Abstract
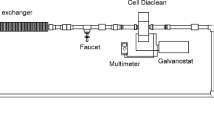
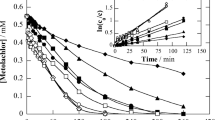
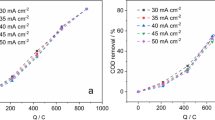
Synthetic solutions of 2-chlorophenol (2-CP, 1 mM) were treated in an undivided continuous flow electrochemical reactor equipped with boron-doped diamond (BDD) electrodes. The process was conducted at different current densities (j = 0.10, 0.125, and 0.14 A cm−2), initial pH (4.0, 7.3, and 9.0), and volumetric flow rate (Q = 0.5, 1.0, and 1.5 L min−1). The results of this study showed that the best operational conditions were: j = 0.14 A cm−2, pH = 7.3, and y Q = 1 L min−1. Under these operational conditions the degradation and mineralization of 2-CP were, 100% and 96%, respectively, after 6 h of electrolysis time. The by-products were identified by UHPLC. Also, it was found that the electrochemical degradation of 2-chlorophenol follows a pseudo-first order kinetics. Furthermore, these results demonstrate that the electrolysis process employed in this work allows high percentages (96%) of mineralization of 2-CP, a relative low treatment cost ($ 3 MXN/ 2.5 L of synthetic solution), and that the process is applicable to remediate wastewater.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajeel MA, Aroua MK, Daud WMAW (2015) Anodic degradation of 2-Chlorophenol by carbon black diamond and activated carbon composite electrodes. Electrochim Acta 180:22–28
Ajeel MA, Aroua MK, Daud WMAW, Mazari SA (2017) Effect of adsorption and passivation phenomena on the electrochemical oxidation of phenol and 2-Chlorophenol at carbon black diamond composite electrode. Ind Eng Chem Res 56(6):1652–1660
Amado-Piña D, Roa-Morales G, Barrera-Díaz C, Balderas-Hernandez P, Romero R, Martín del Campo E, Natividad R (2017) Synergic effect of ozonation and electrochemical methods on oxidation and toxicity reduction: phenol degradation. Fuel 198:82–90
Ba-Abbad MM, Takriff MS, Kadhum AAH, Mohamad AB, Benamor A, Mohammad AW (2017) Solar photocatalytic degradation of 2-chlorophenol with ZnO nanoparticles: optimisation with D-optimal design and study of intermediate mechanisms. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(3):2804–2819
Baskin S, Salem H (1997) Oxidants, antioxidants and free radicals, Taylor & Francis
Borràs N, Oliver R, Arias C, Brillas E (2010) Degradation of atrazine by electrochemical advanced oxidation processes using a boron-doped diamond anode. J Phys Chem A 114(24):6613–6621
Brillas E, Sirés I, Arias C, Cabot PL, Centellas F, Rodríguez RM, Garrido JA (2005) Mineralization of paracetamol in aqueous medium by anodic oxidation with a boron-doped diamond electrode. Chemosphere 58(4):399–406
Brillas E, Sirés I, Oturan MA (2009) Electro-Fenton process and related electrochemical technologies based on Fenton’s reaction chemistry. Chem Rev 109(12):6570–6631
Brown CJ, Pletcher D, Walsh FC, Hammond JK, Robinson D (1992) Local mass transport effects in the FM01 laboratory electrolyser. J Appl Electrochem 22(7):613–619
Cornejo OM, Murrieta MF, Castañeda LF, Nava JL (2019) Characterization of the reaction environment in flow reactors fitted with BDD electrodes for use in electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: A critical review. Electrochim Acta: 135373
Chang C-F, Chen T-Y, Chin C-JM, Kuo Y-T (2017) Enhanced electrochemical degradation of ibuprofen in aqueous solution by PtRu alloy catalyst. Chemosphere 175:76–84
Dercová K, Sejáková Z, Skokanová M, Barančíková G, Makovníková J (2007) Bioremediation of soil contaminated with pentachlorophenol (PCP) using humic acids bound on zeolite. Chemosphere 66(5):783–790
Enache TA, Chiorcea-Paquim A-M, Fatibello-Filho O, Oliveira-Brett AM (2009) Hydroxyl radicals electrochemically generated in situ on a boron-doped diamond electrode. Electrochem Commun 11(7):1342–1345
Ezerskis Z, Jusys Z (2001) Oxidation of chlorophenols on Pt electrode in alkaline solution studied by cyclic voltammetry, galvanostatic electrolysis, and gas chromatographymass spectrometry. Pure Appl Chem 73:1929
Guinea E, Arias C, Cabot PL, Garrido JA, Rodríguez RM, Centellas F, Brillas E (2008) Mineralization of salicylic acid in acidic aqueous medium by electrochemical advanced oxidation processes using platinum and boron-doped diamond as anode and cathodically generated hydrogen peroxide. Water Res 42(1–2):499–511
Huang CP, Chu C-s (2012) Indirect electrochemical oxidation of Chlorophenols in dilute aqueous solutions. J Environ Eng 138(3):375–385
Ikehata K, Jodeiri Naghashkar N, Gamal El-Din M (2006) Degradation of aqueous pharmaceuticals by ozonation and advanced oxidation processes: a review. Ozone Sci Eng 28(6):353–414
Keith L, Telliard W (1979) ES&T Special Report: priority pollutants: I-a perspective view. Environ Sci Technol 13(4):416–423
Kim S, Kim YK (2004) Apparent desorption kinetics of phenol in organic solvents from spent activated carbon saturated with phenol. Chem Eng J 98(3):237–243
Li X-y, Y-h C, Y-j F, Xie Z-m GJ-D (2005) Reaction pathways and mechanisms of the electrochemical degradation of phenol on different electrodes. Water Res 39(10):1972–1981
Lim CH, Ang JJ, Lau S, Tay MG (2017) Optimization of hydroxyl radical production using electro-Fenton method for chemical oxygen demand reduction in diluted palm oil mill effluent. Water Environ J 31(4):578–583
Liu H, Zhang Z, Ren M, Guan J, Lu N, Qu J, Yuan X, Zhang YN (2018) Preparation of the CNTs/AG/ITO electrode with high electro-catalytic activity for 2-chlorophenol degradation and the potential risks from intermediates. J Hazard Mater 359:148–156
Michaud PA, Panizza M, Ouattara L, Diaco T, Foti G, Comninellis C (2003) Electrochemical oxidation of water on synthetic boron-doped diamond thin film anodes. J Appl Electrochem 33(2):151–154
Nava JL, Sirés I, Brillas E (2014) Electrochemical incineration of indigo. A comparative study between 2D (plate) and 3D (mesh) BDD anodes fitted into a filter-press reactor. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(14):8485–8492
Oturan MA, Aaron J-J (2014) Advanced oxidation processes in water/wastewater treatment: principles and applications. A Review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Tech 44(23):2577–2641
Panizza M (2014) Anodic oxidation of benzoquinone using diamond anode. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(14):8451–8456
Panizza M, Cerisola G (2009) Direct and mediated anodic oxidation of organic pollutants. Chem Rev 109(12):6541–6569
Peralta E, Ruiz M, Martinez G, Mentado-Morales J, Zarate LG, Cordero ME, Garcia-Morales MA, Natividad R, Regalado-Mendez A (2018) Degradation of 4-Chlorophenol in a batch electrochemical reactor using BDD electrodes. Int J Electrochem Sci 13(5):4625–4639
Polcaro AM, Palmas S (1997) Electrochemical oxidation of Chlorophenols. Ind Eng Chem Res 36(5):1791–1798
Polcaro AM, Palmas S, Renoldi F, Mascia M (1999) On the performance of Ti/SnO2 and Ti/PbO2 anodesin electrochemical degradation of 2-chlorophenolfor wastewater treatment. J Appl Electrochem 29(2):147–151
Ramírez C, Saldaña A, Hernández B, Acero R, Guerra R, Garcia-Segura S, Brillas E, Peralta-Hernández JM (2013) Electrochemical oxidation of methyl orange azo dye at pilot flow plant using BDD technology. J Ind Eng Chem 19(2):571–579
Regalado-Méndez A, Mentado-Morales J, Vázquez Carlos E, Martínez-Villa G, Cordero Mario E, Zárate LG, Skogestad S, Peralta-Reyes E (2018) Modeling and hydraulic characterization of a filter-press-type electrochemical reactor by using residence time distribution analysis and hydraulic indices. Int J Chem React Eng 16
Skoumal M, Arias C, Cabot PL, Centellas F, Garrido JA, Rodríguez RM, Brillas E (2008) Mineralization of the biocide chloroxylenol by electrochemical advanced oxidation processes. Chemosphere 71(9):1718–1729
Tarr MA (2003) Chemical degradation methods for wastes and pollutants: environmental and industrial applications. CRC press
Yoon J, Lee B, Choi S, Won M, Shim Y (2012) Electrochemical degradation of phenol and 2-chloro phenol using Pt/Ti and boron-doped diamond electrodes. B Korean Chem Soc 33(7):2274–2278
Yoon JH, Jeong ED, Shim YB, Won MS (2004) Anodic degradation of toxic aromatic compound in the flow through cell with carbon Fiber electrode. Key Eng Mat 277-279:445–449
Acknowledgements
Authors thank PRODEP and CONACYT for the financial support (Project DSA/103/14/11350, 2014; CUP: 2 IE1503 and CONACYT No. 269093). Also, Mayra Castellanos thanks PRODEP for the scholarship to complete her bachelor thesis (Through the items ID 32643, 32646, and 32651 of the project DSA/103/14/11350, 2014; CUP: 2 IE1503).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peralta-Reyes, E., Natividad, R., Castellanos, M. et al. Electro-oxidation of 2-chlorophenol with BDD electrodes in a continuous flow electrochemical reactor. J Flow Chem 10, 437–447 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41981-020-00079-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41981-020-00079-5