Abstract
Background
Despite the continual improvements in dialysis treatments, mortality in end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) remains high. Many mortality prediction models are available, but most of them are not precise enough to be used in the clinical practice. We aimed to develop and validate two prediction models for 3-month and 1-year patient mortality after dialysis initiation in our population.
Methods
Using population-based data of insurance claims in Taiwan, we included more than 210,000 patients who initiated dialysis between January 1, 2006, and June 30, 2015. We developed two prognostic models, which included 9 and 11 variables, respectively (including age, sex, myocardial infarction, peripheral vascular disease, cerebrovascular disease, dementia, chronic pulmonary disease, peptic ulcer disease, malignancy, moderate to severe liver disease, and first dialysis in intensive care unit).
Results
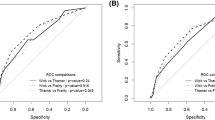
The models showed adequate discrimination (C-statistics were 0.80 and 0.82 for 3-month and 1-year mortality, respectively) and good calibration. In both our models, the first dialysis in the intensive care unit and moderate-to-severe liver disease were the strongest risk factors for mortality.
Conclusion
The prediction models developed in our population had good predictive ability for short-term mortality in patients initiating dialysis in Taiwan and could help in decision-making regarding dialysis initiation, at least in our setting, supporting a patient-centered approach to care.
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Vanholder R, Massy Z, Argiles A, Spasovski G, Verbeke F, Lameire N (2005) Chronic kidney disease as cause of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Nephrol Dial Transplant 20:1048–1056
Schaefer K, von Herrath D, Röhrich B (2001) Outcome of renal replacement therapy in the very elderly. Nephrol Dial Transplant 16:1721–1722
Soucie JM, McClellan WM (1996) Early death in dialysis patients: risk factors and impact on incidence and mortality rates. J Am Soc Nephrol 7:2169–2175
Eckardt KU, Gillespie IA, Kronenberg F, Richards S, Stenvinkel P, Anker SD, Wheeler DC, de Francisco AL, Marcelli D, Froissart M, Floege J (2015) High cardiovascular event rates occur within the first weeks of starting hemodialysis. Kidney Int 88:1117–1125
Chandna SM, Da Silva-Gane M, Marshall C, Warwicker P, Greenwood RN, Farrington K (2011) Survival of elderly patients with stage 5 CKD: comparison of conservative management and renal replacement therapy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 26:1608–1614
Kurella Tamura M, Covinsky KE, Chertow GM, Yaffe K, Landefeld CS, McCulloch CE (2009) Functional status of elderly adults before and after initiation of dialysis. N Engl J Med 361:1539–1547
Carson RC, Juszczak M, Davenport A, Burns A (2009) Is maximum conservative management an equivalent treatment option to dialysis for elderly patients with significant comorbid disease? Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 4:1611–1619
Foley RN, Parfrey PS, Hefferton D, Singh I, Simms A, Barrett BJ (1994) Advance prediction of early death in patients starting maintenance dialysis. Am J Kidney Dis 23:836–845
Barrett BJ, Parfrey PS, Morgan J, Barré P, Fine A, Goldstein MB, Handa SP, Jindal KK, Kjellstrand CM, Levin A, Mandin H, Muirhead N, Richardson RM (1997) Prediction of early death in end-stage renal disease patients starting dialysis. Am J Kidney Dis 29:214–222
Haapio M, Helve J, Grönhagen-Riska C, Finne P (2017) One- and 2-year mortality prediction for patients starting chronic dialysis. Kidney Int Rep 2:1176–1185
Yoshida M, Otsuka M, Watanabe Y, Harigai T, Sakurai N, Kobatake K, Yoshida H, Kobayashi S, Matsumoto T, Sakamoto T, Ueki K (2020) A clinical nomogram for the prediction of early mortality in elderly patients initiating dialysis for end-stage renal disease. Renal Replace Ther 6:11
Pang WF, Kwan BC, Chow KM, Leung CB, Li PK, Szeto CC (2013) Predicting 12-month mortality for peritoneal dialysis patients using the “surprise” question. Perit Dial Int 33:60–66
Cohen LM, Ruthazer R, Moss AH, Germain MJ (2010) Predicting six-month mortality for patients who are on maintenance hemodialysis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 5:72–79
Ueshima H, Okayama A, Saitoh S, Nakagawa H, Rodriguez B, Sakata K, Okuda N, Choudhury SR, Curb JD (2003) Differences in cardiovascular disease risk factors between Japanese in Japan and Japanese-Americans in Hawaii: the INTERLIPID study. J Hum Hypertens 17:631–639
Saran R, Li Y, Robinson B, Abbott KC, Agodoa LY, Ayanian J, Bragg-Gresham J, Balkrishnan R, Chen JL, Cope E, Eggers PW, Gillen D, Gipson D, Hailpern SM, Hall YN, He K, Herman W, Heung M, Hirth RA, Hutton D, Jacobsen SJ, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kovesdy CP, Lu Y, Molnar MZ, Morgenstern H, Nallamothu B, Nguyen DV, O’Hare AM, Plattner B, Pisoni R, Port FK, Rao P, Rhee CM, Sakhuja A, Schaubel DE, Selewski DT, Shahinian V, Sim JJ, Song P, Streja E, Kurella Tamura M, Tentori F, White S, Woodside K, Hirth RA (2016) US renal data system 2015 annual data report: epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis 67:S1-305
Yang WC, Hwang SJ (2008) Incidence, prevalence and mortality trends of dialysis end-stage renal disease in Taiwan from 1990 to 2001: the impact of national health insurance. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23:3977–3982
Chih-Cheng Hsu M-SW, Shang-Jyh Hwang, Yuh-Feng Lin, Yung-Ho Hsu, Yi-Wen Chiu et al: 2019 Annual Report on Kidney Disease in Taiwan. 2020:33,73. https://www.tsn.org.tw/UI/L/L002_2019.aspx
Kohavi R (1995) A study of cross-validation and bootstrap for accuracy estimation and model selection. Int Jt Conf Artif Intell 2:1137–1145
Bagshaw SM, Wald R (2017) Strategies for the optimal timing to start renal replacement therapy in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 91:1022–1032
Chien CC, Wang JJ, Sun YM, Sun DP, Sheu MJ, Weng SF, Chu CC, Chen HA, Chio CC, Hwang JC, Lu YH, Wang HY, Kan WC (2012) Long-term survival and predictors for mortality among dialysis patients in an endemic area for chronic liver disease: a national cohort study in Taiwan. BMC Nephrol 13:43
Hung TH, Tseng CW, Tseng KC, Hsieh YH, Tsai CC, Tsai CC (2014) Is end stage renal disease a risk factor for the mortality of cirrhotic patients with esophageal variceal bleeding? Hepatogastroenterology 61:1871–1875
Tandon P, Garcia-Tsao G (2011) Renal dysfunction is the most important independent predictor of mortality in cirrhotic patients with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 9:260–265
Couchoud CG, Beuscart JB, Aldigier JC, Brunet PJ, Moranne OP (2015) Development of a risk stratification algorithm to improve patient-centered care and decision making for incident elderly patients with end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int 88:1178–1186
Quinn RR, Laupacis A, Hux JE, Oliver MJ, Austin PC (2011) Predicting the risk of 1-year mortality in incident dialysis patients: accounting for case-mix severity in studies using administrative data. Med Care 49:257–266
Wagner M, Ansell D, Kent DM, Griffith JL, Naimark D, Wanner C, Tangri N (2011) Predicting mortality in incident dialysis patients: an analysis of the United Kingdom Renal Registry. Am J Kidney Dis 57:894–902
Robinson BM, Zhang J, Morgenstern H, Bradbury BD, Ng LJ, McCullough KP, Gillespie BW, Hakim R, Rayner H, Fort J, Akizawa T, Tentori F, Pisoni RL (2014) Worldwide, mortality risk is high soon after initiation of hemodialysis. Kidney Int 85:158–165
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the National Health Research Institutes (NHRI-EX109-10926HT) and Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) (MOST109-2314-B-038-106-MY3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mei-Yi Wu, Ping-Jen Hu, Yu-Wei Chen, Tzu-Ting Chen, Mai-Szu Wu and Yih-Giun Cherng contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Mei-Yi Wu, Ping-Jen Hu, Yu-Wei Chen, Li-Chin Sung and Tzu-Ting Chen. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Mei-Yi Wu, Ping-Jen Hu, Yu-Wei Chen, Li-Chin Sung, Tzu-Ting Chen and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors reported that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, MY., Hu, PJ., Chen, YW. et al. Predicting 3-month and 1-year mortality for patients initiating dialysis: a population-based cohort study. J Nephrol 35, 1005–1013 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-021-01185-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-021-01185-w