Abstract
Background
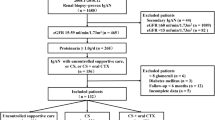
No specific treatment for IgA nephropathy (IgAN) after kidney transplantation is currently available.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective single-center study on 29 patients with biopsy-proven de novo and recurrent IgAN after kidney transplantation, divided into two groups. Group 1 (n = 16) received intravenous methylprednisolone 500 mg per day for three consecutive days at the beginning of months 1, 3 and 5, plus oral prednisone 0.5 mg/kg every other day for 6 months. The control group (n = 13, Group 2) received supportive therapies.
Results
The two groups were comparable for serum creatinine (sCr) and proteinuria at the time of renal biopsy, but differed significantly at the end of follow-up. sCr was 1.8 ± 0.4 mg/dl in Group 1 vs. 2.7 ± 0.9 in Group 2 (p = 0.002), and proteinuria was 0.9 g/day in Group 1 vs. 1.9 in Group 2 (p = 0.04). The composite outcome of death-censored graft loss or doubling of sCr displayed 2 events in Group 1 (12.5 % of the entire group) and 5 events in Group 2 (38.5 % of the entire group), p = 0.19, odds ratio (OR) 4.4 [95 % confidence interval (CI) 0.7–27.8].
Conclusions
In the absence of therapeutic guidelines for de novo or recurrent IgAN after kidney transplantation, our study reports that therapy with pulse and oral steroids for 6 months is associated with an improved renal function. Nevertheless, further randomized controlled studies in larger patient cohorts are necessary to establish the gold standard treatment.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Koyama A, Igarashi M, Kobayashi M (1997) Natural history and risk factors for immunoglobuline A nephropathy in Japan. Research Group on Progressive Renal Diseases. Am J Kidney Dis 4:526–532
Berger J (1998) Recurrence of IgA nephropathy in renal allografts. Am J Kidney Dis 12:371–372
Von Visger JR, Gunay Y, Andreoni KA et al (2014) The risk of recurrent IgA nephropathy in a steroid-free protocol and other modifying immunosuppression. Clin Transplant 28(8):845–854
Ortiz F, Gelpi R, Koskinen P et al (2012) IgA nephropathy recurs early in the graft when assessed by protocol biopsy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 27:2553–2558
Briganti EM, Russ GR, McNeil JJ, Atkins RC, Chadban SJ (2002) Risk of renal allograft loss from recurrent glomerulonephritis. N Engl J Med 347:103–109
Floege J, Gröne HJ (2013) Recurrent IgA nephropathy in the renal allograft: not a benign condition. Nephrol Dial Transplant 28(5):1070–1073
Moroni G, Longhi S, Quaglini S et al (2013) The long-term outcome of renal transplantation of IgA nephropathy and the impact of recurrence on graft survival. Nephrol Dial Transplant 28:1305–1314
Mulay AV, Van Walraven C, Knoll GA (2009) Impact of immunosuppressive medication on the risk of renal allograft failure due to recurrent glomerulonephritis. Am J Transplant 9:804–811
Clayton P, McDonald S, Chadban S (2011) Steroids and recurrent IgA nephropathy after kidney transplantation. Am J Transplant 11:1645–1649
Kukla A, Chen E, Spong R et al (2011) Recurrent glomerulonephritis under rapid discontinuation of steroids. Transplantation 91:1386–1391
Pozzi C, Andrulli S, Del Vecchio L et al (2004) Corticosteroid effectiveness in IgA Nephropathy: long-term results of a randomized, controlled trial. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:157–163
Pozzi C, Balasco PG, Fogazzi GB et al (1999) Corticosteroids in IgA nephropathy; a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 353:883–887
Working Group of the International IgA Nephropathy Network and the Renal Pathology Society, Cattran DC, Coppo R et al (2009) The Oxford Classification of IgA nephropathy: rationale, clinicopathological correlations, and classification. Kidney Int 76(5):534–545
Coppo R, Troyanov S, Bellur S et al (2014) Validation of the Oxford Classification of IgA nephropathy in cohorts with different presentations and treatments. Kidney Int 86(4):828–836
Morozumi K, Takeda A, Otsuka Y et al (2014) Recurrent glomerular disease after kidney transplantation: an update of selected areas and the impact of protocol biopsy. Nephrology 19(Suppl 3):6–10
Oka K, Imai E, Moriyama T et al (2000) A clinicopathological study of IgA nephropathy in renal transplant recipients: beneficial effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor. Nephrol Dial Transplant 15:689–695
Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Glomerulonephritis Work Group (2012) KDIGO clinical practice guideline for glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int Suppl 2(2):139–274
Courtney AE, McNamee PT, Nelson WE, Maxwell AP (2006) Does angiotensin blockade influence graft outcome in renal transplant recipients with IgA nephropathy? Nephrol Dial Transplant 21:3550–3554
Ng R (2003) Fish oil therapy in recurrent IgA nephropathy. Ann Intern Med 138:1011–1012
Hotta K, Fukasawa Y, Akimoto M et al (2013) Tonsillectomy ameliorates histological damage of recurrent immunoglobulin A nephropathy after kidney transplantation. Nephrology 18:808–812
Kennoki T, Ishida H, Yamaguchi Y, Tanabe K (2009) Proteinuria-reducing effects of tonsillectomy alone in IgA nephropathy recurring after kidney transplantation. Transplantation 88:935–941
Koshino K, Ushigome H, Sakai K et al (2013) Outcome of tonsillectomy for recurrent IgA nephropathy after kidney transplantation. Clin Transpl 27:22–28
Ziswiler R, Steinmann-Niggli K, Kappeler A, Daniel C, Marti HP (1998) Mycophenolic acid: a new approach to the therapy of experimental mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 9(11):2055–2066
Chandrakantan A, Ratanapanichkich P, Said M, Barker CV, Julian BA (2005) Recurrent IgA nephropathy after renal transplantation despite immunosuppressive regimens with mycophenolate mofetil. Nephrol Dial Transplant 20:1214–1221
Liang Y, Zhang J, Liu D et al (2014) Retrospective study of mycophenolate mofetil treatment in IgA nephropathy with proliferative pathological phenotype. Chin Med J 127(1):102–108
Frisch G, Lin J, Rosenstock J et al (2005) Mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) vs placebo in patients with moderately advanced IgA nephropathy: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. Nephrol Dial Transplant 20(10):2139–2145
Manno C, Torres DD, Rossini M, Pesce F, Schena FP (2009) Randomized controlled clinical trial of corticosteroids plus ACE inhibitors with long term follow-up in proteinuric IgA nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24:3694–3701
Lv J, Xu D, Perkovic V et al (2012) Corticosteroid therapy in IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 23:1108–1116
Tesar V, Troyanov S, Bellur S, VALIGA study of the ERA-EDTA Immunonephrology Working Group et al (2015) Corticosteroids in IgA nephropathy: a retrospective analysis from the VALIGA study. J Am Soc Nephrol 26:2248–2258
Ibrahim H, Rogers T, Casingal V et al (2006) Graft loss from recurrent glomerulonephritis is not increased with a rapid steroid discontinuation. Transplantation 81(2):214–219
Wyld ML, Chadban SJ (2016) Recurrent IgA nephropathy after kidney transplantation. Transplantation [Epub ahead of print]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
M. Messina and M. C. di Vico equally contributed to the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Messina, M., di Vico, M.C., Ariaudo, C. et al. Treatment protocol with pulse and oral steroids for IgA Nephropathy after kidney transplantation. J Nephrol 29, 575–583 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-016-0314-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-016-0314-5