Abstract
Background and aims
Previous studies have focused mainly on individual factors affecting the balance function of older adults. However, it is largely unknown whether the balance functions of older adults are affected by multiple factors occurring simultaneously, and what is predominant among these factors.
Methods
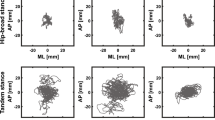
We adopted a cross-sectional study design and recruited 100 older adults from the community. Each participant was required to complete a questionnaire consisting of 20 questions related to four factors: sociodemographic, physical exercise, sleep condition and mental condition. We then evaluated all participants’ static and dynamic balance abilities using two balance tests performed using the Microsoft Kinect™ system. We used MANOVA and FDR corrections to analyze each factor to determine which factors affected the balance parameters. Last, we identified the major factors related to balance by computing the percentage of primary factors with significant effects for each factor.
Results
We found that static balance function was mainly affected by sociodemographic factors, sleep condition and mental condition. The dynamic balance function showed close relationships with physical exercise and sleep condition. Furthermore, sleep condition had a larger effect on static balance function than on dynamic balance function. We also observed an association between static balance function and mental condition.
Conclusion
A wide range of factors were associated with balance function in these older adults. The static and dynamic balance functions were related with different factors; this might provide useful information for older adults on maintaining good balance ability.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Valerio BC, Nobrega JA, Tilbery CP (2004) Neural conduction in hand nerves and the physiological factor of age. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 62(1):114–118
Finkel D, Reynolds CA, McArdle JJ, Pedersen NL (2007) Age changes in processing speed as a leading indicator of cognitive aging. Psychol Aging 22(3):558–568. doi:10.1037/0882-7974.22.3.558
Perry MC, Carville SF, Smith IC, Rutherford OM, Newham DJ (2007) Strength, power output and symmetry of leg muscles: effect of age and history of falling. Eur J Appl Physiol 100(5):553–561. doi:10.1007/s00421-006-0247-0
DeVita P, Hortobagyi T (2000) Age increases the skeletal versus muscular component of lower extremity stiffness during stepping down. J Gerontol Ser A Biol Sci Med Sci 55(12):B593–B600
Melzer I, Benjuya N, Kaplanski J (2004) Postural stability in the elderly: a comparison between fallers and non-fallers. Age Ageing 33(6):602–607. doi:10.1093/ageing/afh218
Lord SR, Sambrook PN, Gilbert C, Kelly PJ, Nguyen T, Webster IW et al (1994) Postural stability, falls and fractures in the elderly: results from the Dubbo Osteoporosis Epidemiology Study. Med J Aust 160(11):684–5, 8–91
Voos MC, Custodio EB, Malaquias J Jr (2011) Relationship of executive function and educational status with functional balance in older adults. J Geriatr Phys Ther 34(1):11–18. doi:10.1097/JPT.0b013e3181ff2452
Wong AM, Lin YC, Chou SW, Tang FT, Wong PY (2001) Coordination exercise and postural stability in elderly people: effect of Tai Chi Chuan. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 82(5):608–612. doi:10.1053/apmr.2001.22615
Seco J, Abecia LC, Echevarria E, Barbero I, Torres-Unda J, Rodriguez V et al (2013) A long-term physical activity training program increases strength and flexibility, and improves balance in older adults. Rehabil Nurs 38(1):37–47. doi:10.1002/rnj.64
Ma J, Yao YJ, Ma RM, Li JQ, Wang T, Li XJ et al (2009) Effects of sleep deprivation on human postural control, subjective fatigue assessment and psychomotor performance. J Int Med Res 37(5):1311–1320
Quach L, Yang FM, Berry SD, Newton E, Jones RN, Burr JA et al (2013) Depression, antidepressants, and falls among community-dwelling elderly people: the MOBILIZE Boston Study. J Gerontol Ser A Biol Sci Med Sci. doi:10.1093/gerona/glt084
Martin KL, Blizzard L, Srikanth VK, Wood A, Thomson R, Sanders LM et al (2013) Cognitive function modifies the effect of physiological function on the risk of multiple falls––a population-based study. J Gerontol Ser A Biol Sci Med Sci 68(9):1091–1097. doi:10.1093/gerona/glt010
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR (1975) “Mini-mental state”. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 12(3):189–198
Report on chronic situation and development trend of elderly people in China. Available at: http://www.lovepama.com/lovepama2.pdf. Accessed 2005
Clark RA, Pua YH, Fortin K, Ritchie C, Webster KE, Denehy L et al (2012) Validity of the Microsoft Kinect for assessment of postural control. Gait Posture 36(3):372–377. doi:10.1016/j.gaitpost.2012.03.033
Obdrzalek S, Kurillo G, Ofli F, Bajcsy R, Seto E, Jimison H et al (2012) Accuracy and robustness of Kinect pose estimation in the context of coaching of elderly population. Conf Proc 2012:1188–1193. doi:10.1109/EMBC.2012.6346149
Yang Y, Pu F, Li Y, Li S, Fan Y, Li D (2014) Reliability and validity of Kinect RGB-D sensor for assessing standing balance. Sens J IEEE 14(5):1633–1635. doi:10.1109/JSEN.2013.2296509
Gulliksen H (1950) Theory of mental tests. Wiley, New York
Boyle GJ (1985) Self-report measures of depression: some psychometric considerations. Br J Clin Psychol 24(1):45–59
Snowdon DA, Ostwald SK, Kane RL, Keenan NL (1989) Years of life with good and poor mental and physical function in the elderly. J Clin Epidemiol 42(11):1055–1066
Nitrini R, Caramelli P, Herrera E Jr, Charchat-Fichman H, Porto CS (2005) Performance in Luria’s fist-edge-palm test according to educational level. Cogn Behav Neurol 18(4):211–214
Patel M, Gomez S, Berg S, Almbladh P, Lindblad J, Petersen H et al (2008) Effects of 24-h and 36-h sleep deprivation on human postural control and adaptation. Exp Brain Res (Experimentelle Hirnforschung Experimentation cerebrale) 185(2):165–173. doi:10.1007/s00221-007-1143-5
Gomez S, Patel M, Berg S, Magnusson M, Johansson R, Fransson PA (2008) Effects of proprioceptive vibratory stimulation on body movement at 24 and 36 h of sleep deprivation. Clin Neurophysiol 119(3):617–625. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2007.10.058
Kvelde T, McVeigh C, Toson B, Greenaway M, Lord SR, Delbaere K et al (2013) Depressive symptomatology as a risk factor for falls in older people: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Geriatr Soc 61(5):694–706. doi:10.1111/jgs.12209
Montero-Odasso M, Verghese J, Beauchet O, Hausdorff JM (2012) Gait and cognition: a complementary approach to understanding brain function and the risk of falling. J Am Geriatr Soc 60(11):2127–2136. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2012.04209.x
Barnett A, Smith B, Lord SR, Williams M, Baumand A (2003) Community-based group exercise improves balance and reduces falls in at-risk older people: a randomised controlled trial. Age Ageing 32(4):407–414
Fatima SS, Rehman R, Saifullah, Khan Y (2013) Physical activity and its effect on forced expiratory volume. JPMA 63(3):310–312
Hamdorf PA, Withers RT, Penhall RK, Haslam MV (1992) Physical training effects on the fitness and habitual activity patterns of elderly women. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 73(7):603–608
Boix C, Rosenbluth F (2006) Bones of contention: the political economy of height inequality. Am Polit Sci Rev 108(1):1–22. doi:10.1017/S00030554130005551
Report on national physical quality in 2010. Available at: http://www.gov.cn/test/2012-04/19/content_2117320.htm. Accessed 2011.9.2
Vaquero-Cristobal R, Martinez Gonzalez-Moro I, Alacid Carceles F, Ros Simon E (2013) Strength, flexibility, balance, resistance and flexibility assessment according to body mass index in active older women. Revista espanola de geriatria y gerontologia 48(4):171–176. doi:10.1016/j.regg.2012.11.003
Mardia KV (1971) The effect of non-normality on some multivariate tests and robustness to non-normality in the linear model. Biometrika 58(1):105–112
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank all subjects who participated in the research and acknowledge the support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61101008, 11072022) and Microsoft Research Asia (FY12-RES-THEME-096).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pu, F., Sun, S., Wang, L. et al. Investigation of key factors affecting the balance function of older adults. Aging Clin Exp Res 27, 139–147 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-014-0253-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-014-0253-8