Abstract
Background
The characteristics of electroencephalogram (EEG) profiles under general anesthesia may depend on age and type of anesthetic.
Aim
This study investigated age-related differences in EEG waveforms between three inhalational anesthetics used at the same minimum alveolar concentration (MAC), which indicates the level of analgesia.
Methods
Patients with American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status I–II were divided into three groups according to age: pediatric (≦ 15 years); adult (16–64 years); and elderly (≧ 65 years). Each group was divided into three subgroups according to the inhalational anesthetic used: sevoflurane, isoflurane, and desflurane. Anesthesia was maintained at 1 MAC, followed by assessment of 95% spectral edge frequency (SEF95) values and amplitude of EEG waveform.
Results
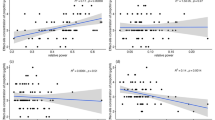
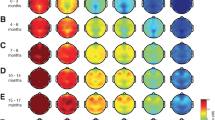
The 3 age groups comprised a total of 180 patients. The mean (± SD) EEG waveform amplitude and SEF95 values for sevoflurane in the pediatric, adult, and elderly age groups, respectively, were: 32.9 ± 2.9 µV and 16.7 ± 2.4 Hz; 16.4 ± 3.6 µV and 12.2 ± 1.3 Hz; and 11.0 ± 2.1 µV and 13.6 ± 1.6 Hz. EEG waveform amplitude and SEF95 values were significantly higher in the pediatric group than in the other groups. SEF95 value was higher in the elderly group than in the adult group. Similar results were obtained for isoflurane and desflurane.
Conclusion
The amplitude of the EEG waveform and SEF95 values varied with age, even at the same analgesic state in patients under general anesthesia. This age-dependent change in EEG waveform was observed for all three inhalational anesthetics, and should be considered in procedures requiring general anesthesia.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Denman WT, Swanson EL, Rosow D et al (2000) Pediatric evaluation of the bispectral index (BIS) monitor and correlation of BIS with end-tidal sevoflurane concentration in infants and children. Anesth Analg 90:872–877
Hagihira S (2015) Changes in the electroencephalogram during anaesthesia and their physiological basis. Br J Anaesth 115:i27–i31
Aho AJ, Kamata K, Jäntti V et al (2015) Comparison of bispectral index and entropy values with electroencephalogram during surgical anaesthesia with sevoflurane. Br J Anaesth 115:258–266
Hagihira S, Takashina M, Mori T et al (2004) Electroencephalographic bicoherence is sensitive to noxious stimuli during isoflurane or sevoflurane anesthesia. Anesthesiology 100:818–825
Bischoff P, Kochs E, Haferkorn D et al (1996) Intraoperative EEG changes in relation to the surgical procedure during isoflurane-nitrous oxide anesthesia: hysterectomy versus mastectomy. J Clin Anesth 8:36–43
Morimoto Y, Hagihira S, Yamashita S et al (2006) Changes in electroencephalographic bicoherence during sevoflurane anesthesia combined with intravenous fentanyl. Anesth Analg 103:641–645
Kochs E, Bischoff P, Pichlmeier U (1994) Schulte am Esch J, Surgical stimulation induces changes in brain electrical activity during isoflurane/nitrous oxide anesthesia. A topographic electroencephalographic analysis. Anesthesiology 80:1026–1034
Davidson AJ (2006) Measuring anesthesia in children using the EEG. Paediatr Anaesth 16:374–387
Tsuda N, Hayashi K, Hagihira S et al (2007) Ketamine, an NMDA-antagonist, increases the oscillatory frequencies of alpha-peaks on the electroencephalographic power spectrum. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 51:472–481
March PA, Muir WW (2005) Bispectral analysis of the electroencephalogram: a review of its development and use in anesthesia. Vet Anaesth Analg 32:241–255
Aranake A, Mashour GA, Avidan MS (2013) Minimum alveolar concentration: ongoing relevance and clinical utility. Anaesthesia 68:512–522
Schultz A, Grouven U, Zander I et al (2004) Age-related effects in the EEG during propofol anaesthesia. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 48:27–34
Tokuwaka J, Satsumae T, Mizutani T et al (2015) The relationship between age and minimum alveolar concentration of sevoflurane for maintaining bispectral index below 50 in children. Anaesthesia 70:318–322
Kanazawa S, Oda Y, Maeda C et al (2016) Age-dependent decrease in desflurane concentration for maintaining bispectral index below 50. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 60:177–182
Davidson AJ, McCann ME, Devavaram P et al (2001) The differences in the bispectral index between infants and children during emergence from anesthesia after circumcision surgery. Anesth Analg 93:326–330
Kanazawa S, Oda Y, Maeda C et al (2017) Electroencephalographic effect of age-adjusted 1 MAC desflurane and sevoflurane in young, middle-aged, and elderly patients. J Anesth 31:744–750
Alkire MT, Nathan SV, McReynolds JR (2005) Memory enhancing effect of low-dose sevoflurane does not occur in basolateral amygdala-lesioned rats. Anesthesiology 103:1167–1173
Alkire MT, Gorski LA (2004) Relative amnesic potency of five inhalational anesthetics follows the Meyer-Overton rule. Anesthesiology 101:417–429
Alkire MT, Nathan SV (2005) Does the amygdala mediate anesthetic-induced amnesia? Basolateral amygdala lesions block sevoflurane-induced amnesia. Anesthesiology 102:754–760
Nickalls RW, Mapleson WW (2003) Age-related iso-MAC charts for isoflurane, sevoflurane and desflurane in man. Br J Anaesth 91:170–174
Lerman J, Sikich N, Kleinman S et al (1994) The pharmacology of sevoflurane in infants and children. Anesthesiology 80:814–824
Taylor RH, Lerman J (1991) Minimum alveolar concentration of desflurane and hemodynamic responses in neonates, infants, and children. Anesthesiology 75:975–979
Matsuura T, Oda Y, Tanaka K et al (2009) Advance of age decreases the minimum alveolar concentrations of isoflurane and sevoflurane for maintaining bispectral index below 50. Br J Anaesth 102:331–335
Onuki K, Onuki N, Imamura T et al (2011) Pentazocine increases bispectral index without surgical stimulation during nitrous oxide-sevoflurane anesthesia. J Anesth 25:946–949
Purdon PL, Pavone KJ, Akeju O et al (2015) The ageing brain: age-dependent changes in the electroencephalogram during propofol and sevoflurane general anaesthesia. Br J Anaesth 115:46–57
Kim JK, Kim DK, Lee MJ (2014) Relationship of bispectral index to minimum alveolar concentration during isoflurane, sevoflurane or desflurane anaesthesia. J Int Med Res 42:130–137
Akeju O, Pavone KJ, Thum JA et al (2015) Age-dependency of sevoflurane-induced electroencephalogram dynamics in children. Br J Anaesth 115:66–76
Sury MR, Worley A, Boyd SG (2014) Age-related changes in EEG power spectra in infants during sevoflurane wash-out. Br J Anaesth 112:686–694
Tsuruta S, Satsumae T, Mizutani T et al (2011) Minimum alveolar concentrations of sevoflurane for maintaining bispectral index below 50 in children. Paediatr Anaesth 21:1124–1127
Matsuura T, Oda Y, Ikeshita K et al (2015) Differential electroencephalographic response to tracheal intubation between young and elderly during isoflurane and sevoflurane nitrous oxide anaesthesia. Anaesthesia 70:318–322
Lee JM, Akeju O, Terzakis K et al (2017) A prospective study of age-dependent changes in propofol-induced electroencephalogram oscillations in children. Anesthesiology 127:293–306
Funding
No sources of funding were used to support this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MT: designed the study, developed materials and methods, performed and analyzed measurements. Wrote draft of manuscript. ST: developed materials and methods. HY: developed materials and methods. Wrote draft of manuscript. TH: analysis of measurements and implemented them in Excel. YK: reviewed and corrected draft of manuscript. TY: conceived and designed the study. Reviewed and corrected draft of manuscript. All authors reviewed and accepted the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee (Ethics Committee of Kyushu University Hospital ref. 28–146) and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest.
Informed consent
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Kyushu University Hospital (28-146). Participants received oral and written information during the preoperative assessment before signing consent.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsukamoto, M., Taura, S., Yamanaka, H. et al. Age-related effects of three inhalational anesthetics at one minimum alveolar concentration on electroencephalogram waveform. Aging Clin Exp Res 32, 1857–1864 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-019-01378-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-019-01378-1