprofloxacin by graphitized mesoporous carbon (GMC)-TiO2 nanocomposite: strong synergy of adsorption-photocatalysis and antibiotics degradation mechanism. J Colloid Interface Sci 527:202–213
Wang M, Cui Z, Yang M, Lin L, Chen X, Wang M, Han J (2019) Core/shell structured CdS/polydopamine/TiO2 ternary hybrids as highly active visible-light photocatalysis. J Colloid Interface Sci 544:1–7
Chang N, Zhang H, Shi MS, Li J, Shao W, Wang T (2017) Metal-organic framework templated synthesis of TiO2@MIL-101 core–shell architectures for high-efficiency adsorption and photocatalysis. Mater Lett 200:55–58
Liu XC, Zhou YY, Zhang JC, Tang L, Lu L, Zeng GM (2017) Iron containing metal-organic frameworks: structure, synthesis, and applications in environmental remediation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 24:20255–20275
Lia NX, Huang HL, Bibi RN, Shen QH, Ngulube RC, Zhoua JC, Liu MC (2019) Noble-metal-free MOF derived hollow CdS/TiO2 decorated with NiS cocatalyst for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Appl Surf Sci 476:378–386
Ma X, Li L, Zeng Z, Chen R, Wang C, Zhou K, Su C, Li H (2019) Synthesis of nitrogenrich nanoporous carbon materials with C3N-type from ZIF-8 for methanol adsorption. Chem Eng J 363:49–56
Dhakshinamoorthy A, Asiri AM, Garcia H (2016) Metal-organic framework (MOF) compounds: photocatalysts for redox reactions and solar fuel production. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 55:5414–5445
Wang B, Lv XL, Feng D, Xie LH, Zhang J, Li M, Xie Y, Li JR, Zhou HC (2016) Highly stable Zr(IV)-based metal-organic frameworks for the detection and removal of antibiotics and organic explosives in water. J Am Chem Soc 138:6204–16
Rosser TE, Windle CD, Reisner E (2016) Electrocatalytic and solar-driven CO2 reduction to CO with a molecular manganese catalyst immobilized on mesoporous TiO2. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 55:7388–7392
Mehrabadi Z, Faghihian H (2018) Comparative photocatalytic performance of TiO2 supported on clinoptilolite and TiO2 /Salicylaldehyde-NH2-MIL-101(Cr) fordegradation of pharmaceutical pollutant atenolol under UV and visible Irradiations. J Photoch Photobio A 356:102–111
Wang W, Xu D, Cheng B, Yu J, Jiang C, Mater J (2017) Hybrid carbon@TiO2 hollow spheres with enhanced photocatalytic CO2 reduction activity. Chem A 5:5020–5029
Fang YY, Zhao GH, Dai W, Ma LY, Ma N (2017) Enhanced adsorption of rubidium ion by a phenol@MIL-101(Cr) composite material. Microporous Mesoporous Mat 25:151–57
Wang CC, Wang X, Liu W (2019) The synthesis strategies and photocatalytic performances of TiO2/MOFs composites: a State-of-the-Art review. Chem Eng J 391:12301
He X, Fang H, Gosztola DJ, Jiang Z, Jena P, Wang WN (2019) Mechanistic insight into photocatalytic pathways of MIL-100(Fe)/TiO2 composites. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:12516–12524
Xie PT, Liu Y, Feng M, Niu M, Liu CZ, Wu NN, Sui KY, Patil RR, Pan D, Guo ZH, Fan RH (2021) Hierarchically porous Co/C nanocomposites for ultralight high-performance microwave absorption. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 4:173–185
Luo F, Liu DQ, Cao TS, Cheng HF, Kuang JC, Deng YJ, Xie W (2021) Study on broadband microwave absorbing performance of gradient porous structure. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00275-4
Lu XK, Zhu DM, Li X, Li MH, Chen Q, Qing YC (2021) Gelatin-derived N-doped hybrid carbon nanospheres with an adjustable porous structure for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00258-5
Wu NN, Du WJ, Hu Q, Vupputuri S, Jiang QL (2021) Recent development in fabrication of Co nanostructures and their carbon nanocomposites for electromagnetic wave absorption. Eng Sci 13:11–23
Yang X, Qi X, Ma GQ, Li ZY, Liu Q, Khan S, Zhao YJ, Zhang LL, Geng Z, Guo YN (2019) Novel Z-Scheme Ag/TiO2 /AgMIL-101(Cr) as an efficient photocatalyst for nitrogen production from nitrate. Appl Surf Sci 479:1048–1056
Yang X, Ma FY, Li KX, Guo YN, Hu JL, Li W, Huo MX, Guo YH (2010) Mixed phase titania nanocomposite codoped with metallic silver and vanadium oxide: new efficient photocatalyst for dye degradation. J Hazard Mater 175:429–438
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21806101), Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (No. 16ZR1412600), Research Center of Resource Recycling Science and Engineering, Shanghai Polytechnic University and Gaoyuan Discipline of Shanghai - Environmental Science and Engineering (Resource Recycling Science and Engineering), Cultivate discipline fund of Shanghai Polytechnic University (No.XXKPY1601), and Postgraduate Foundation of Shanghai Polytechnic University (EGD17YJ0026, EGD18YJ0059, EGD18YJ0062).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Z., Wang, M., Fan, J. et al. TiO2@MIL-101(Cr) nanocomposites as an efficient photocatalyst for degradation of toluene. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 4, 1322–1329 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00337-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00337-7