Abstract
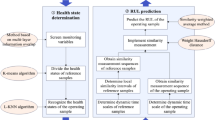
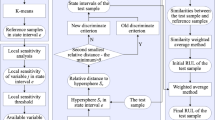
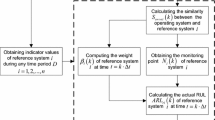
Remaining useful life (RUL) prediction is a significant prognostic activity in many industrial applications. As an emerging data-driven method, the similarity-based residual life prediction (SbRLP) method is vital to RUL prediction. However, its prediction performance is unsatisfactory in the early and middle terms, which limits its application. Therefore, an improved SbRLP method based on the grey Markov model is proposed. First, monitoring variables are evaluated and selected based on five aspects, namely monotonicity, correlation, robustness, difference, and sensitivity, to construct a one-dimensional health index. Next, the grey Markov model is employed to predict the similarity measurement sequence of an operating sample, and a similarity measurement sequence is reconstructed based on the predicted information. Furthermore, the RUL of an operating sample is predicted based on the new similarity measurement sequence. Subsequently, a commercial modular aero-propulsion system simulation dataset is used to verify the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed SbRLP method. Implementation results show that the prediction performance of the proposed SbRLP method improves, particularly in the early and middle stages. Moreover, reasonable values of the prediction step \(F\) and control coefficient \(\alpha\) can further improve its prediction accuracy.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xia T, Dong Y, Xiao L, Du S, Pan E, Xi L (2018) Recent advances in prognostics and health management for advanced manufacturing paradigms. Reliab Eng Syst Safe 178:255–268
Liu Y, Hu X, Zhang W (2019) Remaining useful life prediction based on health index similarity. Reliab Eng Syst Safe 185:502–510
Javed K, Gouriveau R, Zerhouni N (2017) State of the art and taxonomy of prognostics approaches, trends of prognostics applications and open issues towards maturity at different technology readiness levels. Mech Syst Signal Pr 94:214–236
Wang H, Ma X, Zhao Y (2019) An improved Wiener process model with adaptive drift and diffusion for online remaining useful life prediction. Mech Syst Signal Pr 127:370–387
Wang HW, Xu TX, Liu Y (2015) Remaining useful life prediction method based on Gamma processes with random parameters. J Zhejiang Univ 49(4):699–704
Zhang H, Miao Q, Zhang X, Liu Z (2018) An improved unscented particle filter approach for lithium-ion battery remaining useful life prediction. Microelectron Reliab 81:288–298
Chen Z, Li Y, Xia T, Pan E (2019) Hidden Markov model with auto-correlated observations for remaining useful life prediction and optimal maintenance policy. Reliab Eng Syst Safe 184:123–136
Sateesh Babu G, Zhao P, Li XL (2016) Deep convolutional neural network-based regression approach for estimation of remaining useful life. In International conference on database systems for advanced applications, Berlin, pp 214–228
Xia T, Song Y, Zheng Y, Pan E, Xi L (2020) An ensemble framework based on convolutional bi-directional LSTM with multiple time windows for remaining useful life estimation. Comput Ind 115:103182
Yu W, Kim IY, Mechefske C (2020) An improved similarity-based prognostic algorithm for RUL estimation using an RNN autoencoder scheme. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 199:106926
Zio E, Di Maio F (2010) A data-driven fuzzy approach for predicting the remaining useful life in dynamic failure scenarios of a nuclear system. Reliab Eng Syst Safe 95(1):49–57
You MY, Meng G (2011) A generalized similarity measure for similarity-based residual life prediction. Proc Inst Mech Eng, Part E: J Process Mech Eng 225(3):151–160
Liu J, Djurdjanovic D, Ni J, Casoetto N, Lee J (2007) Similarity based method for manufacturing process performance prediction and diagnosis. Comput Ind 58(6):558–566
Yu W, Kim IY, Mechefske C (2020) An improved similarity-based prognostic algorithm for RUL estimation using an RNN autoencoder scheme. Reliab Eng Syst Safe 199:106926
Wang H, Chen J, Qu J, Ni G (2020) A new approach for safety life prediction of industrial rolling bearing based on state recognition and similarity analysis. Saf Sci 122:104530
You MY, Meng G (2013) Toward effective utilization of similarity based residual life prediction methods: weight allocation, prediction robustness, and prediction uncertainty. Proc Inst Mech Eng, Part E: J Process Mech Eng 227(1):74–84
Chen LH, Guo TY (2011) Forecasting financial crises for an enterprise by using the Grey Markov forecasting model. Qual Quant 45(4):911–922
Li ZJ, Wang WW, Chen MY (2009) Improved grey-Markov chain algorithm for forecasting. Kybernetes 38(3/4):329–338
Wang JH, Zhang YT, Wang X, Xue F (2020) Grey Markov method and its application based on kernel and degree of greyness. Syst Eng Electron 42(02):398–404
Hsu YT, Liu MC, Yeh J, Hung HF (2009) Forecasting the turning time of stock market based on Markov-Fourier grey model. Expert Syst Appl 36(4):8597–8603
Xie J, Zhang Y, Jiang W (2008) An improved Grey-Markov chain method with an application to predict the number of Chinese international airlines. In: 2008 international symposium on information science and engineering, Shanghai, vol 2, pp 716–720
Zhao G (2010) Study on distribution demand forecast based on Grey-Markov model. In: 2010 international conference on management and service science, Wuhan, pp 1–4
Kumar U, Jain VK (2010) Time series models (Grey-Markov, Grey Model with rolling mechanism and singular spectrum analysis) to forecast energy consumption in India. Energy 35(4):1709–1716
Benkedjouh T, Medjaher K, Zerhouni N, Rechak S (2013) Remaining useful life estimation based on nonlinear feature reduction and support vector regression. Eng Appl Artif Intel 26(7):1751–1760
Yan J, Koc M, Lee J (2004) A prognostic algorithm for machine performance assessment and its application. Prod Plan Control 15(8):796–801
Guo L, Lei Y, Li N, Xing S (2017) Deep convolution feature learning for health indicator construction of bearings. In: 2017 prognostics and system health management conference (PHM-Harbin). Harbin, pp 1–6
Hou M, Pi D, Li B (2020) Similarity-based deep learning approach for remaining useful life prediction. Measurement 159:107788
Wang T, Yu J, Siegel D, Lee J (2008) A similarity-based prognostics approach for remaining useful life estimation of engineered systems. In: 2008 international conference on prognostics and health management, Denver, pp 1–6
Khelif R, Malinowski S, Chebel-Morello B, Zerhouni N (2014) RUL prediction based on a new similarity-instance based approach. In 2014 IEEE 23rd international symposium on industrial electronics (ISIE), Istanbul, pp 2463–2468
Zhao HL, Chen TM (2022) Engine life prediction based on two-scale similarity. J Propuls Tech. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1813.V.20220127.0819.002.html
Zhang B, Zhang L, Xu J (2016) Degradation feature selection for remaining useful life prediction of rolling element bearings. Qual Reliab Eng Int 32:547–554
Liang ZM, Jiang HQ, Zhou BZ et al (2018) Multi-variable similarity-based information fusion method for remaining useful life prediction. Comput Integ Manuf Syst 24(4):813–819
Xiong X, Yang H, Cheng N, Li Q (2015) Remaining useful life prognostics of aircraft engines based on damage propagation modeling and data analysis. In: 2015 8th international symposium on computational intelligence and design (ISCID), Hangzhou, vol 2, pp 143–147
Funding
The paper is financially supported by the Zhejiang natural science foundation (Project number: LQ20G010008) and open foundation of the key laboratory of intelligent robot for operation and maintenance of Zhejiang Province (Project number: SZKF-2022-R05).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Technical Editor: Andre T. Beck.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, M.Y., Ge, J.Q. & Li, Z.N. Improved similarity-based residual life prediction method based on grey Markov model. J Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 45, 294 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-023-04176-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-023-04176-z