Abstract
Objective
To identify the relationship between binge eating and alcohol consumption.
Methods
This is an integrative literature review of publications from 2015 to 2019, using the Pubmed, Cinhahl, Psynet, Lilacs, Embase and Web of Science virtual databases and the descriptors (“Binge-Eating” OR “Bulimia”) AND Alcohol* in English, Spanish and Portuguese.
Results
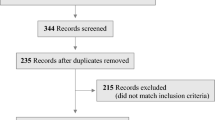
A total of 964 articles were found. After reading the titles and abstracts and excluding duplicates, 36 articles were included in the final sample (35 in English and one in Portuguese). They were grouped into three thematic categories: “sample profile and characterization”, “genetic and environmental factors”, and “emotions and behavior”.
Conclusions
The data indicate the existence of a relationship between binge eating and alcohol use, and some factors were associated with this comorbidity. Still, there were few publications on the theme at the national level, indicating the need for developing more research. These findings may support therapeutic actions and strategies for identification of cases, embracing approaches and more effective treatments to meet the individual’s biopsychosocial demands.
Level of evidence
Level V, narrative review.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association (2013) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 5th edn. American Psychiatric Association, Arlington
Berkman ND, et al (2015) Management and outcomes of binge eating disorder. Comparative Effectiveness Review No. 160. (Prepared by RTI International—University of North Carolina Evidence-based Practice Centre under Contract No. 290-2012-00008-1.) AHRQ Publication No. 15(16)-EHC030-EF. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, December 2015. http://www.effectivehealthcare.ahqr.gov/reports/final.cfm
Soihet ADS, Silva AD (2019) Efeitos psicológicos e metabólicos da restrição alimentar no transtorno de compulsão alimentar. Nutr Bras 18:55–62. https://doi.org/10.33233/nb.v18i1.2563
Udo T, Grilo CM (2018) Prevalence and correlates of DSM-5-defined eating disorders in a nationally representative sample of U.S. adults. Biol Psychiatry 84:345–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2018.03.014
Hilbert A et al (2019) Meta-analysis of the efficacy of psychological and medical treatments for binge-eating disorder. J Consult Clin Psychol 87:91–105. https://doi.org/10.1037/ccp0000358
Lewer M, Bauer A, Hartmann AS, Vocks S (2017) Different facets of body image disturbance in binge eating disorder: a review. Nutrients 9:1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9121294
Olguin P et al (2016) Medical comorbidity of binge eating disorder. Eat Weight Disord 22:13–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-016-0313-5
Cooper Z, Calugi S, Dalle Grave RI (2019) Controlling binge eating and weight: a treatment for binge eating disorder worth researching? Eat Weight Disord. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-019-00734-4
Grucza RA, Przybeck TR, Cloninger CR (2007) Prevalence and correlates of binge eating disorder in a community sample. Compr Psychiatry 48:124–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comppsych.2006.08.002
Stojek MM, Fischer S, Murphy CM, MacKillop J (2014) The role of impulsivity traits and delayed reward discounting in dysregulated eating and drinking among heavy drinkers. Appetite 80:81–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2014.05.004
Mustelin L, Latvala A, Raevuori A, Rose RJ, Kaprio J, Keski Rahkonen A (2016) Risky drinking behaviors among women with eating disorders—a longitudinal community-based study. Int J Eat Disord 49:563–571. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.22526
Gregorowski C, Seedat S, Jordaan GP (2013) A clinical approach to the assessment and management of co-morbid eating disorders and substance use disorders. BMC Psychiatry 13:289. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-244X-13-289
Center on Addiction and Substance Abuse (CASA) (2003) Food for thought: substance abuse and eating disorders. The National Center on Addiction and Substance Abuse, Columbia University, New York. https://www.centeronaddiction.org/addiction-research/reports/food-thought-substance-abuse-and-eating-disorders
Killeen TK et al (2011) Assessment and treatment of co-occurring eating disorders in privately funded addiction treatment programs. Am J Addict 20:205–211. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1521-0391.2011.00122.x
Souza MT, Silva MD, Carvalho R (2010) Revisão integrativa: o que é e como fazer. Einstein (São Paulo) 8:102–106. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1679-45082010rw1134
Mendes KDS, de Silveira RC CP, Galvão CM (2009) Revisão integrativa: método de pesquisa para a incorporação de evidências na saúde e na enfermagem. Texto contexto—enferm 17:758–764
Brasil (2012) Ministério da Saúde. Diretrizes metodológicas: elaboração de revisão sistemática e metanálise de ensaios clínicos randomizado. Editora do Ministério da Saúde, Brasília
Freitas FM, Moraes CL, Braga JU, Reichenheim ME, da Veiga GV (2018) Abusive alcohol consumption among adolescents: a predictive model for maximizing early detection and responses. Public Health 159:99–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.puhe.2018.02.008
Rolland B, Naassila M, Duffau C, Houchi H, Gierski F, André J (2017) Binge eating, but not other disordered eating symptoms, is a significant contributor of binge drinking severity: findings from a cross-sectional study among french students. Front Psychol 8:1878. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.01878
Mitchell JE et al (2015) Eating behavior and eating disorders in adults before bariatric surgery. Int J Eat Disord 48:215–222. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.22275
Solmi F et al (2015) Prevalence of purging at age 16 and associations with negative outcomes among girls in three community-based cohorts. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 56:87–96. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpp.12283
Chapa DAN, Bohrer BK, Forbush KT (2018) Eating behaviors is the diagnostic threshold for bulimia nervosa clinically meaningful? Eat Behav 28:16–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eatbeh.2017.12.002
Stickley A et al (2015) Binge drinking and eating problems in russian adolescents. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 39:540–547. https://doi.org/10.1111/acer.12644
Slane JD et al (2016) Eating behaviors: prevalence, psychiatric comorbidity, and associations with body mass index among male and female Iraq and Afghanistan veterans. Mil Med 181:e1650–e1656. https://doi.org/10.7205/MILMED-D-15-00482
Castañeda G et al (2019) Examining the effect of weight conscious drinking on binge drinking frequency among college freshmen. J Am Coll Health 26:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1080/07448481.2019.1642204
Freire CC, Zanella MT, Arasaki CH, Segal A (2019) Binge eating disorder is not predictive of alcohol abuse disorders in long-term follow-up period after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery. Eat Weight Disord. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-019-00663-2
Łowińska A, Ziółkowska B (2017) Comorbidity of alcohol dependence and abnormal eating behaviours in women in early and middle adulthood. Alcohol Drug Addict 30:279–294. https://doi.org/10.5114/ain.2017.73666
Souza da Silva T, Bisi Molina MDC, Antunes Nunes MA, Perim de Faria C, Valadão Cade N (2016) Binge eating, sociodemographic and lifestyle factors in participants of the ELSA-Brazil. J Eat Disord 4:25. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40337-016-0095-1
Martin JL, Groth G, Longo L, Rocha TL, Martens MP (2015) Disordered eating and alcohol use among college women: associations with race and big five traits. Eat Behav 17:149–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eatbeh.2015.02.002
Fouladi F et al (2015) Prevalence of alcohol and other substance use in patients with eating disorders. Eur Eat Disord Rev 23:531–536. https://doi.org/10.1002/erv.2410
Freitas PHB et al (2015) Transtornos Alimentares e o uso de drogas: Perfil Epidemiológico. Rev Baiana Enfermagem 29:146–155
Cronce LM, Berdard-Gilligan MA, Zimmerman L, Hodge KA, Kaysen D (2017) Alcohol and binge eating as mediators between posttraumatic stress disorder symptom severity and body mass index. Obesity 25:801–806. https://doi.org/10.1002/oby.21809
Baker JH et al (2018) Associations between alcohol involvement and drive for thinness and body dissatisfaction in adolescent twins: a bivariate twin study. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 42:2214–2223. https://doi.org/10.1111/acer.13868
Brewerton TD, Dansky BS, O’neil PM, Kilpatrick DG (2015) The number of divergent purging behaviors is associated with histories of trauma, PTSD, and comorbidity in a national sample of women. Eat Disord 23:422–429. https://doi.org/10.1080/10640266.2015.1013394
Mason TB, Lewis RJ (2018) Clustered patterns of behavioral and health-related variables among young lesbian women. Behav Ther 50:683–695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beth.2018.10.006
Munn-Chernoff MA et al (2015) Bulimic behaviors and early substance use: findings from a Cotwin-control study. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 39:1740–1748. https://doi.org/10.1111/acer.12829
Munn-Chernoff MA et al (2015) Genetic overlap between alcohol use disorder and bulimic behaviors in European American and African American women. Drug Alcohol Depend 153:335–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2015.05.043
Baker JH, Munn-Chernoff MA, Lichtenstein P, Larsson H, Maes H, Kendler KS (2017) Shared familial risk between bulimic symptoms and alcohol involvement during adolescence. J Abnorm Psychol 126:506–518. https://doi.org/10.1037/abn0000268
Vaz-Leal FJ et al (2015) Neurobiological and clinical variables associated with alcohol abuse in bulimia nervosa. Eur Eat Disord Rev 23:185–192. https://doi.org/10.1002/erv.2352
Fazzino TL, Raheel A, Peppercorn N, Forbush K, Kirby T, Sher KJ et al (2018) Motives for drinking alcohol and eating palatable foods: an evaluation of shared mechanisms and associations with drinking and binge eating. Addict Behav 85:113–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2018.04.025
Elmquist JA, Shorey RC, Anderson S, Stuart GL (2018) Experiential avoidance and bulimic symptoms among men in residential treatment for substance use disorders: a preliminary examination. J Psychoactive Drugs 50:81–87. https://doi.org/10.1080/02791072.2017.1368746
Trojanowski PJ, Adams LM, Fischer S (2019) Understanding profiles of student binge drinking and eating: the importance of motives. Addict Behav 96:148–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2019.04.025
Sysko R, Ojserkis R, Schebendach J, Evans SM, Hildebrandt T, Walsh BT (2017) Impulsivity and test meal intake among women with bulimia nervosa. Appetite 112:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2017.01.005
Wakefor G, Kannis-Dymand L, Statham D (2017) Anger rumination, binge eating, and at-risk alcohol use in a university sample. Aust J Psychol. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajpy.12187
Becker DF, Grilo CM (2015) Comorbidity of mood and substance use disorders in patients with binge-eating disorder: associations with personality disorder and eating disorder pathology. J Psychosom Res 79:159–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychores.2015.01.016
Pompili S, Laghi F (2017) Binge eating and binge drinking among adolescents : the role of drinking and eating motives. J Health Psychol 24:1505–1516. https://doi.org/10.1177/1359105317713359
Kim YR et al (2018) Determinants of binge eating disorder among normal weight and overweight female college students in Korea. Eat Weight Disord 23:849–860. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-018-0574-2
Elmquist J, Shorey RC, Anderson SE, Temple JR, Stuart GL (2016) The relationship between eating disorder symptoms and treatment rejection among young adult men in residential substance use treatment. Subst Abuse 10:39–44. https://doi.org/10.4137/SART.S33396
Pisetsky EM et al (2016) An examination of affect prior to and following episodes of getting drunk in women with bulimia nervosa. Psychiatry Res 240:202–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2016.04.044
Mole TB, Irvine MA, Worbe Y, Collins P, Mitchell SP, Bolton S et al (2015) Impulsivity in disorders of food and drug misuse. Psychol Med 45:771–782. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291714001834
Racine SE, Martin SJ (2016) Exploring divergent trajectories: disorder-specific moderators of the association between negative urgency and dysregulated eating. Appetite. 103:45–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2016.03.021
Pompili S, Laghi F (2018) Drunkorexia among adolescents: the role of motivations and emotion regulation. Eat Behav 29:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eatbeh.2018.01.001
Killeen T, Brewerton TD, Campbell A, Cohen LR, Hien DA (2015) Exploring the relationship between eating disorder symptoms and substance use severity in women with comorbid PTSD and substance use disorders. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse 41:547–552. https://doi.org/10.3109/00952990.2015.1080263
Cranford JA, Zucker RA, Jester JM, Puttler LI, Fitzgerald HE (2010) Parental alcohol involvement and adolescent alcohol expectancies predict alcohol involvement in male adolescents. Psychol Addict Behav 24:386–396. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0019801
Bould H, Koupil I, Dalman C, DeStavola B, Lewis G, Magnusson C (2015) Parental mental illness and eating disorders in offspring. Int J Eat Disord 48:383–391. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.22325
Mikheeva OV, Tragesser SL (2016) Personality features, disordered eating, and alcohol use among college students: a latent profile analysis. Pers Individ Dif 94:360–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2016.02.004
Funding
No funding or grants were used for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not include studies conducted with human beings of animals.
Informed consent
Formal consent is not required for this type of study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The article is part of the Topical Collection on Food and Addiction.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azevedo, L.D.S., de Souza, A.P.L., Ferreira, I.M.S. et al. Binge eating and alcohol consumption: an integrative review. Eat Weight Disord 26, 759–769 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-020-00923-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-020-00923-6