Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study is to compare elasticity features between patients with plantar fasciitis (PFis) and an asymptomatic healthy control group using shear wave elastography (SWE) and to correlate SWE values with clinical scores.
Methods
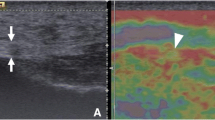
Consecutive patients diagnosed with PFis and asymptomatic subjects were enrolled in the present study. Both groups underwent clinical, ultrasound (US), and SWE evaluation. A plantar fascia thickness > 4 mm was considered pathognomonic of PFis. SWE stiffness elasticity (Young’s modulus in kPa and shear wave velocity in m/s) was measured 1 cm distally from the calcaneal insertion. Correlations with VAS and the 17-Italian Foot Function Index (17-FFI) were determined.
Results
A total of 19 patients satisfied the inclusion criteria for the patient group and were enrolled in the study, and 21 healthy subjects were used as a control group. Statistically significant differences were found for shear wave velocity between the patient and the control group, with SWE findings of 3.8 (5.1; 1.5) m/s and 4.7 (4.07; 7.04) m/s, respectively (p = 0.006). Strong positive correlations were found between the SWE findings and both the pain and the functional scale (VAS: p = 0.001; FFI: p = 0.012).
Conclusion
SWE allows quantitative assessment of the stiffness of the plantar fascia and can show PFis alterations, increasing the diagnostic performance of B-mode US. In addition, SWE shows a strong correlation with clinical scores, improving patient assessment and follow-up.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beeson P (2014) Plantar fasciopathy: revisiting the risk factors. J Foot Ankle Surg 20:160–165
Rosenbaum AJ, DiPreta JA, Misener D (2014) Plantar heel pain. Med Clin N Am 98:339–352
Schneider HP, Baca JM, Carpenter BB, Dayton PD, Fleischer AE, Sachs BD (2018) American College of Foot and Ankle Surgeons Clinical Consensus Statement: diagnosis and treatment of adult acquired infracalcaneal heel pain. J Foot Ankle Surg 57(2):370–381
Tong KB, Furia J (2010) Economic burden of plantar fasciitis treatment in the United States. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ) 39(5):227–231
Lemont H, Ammirati KM, Usen N (2003) Plantar fasciitis: a degenerative process (fasciosis) without inflammation. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 93:234–237
Snider MP, Clancy WG, McBeath AA (1983) Plantar fascia release for chronic plantar fasciitis in runners. Am J Sports Med 11:215–219
McNally EG, Shetty S (2010) Plantar fascia: imaging diagnosis and guided treatment. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol 14(3):334–343
Theodorou DJ, Theodorou SJ, Kakitsubata Y, Lektrakul N, Gold GE, Roger B, Resnick D (2000) Plantar fasciitis and fascial rupture: MR imaging findings in 26 patients supplemented with anatomic data in cadavers. Radiographics 20:S181–S197
Wearing SC, Smeathers JE, Urry SR, Hennig EM, Hills AP (2006) The pathomechanics of plantar fasciitis. Sports Med 36(7):585–611
Theodorou DJ, Theodorou SJ, Resnick D (2002) MR imaging of abnormalities of the plantar fascia. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol 6(2):105–118
Tsai WC, Chiu MF, Wang CL, Tang FT, Wong MK (2000) Ultrasound evaluation of plantar fasciitis. Scand J Rheumatol 29(4):255–259
McMillan AM, Landorf KB, Barrett JT, Menz HB, Bird AR (2009) Diagnostic imaging for chronic plantar heel pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Foot Ankle Res 2:32
Prado-Costa R, Rebelo J, Monteiro-Barroso J, Preto AS (2018) Ultrasound elastography: compression elastography and shear-wave elastography in the assessment of tendon injury. Insights Imaging 9(5):791–814
Wu CH, Chen WS, Wang TG, Lew HL (2012) Can sonoelastography detect plantar fasciitis earlier than traditional B-mode ultrasonography? Am J Phys Med Rehabil 91(2):185
Alviti F, Gurzì M, Santilli V, Paoloni M, Padua R, Bernetti A, Bernardi M, Mangone M (2017) Achilles tendon open surgical treatment with platelet-rich fibrin matrix augmentation: biomechanical evaluation. J Foot Ankle Surg 56(3):581–585
Walshe AD, Wilson GJ, Murphy AJ (1996) The validity and reliability of a test of lower body musculotendinous stiffness. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 73:332–339
Piskin FC, Yavuz S, Kose S et al (2020) A comparative study of the pancreas in pediatric patients with cystic fibrosis and healthy children using two-dimensional shear wave elastography. J Ultrasound. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40477-020-00432-3
Săftoiu A, Gilja OH, Sidhu PS, Dietrich CF, Cantisani V et al (2019) The EFSUMB guidelines for the clinical practice of elastography in non-hepatic application: update 2018. Ultraschall Med 40(4):425–453
Cocco G, Ricci V, Boccatonda A, Abate M, Guagnano MT, Schiavone C (2019) Ultrasound follow-up of spontaneous tears of the plantar fascia treated with conservative therapies. Two cases reports. Medicine 98:52
Di Serafino M, Severino R, Gioioso M et al (2020) Paediatric liver ultrasound: a pictorial essay. J Ultrasound 23:87–103
Cook JL, Purdam CR (2009) Is tendon pathology a continuum? A pathology model to explain the clinical presentation of load-induced tendinopathy. Br J Sports Med 43:409–416
Sconfienza LM, Silvestri E, Cimmino MA (2010) Sonoelastography in the evaluation of painful Achilles tendon in amateur athletes. Clin Exp Rheumatol 28(3):373–378
De Zordo T, Chhem R, Smekal V et al (2010) Realtime sonoelastography: findings in patients with symptomatic Achilles tendons and comparison to healthy volunteers. Ultraschall Med 31(4):394–400
Drakonaki EE, Allen GM, Wilson DJ (2009) Realtime ultrasound elastography of the normal Achilles tendon: reproducibility and pattern description. Clin Radiol 64(12):1196–1202
De Zordo T, Lill SR, Fink C et al (2009) Real-time sonoelastography of lateral epicondylitis: comparison of findings between patients and healthy volunteers. Am J Roentgenol 193(1):180–185
Sconfienza LM, Silvestri E, Bartolini B, Garlaschi G, Cimmino MA (2010) Sonoelastography may help in the differential diagnosis between rheumatoid nodules and tophi. Clin Exp Rheumatol 28(1):144–145
Silvestri E, Garlaschi G, Bartolini B et al (2007) Sonoelastography can help in the localization of soft tissue damage in polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR). Clin Exp Rheumatol 25(5):796
Wu CH, Chang KV, Mio S, Chen WS, Wang TG (2011) Sonoelastography of the plantar fascia. Radiology 259(2):502–507
Wu CH, Chen WS, Wang TG (2015) Plantar fascia softening in plantar fasciitis with normal B-mode sonography. Skeletal Radiol 44(11):1603–1607
Sconfienza LM, Silvestri E, Orlandi D, Fabbro E, Ferrero G, Martini C, Sardanelli F, Cimmino MA (2013) Real-time sonoelastography of the plantar fascia: comparison between patients with plantar fasciitis and healthy control subjects. Radiology 267(1):195–200
Alviti F, D'Ercole C, Schillizzi G, Mangone M, Bernetti A, Ioppolo F, Di Sante L, Minafra P, Santilli V, Elia D, Vallone G, D'ambrosio F, Cantisani V (2019) Elastosonographic evaluation after extracorporeal shockwave treatment in plantar fasciopathy. Med Ultrason 21(4):399–404
Kersten P, Küçükdeveci AA, Tennant A (2012) The use of the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) in rehabilitation outcomes. J Rehabil Med 44(7):609–610
Venditto T, Tognolo L, Rizzo RS, Iannuccelli C, Di Sante L, Trevisan M et al (2015) 17-Italian Foot Function Index with numerical rating scale: development, reliability, and validity of a modified version of the original Foot Function Index. Foot (Edinb) 25:12–18
Sabir N, Demirlenk S, Yagci B, Karabulut N, Cubukcu S (2005) Clinical utility of sonography in diagnosing plantar fasciitis. J Ultrasound Med 24:1041–1048
Draghi F, Gitto S, Bortolotto C, Guja Draghi A, Belometti GO (2017) Imaging of plantar disorder: findings on plain radiolography, ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging. Insights Imaging 8:69–78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13244-016-0533-2
Gatz M, Bejder L, Quack V, Schrading S, Dirrichs T, Tingart M, Kuhl C, Betsch M (2019) Shear wave elastography (SWE) for the evaluation of patients with plantar fasciitis. Acad Radiol 27(3):363–370
Funding
No funds were received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schillizzi, G., Alviti, F., D’Ercole, C. et al. Evaluation of plantar fasciopathy shear wave elastography: a comparison between patients and healthy subjects. J Ultrasound 24, 417–422 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40477-020-00474-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40477-020-00474-7