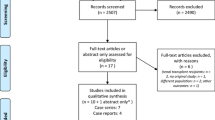
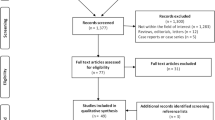
Abstract
Background
The effect of urolithiasis on pregnancy-related outcomes remains unknown. The aim of this study was to determine the risk of adverse maternal and neonatal outcomes.
Methods
We searched PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Library through December 2020 for studies reporting on adverse maternal and neonatal outcomes in patients with urolithiasis. Risk ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated for these outcomes in pregnant mothers with urolithiasis and compared to healthy controls.
Results
Eight studies comprising 26,577 mothers with urolithiasis were included in our analysis. Preterm birth (OR = 1.63; 95% CI 1.37–1.95, p < 0.001) or very preterm birth risk (OR = 1.49, 95% CI 1.06–2.11, p = 0.02) was more common in patients with urolithiasis compared to healthy controls. Mothers with urolithiasis had an increased incidence of preeclampsia (OR = 1.75, 95% CI 1.33–2.3, p < 0.001), hypertension (OR = 2.97, 95% CI 1.31–6.71, p = 0.009), caesarean section (OR 1.31, 95% CI 1.11–1.55, p = 0.001), and gestational diabetes mellitus (OR 1.84, 95% CI 1.37–2.46, p < 0.001).
Conclusion
Patients with urolithiasis may be at increased risk of developing adverse maternal or neonatal outcomes.
Graphic abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Semins MJ, Matlaga BR (2014) Kidney stones during pregnancy. Nat Rev Urol 11:163–168
Semins MJ, Matlaga BR (2010) Management of stone disease in pregnancy. Curr Opin Urol 20:174–177
Kerns E, Lanis A, Onwugbenu N, Bourjeily G (2017) A case report: urolithiasis, hydronephrosis, and acute kidney injury in pregnancy. J Obstet Gynaecol 37:1085–1086
Whittington JR, Simmons PM, Eltahawy EA, Magann EF (2018) Bladder stone in pregnancy: a case report and review of the literature. Am J Case Rep 19:1546–1549
Banhidy F, Acs N, Puho EH, Czeizel AE (2007) Maternal kidney stones during pregnancy and adverse birth outcomes, particularly congenital abnormalities in the offspring. Arch Gynecol Obstet 275:481–487
Swartz MA, Lydon-Rochelle MT, Simon D, Wright JL, Porter MP (2007) Admission for nephrolithiasis in pregnancy and risk of adverse birth outcomes. Obstet Gynecol 109:1099–1104
Rosenberg E, Sergienko R, Abu-Ghanem S, Wiznitzer A, Romanowsky I, Neulander EZ, Sheiner E (2011) Nephrolithiasis during pregnancy: characteristics, complications, and pregnancy outcome. World J Urol 29:743–747
Tangren JS, Powe CE, Ecker J, Bramham K, Ankers E, Karumanchi SA, Thadhani R (2018) Metabolic and hypertensive complications of pregnancy in women with nephrolithiasis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 13:612–619
Drescher M, Blackwell RH, Patel PM, Kuo PC, Turk TMT, Baldea KG (2019) Antepartum nephrolithiasis and the risk of preterm delivery. Urolithiasis 47:441–448
Clennon EK, Garg B, Duty BD, Caughey AB (2020) Obstetric outcomes of pregnancy complicated by urolithiasis: a retrospective cohort study. J Perinat Med 218(1):S468
Ordon M, Dirk J, Slater J, Kroft J, Dixon S, Welk B (2020) Incidence, treatment, and implications of kidney stones during pregnancy: a matched population-based cohort study. J Endourol 34:215–221
Sohlberg EM, Brubaker WD, Zhang CA, Anderegg LDL, Dallas KB, Song S, Ganesan C, Chertow GM, Pao AC, Liao JC, Leppert JT, Elliott CS, Conti SL (2020) Urinary stone disease in pregnancy: a claims based analysis of 1.4 million patients. J Urol 203:957–961
Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, Olkin I, Williamson GD, Rennie D, Moher D, Becker BJ, Sipe TA, Thacker SB (2000) Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA 283:208–212
Higgins JP. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1.0. (2014) The cochrane collaboration. www.cochrane-handbook.org. Accessed 6 Dec 2014
Higgins JP, Thompson SG (2002) Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 21:1539–1558
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327:557–560
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C (1997) Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315:629–634
Lau J, Ioannidis JP, Terrin N, Schmid CH, Olkin I (2006) The case of the misleading funnel plot. BMJ 333:597–600
Body C, Christie JA (2016) Gastrointestinal diseases in pregnancy: nausea, vomiting, hyperemesis gravidarum, gastroesophageal reflux disease, constipation, and diarrhea. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 45:267–283
Kowalewski MP, Kautz E, Högger E, Hoffmann B, Boos A (2014) Interplacental uterine expression of genes involved in prostaglandin synthesis during canine pregnancy and at induced prepartum luteolysis/abortion. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 12:46
Park JY, Romero R, Lee J, Chaemsaithong P, Chaiyasit N, Yoon BH (2016) An elevated amniotic fluid prostaglandin F2α concentration is associated with intra-amniotic inflammation/infection, and clinical and histologic chorioamnionitis, as well as impending preterm delivery in patients with preterm labor and intact membranes. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 29:2563–2572
Pohl O, Chollet A, Kim SH, Riaposova L, Spézia F, Gervais F, Guillaume P, Lluel P, Méen M, Lemaux F, Terzidou V, Bennett PR, Gotteland JP (2018) OBE022, an oral and selective prostaglandin F(2)(α) receptor antagonist as an effective and safe modality for the treatment of preterm labor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 366:349–364
Hoffman MK, Goudar SS, Kodkany BS, Metgud M, Somannavar M, Okitawutshu J, Lokangaka A, Tshefu A, Bose CL, Mwapule A, Mwenechanya M, Chomba E, Carlo WA, Chicuy J, Figueroa L, Garces A, Krebs NF, Jessani S, Zehra F, Saleem S, Goldenberg RL, Kurhe K, Das P, Patel A, Hibberd PL, Achieng E, Nyongesa P, Esamai F, Liechty EA, Goco N, Hemingway-Foday J, Moore J, Nolen TL, McClure EM, Koso-Thomas M, Miodovnik M, Silver R, Derman RJ (2020) Low-dose aspirin for the prevention of preterm delivery in nulliparous women with a singleton pregnancy (ASPIRIN): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 395:285–293
Brain E, Geraghty RM, Cook P, Roderick P, Somani B (2021) Risk of UTI in kidney stone formers: a matched-cohort study over a median follow-up of 19 years. World J Urol 5:1–7
Elias D, Gimenez L, Poletta F, Campaña H, Gili J, Ratowiecki J, Pawluk M, Rittler M, Santos MR, Uranga R, Heisecke SL, Cosentino V, Saleme C, Gadow E, Krupitzki H, Camelo JSL (2020) Preterm birth and genitourinary tract infections: assessing gene-environment interaction. Pediatr Res 1:1–17
El-Zoghby ZM, Lieske JC, Foley RN, Bergstralh EJ, Li X, Melton LJ 3rd, Krambeck AE, Rule AD (2012) Urolithiasis and the risk of ESRD. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 7:1409–1415
Rule AD, Bergstralh EJ, Melton LJ 3rd, Li X, Weaver AL, Lieske JC (2009) Kidney stones and the risk for chronic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 4:804–811
Vodanović M, Lucijanić M, Zupančić Šalek S, Pećin I (2021) Prevalence of and risk factors for urolithiasis in Croatian patients with hemophilia. Int J Hematol 113(5):656–661
Voerman E, Santos S, Inskip H, Amiano P, Barros H, Charles MA, Chatzi L, Chrousos GP, Corpeleijn E, Crozier S, Doyon M, Eggesbø M, Fantini MP, Farchi S, Forastiere F, Georgiu V, Gori D, Hanke W, Hertz-Picciotto I, Heude B, Hivert MF, Hryhorczuk D, Iñiguez C, Karvonen AM, Küpers LK, Lagström H, Lawlor DA, Lehmann I, Magnus P, Majewska R, Mäkelä J, Manios Y, Mommers M, Morgen CS, Moschonis G, Nohr EA, Nybo Andersen AM, Oken E, Pac A, Papadopoulou E, Pekkanen J, Pizzi C, Polanska K, Porta D, Richiardi L, Rifas-Shiman SL, Roeleveld N, Ronfani L, Santos AC, Standl M, Stigum H, Stoltenberg C, Thiering E, Thijs C, Torrent M, Trnovec T, van Gelder M, van Rossem L, von Berg A, Vrijheid M, Wijga A, Zvinchuk O, Sørensen TIA, Godfrey K, Jaddoe VWV, Gaillard R (2019) Association of gestational weight gain with adverse maternal and infant outcomes. JAMA 321:1702–1715
Evan AP, Lingeman J, Coe F, Shao Y, Miller N, Matlaga B, Phillips C, Sommer A, Worcester E (2007) Renal histopathology of stone-forming patients with distal renal tubular acidosis. Kidney Int 71:795–801
Piccoli GB, Attini R, Vasario E, Conijn A, Biolcati M, D’Amico F, Consiglio V, Bontempo S, Todros T (2010) Pregnancy and chronic kidney disease: a challenge in all CKD stages. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 5:844–855
Piccoli GB, Cabiddu G, Attini R, Vigotti FN, Maxia S, Lepori N, Tuveri M, Massidda M, Marchi C, Mura S, Coscia A, Biolcati M, Gaglioti P, Nichelatti M, Pibiri L, Chessa G, Pani A, Todros T (2015) Risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes in women with CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol 26:2011–2022
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QZ and JHC conceived the study and revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content. QZ and WQC made substantial contributions to its design, acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data. XSX, SLX, and HY participated in the design, acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Q., Chen, WQ., Xie, XS. et al. Maternal and neonatal outcomes of pregnancy complicated by urolithiasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Nephrol 34, 1569–1580 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-021-01093-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-021-01093-z