Abstract
Purpose
Sorafenib has recently been recognized as an important standard option for the management of patients with differentiated thyroid cancer. Although data concerning cardiac safety are available in pan-tumor studies, no data are available on its use in everyday clinical practice in patients with thyroid cancer.
Methods
In the off-label program of our institution, we enrolled 14 patients with different histological types of thyroid cancer suitable for treatment with sorafenib. Our aims were to evaluate cardiac safety factors—LVEF (left ventricular ejection fraction), heart rate and blood pressure—the cardiac markers NT-proBNP and troponin I, radiological response evaluated by CT and 18FDG-PET (according to RECIST 1.1 criteria) and biomarker reduction (Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status: ECOG PS) 0–2.
Results
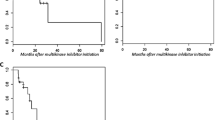
Patients with ECOG PS 2 accounted for 36 %. After starting sorafenib, many patients displayed reduced or stabilized metabolic activity in target lesions (clinical benefit = 44 %), radiologic reduction or stabilization (74 %) and decreased cancer markers (90 %). Lung metastases displayed the largest reductions in size. Median overall survival (OS) was 7 months and median progression-free survival (PFS) was 3 months. No sign of cardiotoxicity was observed in almost all patients. LVEF was altered in two patients and proved symptomatic in one.
Conclusions
Sorafenib seems to be effective in reducing disease progression in the early stages of treatment (3–6 months). Responses varied considerably according to the criteria investigated. Cardiac toxicities did not raise concerns and were in line with data reported in other malignancies. However, cardiac monitoring is recommended.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Surveillance, epidemiology, and end results program (seer) database 2014 for thyroid cancer. Downloadable at http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/thyro.html. Accessed 24 Aug 2014
Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, Neyman N, Aminou R, Waldron W, Altekruse SF, Kosary CL, Ruhl J, Tatalovich Z, Cho H, Mariotto A, Eisner MP, Lewis DR, Chen HS, Feuer EJ, Cronin KA (eds) (1975–2009) SEER cancer statistics review (vintage 2009 populations), National Cancer Institute, Bethesda
Tuttle MDJ, Pacini F (2014) NCCN guideline: practice guidelines in oncology v 1.2014 J Natl Cancer Inst. Available at www.nccn.org
Puxeddu E, Durante C, Avenia N, Filetti S, Russo D (2008) Clinical implications of BRAF mutation in thyroid carcinoma. Trends Endocrinol Metab 19(4):138–145. doi:10.1016/j.tem.2007.12.003
Pacini F (2012) New insight in the follow-up strategies of differentiated thyroid cancer. J Endocrinol Invest 35(Suppl. to no. 6):36
Tuttle MDJ, Pacini F (2007) NCCN Clinical practice guidelines in oncology thyroid carcinoma V.2.2007 J Natl Cancer Inst. Downloadable at http://www.unifesp.br/dmed/climed/liga/consensos/cancertireoide2007.PDF
Witteles RM, Telli M (2012) Underestimating cardiac toxicity in cancer trials: lessons learned? J Clin Oncol 30(16):1916–1918. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.40.4012
Haraldsdottir S, Shah MH (2014) New era for treatment in differentiated thyroid cancer. Lancet. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60663-2
Lam ET, Ringel MD, Kloos RT, Prior TW, Knopp MV, Liang J, Sammet S, Hall NC, Wakely PE Jr, Vasko VV, Saji M, Snyder PJ, Wei L, Arbogast D, Collamore M, Wright JJ, Moley JF, Villalona-Calero MA, Shah MH (2010) Phase II clinical trial of sorafenib in metastatic medullary thyroid cancer. J Clin Oncol 28(14):2323–2330. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.25.0068
Ahmed M, Barbachano Y, Riddell A, Hickey J, Newbold KL, Viros A, Harrington KJ, Marais R, Nutting CM (2011) Analysis of the efficacy and toxicity of sorafenib in thyroid cancer: a phase II study in a UK based population. Eur J Endocrinol/Eur Fed Endocr Soc 165(2):315–322. doi:10.1530/EJE-11-0129
Kloos RT, Ringel MD, Knopp MV, Hall NC, King M, Stevens R, Liang J, Wakely PE Jr, Vasko VV, Saji M, Rittenberry J, Wei L, Arbogast D, Collamore M, Wright JJ, Grever M, Shah MH (2009) Phase II trial of sorafenib in metastatic thyroid cancer. J Clin Oncol 27(10):1675–1684. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.18.2717
Hoftijzer H, Heemstra KA, Morreau H, Stokkel MP, Corssmit EP, Gelderblom H, Weijers K, Pereira AM, Huijberts M, Kapiteijn E, Romijn JA, Smit JW (2009) Beneficial effects of sorafenib on tumor progression, but not on radioiodine uptake, in patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Eur J Endocrinol/Eur Fed Endocr Soc 161(6):923–931. doi:10.1530/EJE-09-0702
Schneider TC, Abdulrahman RM, Corssmit EP, Morreau H, Smit JW, Kapiteijn E (2012) Long-term analysis of the efficacy and tolerability of sorafenib in advanced radio-iodine refractory differentiated thyroid carcinoma: final results of a phase II trial. Eur J Endocrinol/Eur Fed Endocr Soc 167(5):643–650. doi:10.1530/EJE-12-0405
Brose MS, Nutting CM, Jarzab B, Elisei R, Siena S, Bastholt L, de la Fouchardiere C, Pacini F, Paschke R, Shong YK, Sherman SI, Smit JW, Chung J, Kappeler C, Pena C, Molnar I, Schlumberger MJ, On behalf of the Di (2014) Sorafenib in radioactive iodine-refractory, locally advanced or metastatic differentiated thyroid cancer: a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet 384(9940):319–328. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60421-9
Capdevila J, Iglesias L, Halperin I, Segura A, Martinez-Trufero J, Vaz MA, Corral J, Obiols G, Grande E, Grau JJ, Tabernero J (2012) Sorafenib in metastatic thyroid cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 19(2):209–216. doi:10.1530/ERC-11-0351
Gupta-Abramson V, Troxel AB, Nellore A, Puttaswamy K, Redlinger M, Ransone K, Mandel SJ, Flaherty KT, Loevner LA, O’Dwyer PJ, Brose MS (2008) Phase II trial of sorafenib in advanced thyroid cancer. J Clin Oncol 26(29):4714–4719. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.16.3279
Giusti M, Melle G, Fenocchio M, Mortara L, Cecoli F, Caorsi V, Ferone D, Minuto F, Rasore E (2011) Five-year longitudinal evaluation of quality of life in a cohort of patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 12(3):163–173. doi:10.1631/jzus.B1000382
Marotta V, Ramundo V, Camera L, Del Prete M, Fonti R, Esposito R, Palmieri G, Salvatore M, Vitale M, Colao A, Faggiano A (2013) Sorafenib in advanced iodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer: efficacy, safety and exploratory analysis of role of serum thyroglobulin and FDG-PET. Clin Endocrinol 78(5):760–767. doi:10.1111/cen.12057
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S, Mooney M, Rubinstein L, Shankar L, Dodd L, Kaplan R, Lacombe D, Verweij J (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 45(2):228–247. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2008.10.026
Are C, Shaha AR (2006) Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma: biology, pathogenesis, prognostic factors, and treatment approaches. Ann Surg Oncol 13(4):453–464. doi:10.1245/ASO.2006.05.042
Hadar T, Mor C, Shvero J, Levy R, Segal K (1993) Anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid. Eur J Surg Oncol 19(6):511–516
Force T, Krause DS, Van Etten RA (2007) Molecular mechanisms of cardiotoxicity of tyrosine kinase inhibition. Nat Rev Cancer 7(5):332–344. doi:10.1038/nrc2106
Orphanos GS, Ioannidis GN, Ardavanis AG (2009) Cardiotoxicity induced by tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Acta Oncol 48(7):964–970. doi:10.1080/02841860903229124
Schmidinger M, Zielinski CC, Vogl UM, Bojic A, Bojic M, Schukro C, Ruhsam M, Hejna M, Schmidinger H (2008) Cardiac toxicity of sunitinib and sorafenib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 26(32):5204–5212. doi:10.1200/JCO.2007.15.6331
Tolcher AW, Appleman LJ, Shapiro GI, Mita AC, Cihon F, Mazzu A, Sundaresan PR (2011) A phase I open-label study evaluating the cardiovascular safety of sorafenib in patients with advanced cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 67(4):751–764. doi:10.1007/s00280-010-1372-3
Aaron Benjamin Cohen Mark Yarchoan ABT, Puttaswamy K, Harlacker K, Loevner LA, Brose MS Department of Internal Medicine (2014) Phase II trial of sorafenib in advanced thyroid cancer: A disease site analysis. J Clin Oncol 32 (suppl; abstr e17000)
Cabanillas ME, Sherman SI (2012) Applying new clinicopathological characteristics to prognostication in advanced thyroid carcinoma. Endocr Relat Cancer 19(2):C19–C22. doi:10.1530/ERC-11-0371
Prior JO, Montemurro M, Orcurto MV, Michielin O, Luthi F, Benhattar J, Guillou L, Elsig V, Stupp R, Delaloye AB, Leyvraz S (2009) Early prediction of response to sunitinib after imatinib failure by 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumor. J Clin Oncol 27(3):439–445. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.17.2742
Vercellino L, Bousquet G, Baillet G, Barre E, Mathieu O, Just PA, Desgrandchamps F, Misset JL, Hindie E, Moretti JL (2009) 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging for an early assessment of response to sunitinib in metastatic renal carcinoma: preliminary study. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 24(1):137–144. doi:10.1089/cbr.2008.0527
Acknowledgments
M. Giusti received a research grant from the BAYER pharmaceutical company to perform this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mortara, L., Pera, G., Monti, E. et al. Efficacy of sorafenib and impact on cardiac function in patients with thyroid cancer: a retrospective analysis. J Endocrinol Invest 37, 1099–1108 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-014-0177-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-014-0177-3