Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the value of quantitative features extracted from multi-modality ultrasound, composed of B-mode ultrasound (BUS), strain elastography (SE), and contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS), in the early differentiation of residual tumors from hyperemic rim after ablation for rabbit VX2 liver tumors.
Methods
The study included sixteen rabbits undergoing ablation for normal liver tissue or VX2 liver tumors. BUS, SE, and CEUS examinations of rabbit livers were performed on day 3 and day 7 after ablation. A total of 108 radiomics features were extracted. Spearman rank correlation, the t-test, Kruskal-Wallis test (KW-test), and the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) method were applied to analyze data. The support vector machine (SVM) and logistic regression (LR) classifiers were used to classify hyperemic rim and residual tumors under the leave-one-out cross-validation. Model performance was validated by the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC).
Results
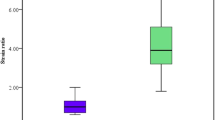
All ultrasound modalities had features that significantly differed between hyperemic rim and residual tumors, such as the maximal value of BUS, the entropy of brightness of SE, and the skewness value of CEUS (all p < 0.05). For the differentiation between hyperemic rim and residual tumors after ablation, the AUC of multi-modality ultrasound was 93.3% on day 3 and 82.1% on day 7.
Conclusion
The multi-modality ultrasound radiomics is helpful for the early differentiation between hyperemic rim and residual tumors around the ablation area in a rabbit model, which might improve future ablation for liver tumors.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ziemlewicz, T. J., Wells, S. A., Lubner, M. G., Brace, C. L., Lee, F. T., & Hinshaw, J. L. (2016).Hepatic Tumor Ablation. Surgical Clinics. 96(2),315–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suc
Shiina, S., Tateishi, R., Arano, T., Uchino, K., Enooku, K., Nakagawa, H., asaoka, Y., Sato, T., Masuzaki, R., Kondo, Y., Goto, T., Yoshida, H., Omata, M., & Koike, K. (2012). Radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: 10-year outcome and prognostic factors. American Journal Of Gastroenterology, 107(4), 569. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2011.425.
Nakajima, K., Yamanaka, T., Nakatsuka, A., Haruyuki, T., Fujimori, M., Sugino, Y., Matsushita, N., Sakuma, H., Isaji, S., Takei, Y., & Yamakado, K. (2016). Clinical utility of radiofrequency ablation following transarterial injection of miriplatin-iodized oil suspension in small hepatocellular carcinoma. Japanese journal of radiology, 34(9), 640–646. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-016-0567-x
McWilliams, J. P., Yamamoto, S., Raman, S. S., Loh, C. T., Lee, E. W., Liu, D. M., & Kee, S. T. (2010). Percutaneous ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: Current status. Journal Of Vascular And Interventional Radiology, 21(8), S204–S213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvir.2009.11.025
Nahum Goldberg, S., Grassi, C. J., Cardella, J. F., Charboneau, J. W., Dodd, G. D., Dupuy, D. E., Gervais, D., Gillams, A.R., Kane, R.A., LeeJr, F.T., Livraghi, T., McGahan, J., Phillips, D.A., Rhim, H., & Silverman, S.G. (2009). Image-guided tumor ablation: Standardization of terminology and reporting criteria. Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology, 20, 377–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvir.2009.04.011
Clasen, S., Boss, A., Schmidt, D., Fritz, J., Schraml, C., Claussen, C. D., & Pereira, P. L. (2006). Magnetic resonance imaging for hepatic radiofrequency ablation. European journal of radiology, 59, 140–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2006.04.006
Kim, T. J., Moon, W. K., Cha, J. H., Goo, J. M., Lee, K. H., Kim, K. H., Lee, J. W., Han, J. G., Weinmann, H. J., & Chang, K. H. (2005). VX2 carcinoma in rabbits after radiofrequency ablation: Comparison of MR contrast agents for help in differentiating benign periablational enhancement from residual tumor. Radiology, 234, 423–430. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2342031456
Li, Y., Shi, G., Wang, S., Wang, S., & Wu, R. (2013). Iodine quantification with dual-energy CT: Phantom study and preliminary experience with VX2 residual tumour in rabbits after radiofrequency ablation. British Journal of Radiology, 86, 20130143. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20130143.
Wu, H., Patel, R. B., Zheng, Y., Solorio, L., Krupka, T. M., Ziats, N. P., Haaga, J. R., & Exner, A. A. (2012). Differentiation of benign periablational enhancement from residual tumor following radio-frequency ablation using contrast-enhanced ultrasonography in a rat subcutaneous colon cancer model. Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology, 38, 443–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2011.12.008
Fusco, R., Granata, V., Grazzini, G., Pradella, S., Borgheresi, A., Bruno, A., Palumbo, P., Bruno, F., Grassi, R., Giovagnoni, A., & Grassi, R. (2022). Radiomics in medical imaging: pitfalls and challenges in clinical management. Japanese Journal of Radiology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-022-01271-4
Cameron, A., Khalvati, F., Haider, M. A., & Wong, A. (2016). MAPS: A Quantitative Radiomics Approach for Prostate Cancer Detection. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 63, 1145–1156. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2015.2485779.
Zhang, Q., Xiao, Y., Suo, J., Shi, J., Yu, J., Guo, Y., Wang, Y., & Zheng, H. (2017). Sonoelastomics for breast tumor classification: A radiomics approach with clustering-based feature selection on sonoelastography. Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology, 43, 1058–1069. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2016.12.016
Peeken, J. C., Bernhofer, M., Wiestler, B., Goldberg, T., Cremers, D., Rost, B., Wilkens, J. J., Combs, S. E., & Nüsslin, F. (2018). Radiomics in radiooncology–challenging the medical physicist. Physica medica, 48, 27–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmp.2018.03.012
Petzold, G., Lasser, J., Rühl, J., Bremer, S. C., Knoop, R. F., Ellenrieder, V., Kunsch, S., & Neesse, A. (2020). Diagnostic accuracy of B-Mode ultrasound and Hepatorenal Index for graduation of hepatic steatosis in patients with chronic liver disease. PLoS One, 15(5), e0231044. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0231044
Ranjkesh, M., Hajibonabi, F., Seifar, F., Tarzamni, M. K., Moradi, B., & Khamnian, Z. (2020). Diagnostic value of elastography, strain ratio, and elasticity to B-mode ratio and color doppler ultrasonography in breast lesions. International Journal of General Medicine, 13, 215. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJGM.S247980.
Dietrich, C. F., Nolsøe, C. P., Barr, R. G., Berzigotti, A., Burns, P. N., Cantisani, V., Chammas, M. C., Chaubal, N., Choi, B. I., Clevert, D. A., & Cui, X. (2020). Guidelines and good Clinical Practice Recommendations for Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS) in the liver-update 2020 WFUMB in cooperation with EFSUMB, AFSUMB, AIUM and FLAUS: WFUMB in cooperation with EFSUMB, AFSUMB, AIUM and FLAUS. Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology, 41, 562–585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2020.04.030
Yao, Z., Dong, Y., Wu, G., Zhang, Q., Yang, D., Yu, J. H., & Wang, W. P. (2018). Preoperative diagnosis and prediction of hepatocellular carcinoma: Radiomics analysis based on multi-modal ultrasound images. Bmc Cancer, 18, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-5003-4
Lee, D. H., & Lee, J. M. (2018). Recent advances in the image-guided tumor ablation of liver malignancies: Radiofrequency ablation with multiple electrodes, real-time multimodality fusion imaging, and new energy sources. In Korean Journal of Radiology, 19, 545–559. https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.19.4.545.
Vilana, R., Bianchi, L., Varela, M., et al. (2006). Is microbubble enhanced ultrasonography sufficient for assessment of response to percutaneous treatment in patients with early hepatocellular carcinoma? European Radiology, 16, 2454–2462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-006-0264-8.
Yi, H., Cai, B., Ai, X., Li, K., Song, P., & Zhang, W. (2020). Early identification of residual tumors following microwave ablation using contrast-enhanced ultrasonography in a rabbit VX2 liver cancer model. BioMed Research International. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2462058
Yi, H. M., Cai, B. H., Ai, X., Li, K. Y., & Zhang, W. (2019). Establishment of rabbit liver VX2 tumor model using percutaneous puncture inoculation of tumor fragment guided and evaluated by ultrasonography. Current Medical Science, 39(5), 820–824.
Han, H., Jin, Y., Liu, R., Ji, Z., Pu, M., & Wang, W. (2021). Experimental study of shear wave dispersion imaging in evaluating inflammatory reaction zone after ablation in normal rabbit liver. Chinese Journal of Ultrasonography, 30(05), 441–445.
Gupta, S., Wallace, M. J., Cardella, J. F., Kundu, S., Miller, D. L., & Rose, S. C. (2010). Quality improvement guidelines for percutaneous needle biopsy. Journal of vascular and interventional radiology, 21, 969–975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvir.2010.01.011.
Abd Raziff, H. H., Tan, D., Tan, S. H., Wong, Y. H., Lim, K. S., Yeong, C. H., Sulaiman, N., Abdullah, B. J., Wali, H. A., Zailan, N. A., & Ahmad, H. (2021). Laser-heated needle for biopsy tract ablation: In vivo study of rabbit liver biopsy. Physica Medica, 82, 40–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmp.2021.01.067
Zhang, Q., Cai, Y., Hua, Y., Shi, J., Wang, Y., & Wang, Y. (2017). Sonoelastography shows that Achilles tendons with insertional tendinopathy are harder than asymptomatic tendons. Knee Surgery Sports Traumatology Arthroscopy, 25, 1839–1848. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-016-4197-8.
Lambin, P., Rios-Velazquez, E., Leijenaar, R., Carvalho, S., van Stiphout, R. G., Granton, P., & ML Z. C., Gillies, R., Boellard, R. Dekker, A., and Aerts, HJ,. (2012). Radiomics: Extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis. European journal of cancer, 48, 441–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2011.11.036
Xia, W., Hu, B., Li, H., Geng, C., Wu, Q., Yang, L., Yin, B., Gao, X., Li, Y., & Geng, D. (2021). Multiparametric-MRI-based radiomics model for differentiating primary central nervous system lymphoma from glioblastoma: Development and cross-vendor validation. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 53(1), 242–250. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.27344
Fusco, R., Sansone, M., Filice, S., Carone, G., Amato, D. M., Sansone, C., & Petrillo, A. (2016). Pattern recognition approaches for breast cancer DCE-MRI classification: A systematic review. Journal of Medical and Biological Engineering, 36(4), 449–459.
Chen, W., Hua, Y., Mao, D., Wu, H., Tan, M., Ma, W., & Li, M. (2021). A Computed tomography-derived radiomics approach for predicting uncommon EGFR mutation in patients With NSCLC. Frontiers in Oncology. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.722106
Ubaldi, L., Valenti, V., Borgese, R. F., Collura, G., Fantacci, M. E., Ferrera, G., Iacoviello, G., Abbate, B. F., Laruina, F., Tripoli, A., & Retico, A. (2021). Strategies to develop radiomics and machine learning models for lung cancer stage and histology prediction using small data samples. Physica Medica, 90, 13–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmp.2021.08.015
Moon, W. K., Lee, Y. W., Huang, Y. S., Lee, S. H., Bae, M. S., Yi, A., Huang, C. S., & Chang, R. F. (2017). Computer-aided prediction of axillary lymph node status in breast cancer using tumor surrounding tissue features in ultrasound images. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 146, 143–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2017.06.001
Wu, H., Patel, R. B., Zheng, Y., Solorio, L., Krupka, T. M., Ziats, N. P., et al. (2012). Differentiation of benign periablational enhancement from residual tumor following radio-frequency ablation using contrast-enhanced ultrasonography in a rat subcutaneous colon cancer model. Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology, 38, 443–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2011.12.008
Wu, H., Exner, A. A., Krupka, T. M., Weinberg, B. D., Patel, R., & Haaga, J. R. (2009). Radiofrequency ablation: post-ablation assessment using CT perfusion with pharmacological modulation in a rat subcutaneous tumor model. Academic radiology, 16, 321–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acra.2008.09.008
Wei, J., Jiang, H., Gu, D., Niu, M., Fu, F., Han, Y., Song, B., & Tian, J. (2020). Radiomics in liver diseases: Current progress and future opportunities. Liver International, 40, 2050–2063. https://doi.org/10.1111/liv.14555
Han, H., Jin, Y., Liu, R., Ji, Z. F. Z., & Wang, W. (2022). Early differentiation of residual tumor and inflammation rim after ablation of rabbit VX2 liver tumor by quantitative analysis of contrast-enhanced ultrasound. Fudan University Journal of Medical, 49(01), 44–49. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1672-8467.2022.01.006.
Kan, X., Zhang, Y., Zheng, C., Li, L., Chen, J., Wu, Y., Guo, T., & Xiong, B. (2016). Stress test of contrast-enhanced US with Phenylephrine in a rabbit VX2 liver tumor model: Differentiating benign periablational enhancement from residual tumor after radiofrequency ablation. Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology, 27, 1077–1085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvir.2016.02.012
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 62071285) and Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (grant number: 19ZR1450700).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. YJ, ZJ, HH and WW: Material preparation and data collection were performed. YD, QZ and HC: designed the studies. YD, QZ and HH: drafted and critically revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical Approval
All applicable institutional and/or national guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Consent to Participate
For this study consent to participate is not required.
Consent to Participate
For this study consent for publication is not required.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, Y., Zhang, Q., Chen, H. et al. Radiomics of Multi-modality Ultrasound in Rabbit VX2 Liver Tumors: Differentiating Residual Tumors from Hyperemic Rim After Ablation. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 42, 780–789 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40846-022-00763-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40846-022-00763-y