Abstract
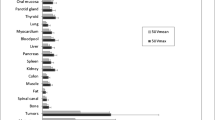
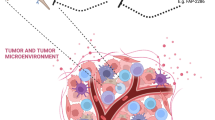
Fibroblast activation protein (FAP)-targeted radiopharmaceuticals recently emerged as potential pantumoral agent for PET imaging. FAPi PET provides the opportunity to explore the tumor microenvironment, a highly heterogeneous and dynamic system of various non-malignant cells, by assessing the overexpression of FAP in cancer-associated fibroblasts. A significant increase in FAP expression can be found in several tumor subtypes, in which has been observed an increased tumor lesion uptake associated with low and favorable background, leading to a high detection rate of tumor location(s). This pictorial essay aims to present a selection of clinical cases highlighting the potential benefit of FAPi PET in different tumor subtypes, especially considering the higher diagnostic accuracy compared to FDG PET. We present clinical cases of breast cancer, lung cancer, gastric cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, gynecological cancers and peritoneal carcinomatosis, as well as an introduction of the biodistribution of FAPi.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jansen K, Heirbaut L, Cheng JD, Joossens J, Ryabtsova O, Cos P, Maes L, Lambeir AM, De Meester I, Augustyns K, Van der Veken P (2013) Selective inhibitors of fibroblast activation protein (FAP) with a (4-Quinolinoyl)-glycyl-2-cyanopyrrolidine scaffold. ACS Med Chem Lett 4(5):491–496. https://doi.org/10.1021/ml300410d
Scanlan MJ, Raj BK, Calvo B, Garin-Chesa P, Sanz-Moncasi MP, Healey JH, Old LJ, Rettig WJ (1994) Molecular cloning of fibroblast activation protein alpha, a member of the serine protease family selectively expressed in stromal fibroblasts of epithelial cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91(12):5657–5661. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.91.12.5657
Balkwill FR, Capasso M, Hagemann T (2012) The tumor microenvironment at a glance. J Cell Sci 125(Pt 23):5591–5596. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.116392
Dvorak HF (1986) Tumors wounds that do not heal similarities between tumor stroma generation and wound healing. New Engl J Med 315(26):1650–1659. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM198612253152606
Lindner T, Loktev A, Altmann A, Giesel F, Kratochwil C, Debus J, Jäger D, Mier W, Haberkorn U (2018) Development of quinoline-based theranostic ligands for the targeting of fibroblast activation protein. J Nucl Med 59:1415–1422. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.118.210443
Giesel FL, Kratochwil C, Lindner T, Marschalek MM, Loktev A, Lehnert W, Debus J, Jäger D, Flechsig P, Altmann A, Mier W, Haberkorn U (2019) 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT: biodistribution and preliminary dosimetry estimate of 2 DOTA-containing FAP-targeting agents in patients with various cancers. J Nucl Med 60(3):386–392. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.118.215913
Kratochwil C, Flechsig P, Lindner T, Abderrahim L, Altmann A, Mier W, Adeberg S, Rathke H, Röhrich M, Winter H, Plinkert PK, Marme F, Lang M, Kauczor HU, Jäger D, Debus J, Haberkorn U, Giesel FL (2019) 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT: tracer uptake in 28 different kinds of cancer. J Nucl Med 60(6):801–805. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.119.227967
Çermik TF, Ergül N, Yılmaz B, Mercanoğlu G (2022) Tumor imaging With 68Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 PET/CT: comparison with 18F-FDG PET/CT in 22 different cancer types. Clin Nucl Med 47(4):e333–e339. https://doi.org/10.1097/RLU.0000000000004073
Mona CE, Benz MR, Hikmat F, Grogan TR, Lückerath K, Razmaria A, Riahi R, Slavik R, Girgis MD, Carlucci G, Kelly KA, French SW, Czernin J, Dawson DW, Calais J (2021) Correlation of 68Ga-FAPi-46 PET biodistribution with FAP expression by immunohistochemistry in patients with solid cancers: a prospective translational exploratory study. J Nucl Med. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.121.262426
Hu K, Wang L, Wu H, Huang S, Tian Y, Wang Q, Xiao C, Han Y, Tang G (2021) [18F]FAPI-42 PET imaging in cancer patients: optimal acquisition time, biodistribution, and comparison with [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-021-05646-z
Kalluri R (2016) The biology and function of fibroblasts in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 16:582–598. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2016.73
Kömek H, Can C, Güzel Y, Oruç Z, Gündoğan C, Yildirim ÖA, Kaplan İ, Erdur E, Yıldırım MS, Çakabay B (2021) 68Ga-FAPI-04 PET/CT, a new step in breast cancer imaging: a comparative pilot study with the 18F-FDG PET/CT. Ann Nucl Med 35:744–752. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-021-01616-5
Elboga U, Sahin E, Kus T, Cayirli YB, Aktas G, Uzun E, Cinkir HY, Teker F, Sever ON, Aytekin A, Yilmaz L, Aytekin A, Cimen U, Mumcu V, Kilbas B, Çelen YZ (2021) Superiority of 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT scan in detecting additional lesions compared to 18FDG PET/CT scan in breast cancer. Ann Nucl Med 35(12):1321–1331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-021-01672-x
Farsad M (2020) FDG PET/CT in the staging of lung cancer. Curr Radiopharm 13(3):195–203. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874471013666191223153755
Wang L, Tang G, Hu K, Liu X, Zhou W, Li H, Huang S, Han Y, Chen L, Zhong J, Wu H (2022) Comparison of 68Ga-FAPI and 18F-FDG PET/CT in the evaluation of advanced lung cancer. Radiology 303(1):191–199. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.211424
Li Y, Lin X, Li Y, Lv J, Hou P, Liu S, Chen P, Wang M, Zhou C, Wang X (2022) Clinical utility of F-18 labeled fibroblast activation protein inhibitor (FAPI) for primary staging in lung adenocarcinoma: a prospective study. Mol Imaging Biol 24(2):309–320. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-021-01679-w
Wei Y, Cheng K, Fu Z, Zheng J, Mu Z, Zhao C, Liu X, Wang S, Yu J, Yuan S (2022) [18F]AlF-NOTA-FAPI-04 PET/CT uptake in metastatic lesions on PET/CT imaging might distinguish different pathological types of lung cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 49(5):1671–1681. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-021-05638-z
Yun M (2014) Imaging of gastric cancer metabolism using 18 F-FDG PET/CT. J Gastric cancer 14(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.5230/jgc.2014.14.1.1
Pang Y, Zhao L, Luo Z, Hao B, Wu H, Lin Q, Sun L, Chen H (2021) Comparison of 68Ga-FAPI and 18F-FDG Uptake in gastric, duodenal, and colorectal cancers. Radiology 298(2):393–402. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2020203275
Erkan M, Hausmann S, Michalski CW, Fingerle AA, Dobritz M, Kleeff J, Friess H (2012) The role of stroma in pancreatic cancer: diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 9(8):454–467. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2012.115
Zhang Z, Jia G, Pan G, Cao K, Yang Q, Meng H, Yang J, Zhang L, Wang T, Cheng C, Zuo C (2022) Comparison of the diagnostic efficacy of 68 Ga-FAPI-04 PET/MR and 18F-FDG PET/CT in patients with pancreatic cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-022-05729-5
Kauhanen SP, Komar G, Seppänen MP, Dean KI, Minn HR, Kajander SA, Rinta-Kiikka I, Alanen K, Borra RJ, Puolakkainen PA, Nuutila P, Ovaska JT (2009) A prospective diagnostic accuracy study of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography, multidetector row computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging in primary diagnosis and staging of pancreatic cancer. Ann Surg 250(6):957–963. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181b2fafa
Marrero JA, Kulik LM, Sirlin CB, Zhu AX, Finn RS, Abecassis MM, Roberts LR, Heimbach JK (2018) Diagnosis, staging, and management of hepatocellular carcinoma: 2018 practice guidance by the american association for the study of liver diseases. Hepatology (Baltimore, MD) 68(2):723–750. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.29913
Oliva MR, Saini S (2004) Liver cancer imaging: role of CT, MRI US and PET. Cancer Imaging 4 Spec No A(Spec No A):S42–S46. https://doi.org/10.1102/1470-7330.2004.0011
Gallagher BM, Fowler JS, Gutterson NI, MacGregor RR, Wan CN, Wolf AP (1978) Metabolic trapping as a principle of oradiopharmaceutical design: some factors resposible for the biodistribution of [18F] 2-deoxy-2-fluoro-D-glucose. J Nucl Med 19(10):1154–1161
Wang H, Zhu W, Ren S, Kong Y, Huang Q, Zhao J, Guan Y, Jia H, Chen J, Lu L, Xie F, Qin L (2021) 68Ga-FAPI-04 versus 18F-FDG PET/CT in the detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Oncol 11:693640. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.693640
Carmona-Bozo JC, Manavaki R, Woitek R, Torheim T, Baxter GC, Caracò C, Provenzano E, Graves MJ, Fryer TD, Patterson AJ, Gilbert FJ (2021) Hypoxia and perfusion in breast cancer: simultaneous assessment using PET/MR imaging. Eur Radiol 31(1):333–344. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-020-07067-2
Siripongsatian D, Promteangtrong C, Kunawudhi A, Kiatkittikul P, Boonkawin N, Chinnanthachai C, Jantarato A, Chotipanich C (2022) Comparisons of quantitative parameters of Ga-68-labelled fibroblast activating protein inhibitor (FAPI) PET/CT and [18F]F-FDG PET/CT in patients with liver malignancies. Mol Imaging Biol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-022-01732-2
Lakhani A, Khan SR, Bharwani N, Stewart V, Rockall AG, Khan S, Barwick TD (2017) FDG PET/CT pitfalls in gynecologic and genitourinary oncologic imaging. Radiographics 37(2):577–594. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.2017160059
Dendl K, Koerber SA, Finck R, Mokoala KMG, Staudinger F, Schillings L, Heger U, Röhrich M, Kratochwil C, Sathekge M, Jäger D, Debus J, Haberkorn U, Giesel FL (2021) 68Ga-FAPI-PET/CT in patients with various gynecological malignancies. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 48(12):4089–4100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-021-05378-0
Coccolini F, Gheza F, Lotti M, Virzì S, Iusco D, Ghermandi C, Melotti R, Baiocchi G, Giulini SM, Ansaloni L, Catena F (2013) Peritoneal carcinomatosis. World J Gastroenterol 19(41):6979–6994. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i41.6979
Zhao L, Pang Y, Luo Z, Fu K, Yang T, Zhao L, Sun L, Wu H, Lin Q, Chen H (2021) Role of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 PET/CT in the evaluation of peritoneal carcinomatosis and comparison with [18F]-FDG PET/CT. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 48(6):1944–1955. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-020-05146-6
Acknowledgements
Authors would thank the Nuclear Medicine Division of the Faculty of Medicine of the Yeditepe University, Turkey and the Division of Nuclear Medicine of the S. Orsola-Malpighi University Hospital IRCCS of Bologna, Italy for providing clinical cases. At Yeditepe University 68Ga-FAPi-04 synthesis was performed within the scope of the magistral drug production permit given by the Turkey Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (E-24931227-000-535219). The evaluation of data was approved by the local ethics committee of the Yeditepe University (Decision no: 1576).
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest in relation to this work.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
All participants signed informed consent form prior any imaging procedures.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Airò Farulla, L.S., Demirci, E., Castellucci, P. et al. Radiolabeled FAP inhibitors as new pantumoral radiopharmaceuticals for PET imaging: a pictorial essay. Clin Transl Imaging 11, 95–106 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40336-022-00506-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40336-022-00506-8