Abstract
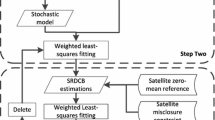
Global navigation satellite systems and positioning, navigation, and timing services, such as the newly developed BeiDou satellite system (BDS), require high-accuracy satellite observations. Satellite-induced code bias is present in BDS-2 satellite observations while it is negligibly present in BDS-3 satellite observations. The traditional method of mitigating BDS code bias involves two steps, first addressing multipath delay and then code bias, and does not obtain optimal results. A one-step strategy is therefore proposed to model and eliminate code bias and multipath delay considering BDS-2 and BDS-3 integrated processing. A combined least-square and autoregressive strategy is selected to estimate the model coefficients of code bias and construct the multipath delay with one solution. Moreover, inter-satellite correlations of BDS-2 and BDS-3 are extracted to improve the weight matrix in the estimation of model coefficients. To verify the proposed strategy, experiments are designed for eight schemes to analyze the coefficients and residuals of modelling code bias. Experimental results indicate that a more stable and accurate code bias model is acquired by introducing inter-satellite correlation; with the one-step strategy, the model residuals are reduced and a more optimal code bias model is output. Meanwhile, the single-frequency precise point positioning (PPP) and real-time PPP of BDS-2 and BDS-3 combined estimations are tested for different stations, frequencies, and code bias models. The results of final positions reveal that accuracy in the Up (U) direction is improved compared with that in the East (E) and North (N) directions; improvements are greater for B1I than for B3I. In general, the one-step strategy enhances the precision of single-frequency (B1I/B3I) PPP, especially in the U direction. However, the effects on BDS ultra-rapid orbit determination are negligible. Equally, the double-frequency real-time PPP solution is improved, compared with adopting the traditional method, by 10.6–64.9%, 0.0–59.1%, and 12.6–67.2% for E, N, and U directions, respectively, through BDS-2/BDS-3 integrated processing. The proposed one-step strategy therefore outperforms the two-step strategy in terms of rapidly processing high-precision BDS observations.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaike H (1981) Likelihood of a model and information criteria. J Econ 16(1):3–14
Cai C, He C, Santerre R et al (2016) A comparative analysis of measurement noise and multipath for four constellations: GPS, BeiDou GLONASS and Galileo. Surv Rev 48(349):287–295
Chang G, Chen C, Yang Y et al (2018) Tikhonov regularization based modeling and sidereal filtering mitigation of GNSS multipath errors. Remote Sens 10:1801
Chen C, Chang G, Zheng N et al (2019a) GNSS multipath error modeling and mitigation by using sparsity-promoting regularization. IEEE Access 7:24096–24108
Chen J, Yue D, Zhu S et al (2019b) Correction model of BDS satellite-induced code bias and its impact on precise point positioning. Adv Space Res 63(7):2155–2163
Dong D, Wang M, Chen W et al (2016) (2016) Mitigation of multipath effect in GNSS short baseline positioning by the multipath hemispherical map. J Geod 90(3):255–262
Guo J, Li G, Kong Q et al (2014) Modeling GPS multipath effect based on spherical cap harmonic analysis. Trans Nonfferous Metals Soc China 24(6):1874–1879
Guo F, Li X, Liu W (2016) Mitigating BeiDou satellite-induced code bias: taking into account the stochastic model of corrections. Sensors 16(6):909
Hauschild A, Montenbruck O, Sleewaegen J et al (2012) Characterization of compass M-1 signals. GPS Solut 16(1):117–126
Hu C (2020) An investigation of key technologies related to combining BDS-2 and BDS-3 observations in data processing. China University of Mining and Technology Xuzhou China
Hu C, Wang Q, Wang Z et al (2018) New-generation BeiDou (BDS-3) experimental satellite precise orbit determination with an improved cycle-slip detection and repair algorithm. Sensors 18(5):1402
Hu C, Wang Q, Min Y et al (2019) An improved model for BDS satellite ultra-rapid clock offset prediction based on BDS-2 and BDS-3 combined estimation. Acta Geod Geoph 54(4):513–543
Hu C, Wang Z, Wang Q et al (2020) An improved model for inter-system bias estimation based on BDS-2/BDS-3 combined precise orbit determination. Geo Inf Sci Wuhan Univ. https://doi.org/10.13203/j.whugis20190132
Li X, Li X, Zhang X, et al (2016) An improved method for eliminating BeiDou satellite induced code bias. In: EGU general assembly conference. EGU general assembly conference abstracts 18:10984
Mao Y, Wang Q, Hu C et al (2019) New clock offset prediction method for BeiDou satellites based on inter-satellite correlation. Acta Geoda Geoph 54(4):35–54
Montenbruck O, Hauschild A, Steigenberger P et al (2013) Initial assessment of the COMPASS/BeiDou-2 regional navigation satellite system. GPS Solut 17(2):211–222
Park K, Nerem R, Schenewerk M et al (2004) Site-specific multipath characteristics of global IGS and CORS GPS sites. J Geod 77(12):799–803
Qing Y, Lou Y, Dai X et al (2017) Benefits of satellite clock modeling in BDS and Galileo orbit determination. Adv Space Res 60(12):2550–2560
Shi C, Zhao Q, Hu Z et al (2012) Precise relative positioning using real tracking data from COMPASS GEO and IGSO satellites. GPS Solut 17(1):103–119
Su M, Zheng J, Yang Y et al (2018) A new multipath mitigation method based on adaptive thresholding wavelet denoising and double reference shift strategy. GPS Solut 22:40
Tan S (2017) Innovative development and forecast of BeiDou System. Acta Geod Cart Sini 46(10):1284–1289
Wang J, Stewart M, Sakiri M (1998) Stochastic modeling for static GPS baseline data processing. J Surv Eng 124(4):171–181
Wang Q, Hu C, Zhang K (2019) A BDS-2/BDS-3 integrated method for ultra-rapid orbit determination with the aid of precise satellite clock offsets. Remote Sens 11(15):1758
Wanninger L, Beer S (2015) BeiDou satellite-induced code pseudorange variations diagnosis and therapy. GPS Solut 19:639–648
Wu F, Deng K, Chang G et al (2018) The application of a combination of weighted least-squares and autoregressive methods in predictions of polar motion parameters. Acta Geod Geoph 53(2):247–257
Wu F, Chang G, Deng K et al (2019) Selecting data for autoregressive modeling in polar motion prediction. Acta Geod Geoph 54(4):557–566
Yang X (2019) Models and methods of data processing for real-time precise point positioning based on multi-GNSS. China University of Mining and Technology Xuzhou China
Yang Y, Li J, Xu J et al (2011) Contribution of the Compass satellite navigation system to global PNT users. Chinese Sci Bull 56(26):2813
Yang X, Chang G, Wang Q et al (2019) An adaptive Kalman filter based on variance component estimation for a real-time ZTD solution. Acta Geod Geoph 54:89–121
Yang Y, Mao Y, Sun B (2020) Basic performance and future developments of BeiDou global navigation satellite system. Satell Navig 1(1):1
Zhang X, Wu M, Li X et al (2017) Initial assessment of the COMPASS/BeiDou-3: new-generation navigation signals. J Geod 91(10):1225–1240
Zheng D, Zhong P, Ding X et al (2005) Filtering GPS time-series using a vondrak filter and cross-validation. J Geod 79:363–369
Zhou F (2018) Theory and methodology of Multi-GNSS undifferenced and uncombined precise point positioning. East China Normal University Shanghai China
Zhou S, Hu X, Cao Y, et al (2019) Analysis on the impact of BeiDou code bias on the accuracy of spatial signal. The 10th China Satellite Navigation Conference 2019 Beijing China
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No: 41874039) and the Jiangsu Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. BK20181361). The authors thank the International GNSS Monitoring and Assessment Service (iGMAS) for the use of its data and products.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CH conceived and designed the experiments; ZW and CH performed the experiments, analyzed the data and wrote the paper; CH, PR and TC contributed to discussions and revisions.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, C., Wang, Z., Rao, P. et al. One-step correction strategy for BDS-2/BDS-3 satellite observation code bias and multipath delay. Acta Geod Geophys 56, 29–59 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40328-020-00327-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40328-020-00327-z