Abstract
Background
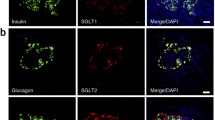
Although sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors have many beneficial effects for type 2 diabetes, including decreased cardiovascular death, recent reports that they increased glucagon through SGLT2 inhibition raised some concern. Troglitazone, Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPAR-γ) agonist, was reported to increase SGLT2 in renal proximal tubule cells, but its role on pancreatic alpha cells have not been reported. We investigated the effect of troglitazone on SGLT2 expression in alpha cells and subsequent glucagon regulation in hyperglycemia.
Methods
An Alpha TC1-6 cell line was cultured in control (5 mM) or hyperglycemia (HG, 15 mM) for 72 h. We applied troglitazone with or without PPARγ antagonist (GW9662 10 μM). To investigate the involvement of PI3K/Akt pathway, we applied troglitazone with or without Wortmanin. We measured sodium glucose transporter 2 (SGLT2) and glucagon (GCG) mRNA and protein expression. PPAR gamma, PI3K and Akt protein were also measured.
Results
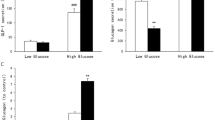
Exposure of alpha TC cells to HG for 72 h increased glucagon mRNA and protein expression. HG decreased SGLT2 mRNA and protein expression. Troglitazone significantly reversed HG-induced reduction of SGLT2 expression and increase of glucagon secretion. PPARγ antagonist (GW9662 10 μM) decreased the expression of SGLT2 and increased glucagon as HG did. Hyperglycemia increased PI3K and pAkt expression in alpha cells. Wortmanin (PI3K inhibitor, 1 μM) reversed HG-induced SGLT2 decrease and glucagon increase. Troglitazone treatment decreased PI3K and pAkt expression in HG.
Conclusion
In conclusion, PPARγ agonist, troglitazone improved glucose transport SGLT2 dysfunction and subsequent glucagon dysregulation in alpha cell under hyperglycemia. Those effects were through the involvement of PI3K/pAkt signaling pathway. This study may add one more reason for the ideal combination of PPARγ agonist and SGLT2 inhibitor in clinical practice.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Unger RH, Cherrington AD (2012) Glucagonocentric restructuring of diabetes: a pathophysiologic and therapeutic makeover. J Clin Investig 122:4–12
Ferrannini E, Muscelli E, Frascerra S, Baldi S, Mari A et al (2014) Metabolic response to sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition in type 2 diabetic patients. J Clin Investig 124:499–508
Merovci A, Solis-Herrera C, Daniele G, Eldor R, Fiorentino TV et al (2014) Dapagliflozin improves muscle insulin sensitivity but enhances endogenous glucose production. J Clin Investig 124:509–514
Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, Bluhmki E et al (2015) Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 373:2117–2128
Seino S, Shibasaki T, Minami K (2011) Dynamics of insulin secretion and the clinical implications for obesity and diabetes. J Clin Investig 121:2118–2125
Gromada J, Franklin I, Wollheim CB (2007) Alpha-cells of the endocrine pancreas: 35 years of research but the enigma remains. Endocr Rev 28:84–116
Ishihara H, Maechler P, Gjinovci A, Herrera PL, Wollheim CB (2003) Islet beta-cell secretion determines glucagon release from neighbouring alpha-cells. Nat Cell Biol 5:330–335
Rorsman P, Berggren PO, Bokvist K, Ericson H, Mohler H et al (1989) Glucose-inhibition of glucagon secretion involves activation of GABAA-receptor chloride channels. Nature 341:233–236
Cheng-Xue R, Gomez-Ruiz A, Antoine N, Noel LA, Chae HY et al (2013) Tolbutamide controls glucagon release from mouse islets differently than glucose: involvement of K(ATP) channels from both alpha-cells and delta-cells. Diabetes 62:1612–1622
de Heer J, Rasmussen C, Coy DH, Holst JJ (2008) Glucagon-like peptide-1, but not glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide, inhibits glucagon secretion via somatostatin (receptor subtype 2) in the perfused rat pancreas. Diabetologia 51:2263–2270
Sherck SM, Shiota M, Saccomando J, Cardin S, Allen EJ et al (2001) Pancreatic response to mild non-insulin-induced hypoglycemia does not involve extrinsic neural input. Diabetes 50:2487–2496
Shen XX, Li HL, Pan L, Hong J, Xiao J et al (2012) Glucotoxicity and alpha cell dysfunction: involvement of the PI3K/Akt pathway in glucose-induced insulin resistance in rat islets and clonal alphaTC1-6 cells. Endocr Res 37:12–24
Bonner C, Kerr-Conte J, Gmyr V, Queniat G, Moerman E et al (2015) Inhibition of the glucose transporter SGLT2 with dapagliflozin in pancreatic alpha cells triggers glucagon secretion. Nat Med 21:512–517
Ahmadian M, Suh JM, Hah N, Liddle C, Atkins AR et al (2013) PPARgamma signaling and metabolism: the good, the bad and the future. Nat Med 19:557–566
Kim HI, Kim JW, Kim SH, Cha JY, Kim KS et al (2000) Identification and functional characterization of the peroxisomal proliferator response element in rat GLUT2 promoter. Diabetes 49:1517–1524
Lee YJ, Han HJ (2010) Troglitazone ameliorates high glucose-induced EMT and dysfunction of SGLTs through PI3K/Akt, GSK-3beta, Snail1, and beta-catenin in renal proximal tubule cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 298: F1263–1275.
Miki T, Liss B, Minami K, Shiuchi T, Saraya A et al (2001) ATP-sensitive K + channels in the hypothalamus are essential for the maintenance of glucose homeostasis. Nat Neurosci 4:507–512
Ostenson CG (1979) Regulation of glucagon release: effects of insulin on the pancreatic A2-cell of the guinea pig. Diabetologia 17:325–330
Starke A, Imamura T, Unger RH (1987) Relationship of glucagon suppression by insulin and somatostatin to the ambient glucose concentration. J Clin Invest 79:20–24
Han HJ, Choi HJ, Park SH (2000) High glucose inhibits glucose uptake in renal proximal tubule cells by oxidative stress and protein kinase C. Kidney Int 57:918–926
Rosenstock J, Ferrannini E (2015) Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis: a predictable, detectable, and preventable safety concern with SGLT2 inhibitors. Diabetes Care 38:1638–1642
Dormandy JA, Charbonnel B, Eckland DJ, Erdmann E, Massi-Benedetti M et al (2005) Secondary prevention of macrovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes in the PROactive Study (PROspective pioglitAzone Clinical Trial In macroVascular Events): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 366:1279–1289
DeFronzo RA, Chilton R, Norton L, Clarke G, Ryder RE et al. (2016) Revitalization of pioglitazone: the optimal agent to be combined with an SGLT2 inhibitor. Diabetes Obes Metab 18:454–462
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, M., Lee, E.J., Shin, H.M. et al. The effect of PPARγ agonist on SGLT2 and glucagon expressions in alpha cells under hyperglycemia. J Endocrinol Invest 40, 1069–1076 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-017-0659-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-017-0659-1