Abstract
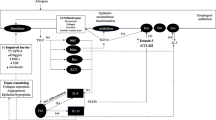
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic immune-mediated inflammatory disorder characterized by symptomatic esophageal dysfunction and an eosinophil-predominant inflammation of the esophagus. EoE arises from interaction between genetic and environmental factors. In pediatric patients, clinical manifestations vary depending on age, from a gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)-like condition to severe dysphagic symptoms. Upper endoscopy is considered the gold standard for diagnosis and monitoring of EoE; however, significant efforts are underway to identify noninvasive diagnostic tools and biomarkers to avoid repetitive invasive procedures. Therapeutic first-line options currently available for EoE are elimination diets, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), and steroids. The aim of treatment is to improve clinical symptoms while obtaining mucosal healing and avoiding long-term complications. Dietary treatment options comprise different empiric diets or an exclusively amino acid formula. Despite the efficacy of diets, compliance is often challenging. PPIs and topical steroids represent the main pharmacological options for EoE, and both can induce and maintain remission. Topical steroids have been reported as more effective, but data on long-term safety remain insufficient for both these and PPIs. Endoscopic dilations are currently reserved for severe untreated fibrostenotic disease unresponsive to medical therapies. Several biologic agents are available but not yet approved for EoE.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lucendo AJ, Molina-Infante J, Arias Á, von Arnim U, Bredenoord AJ, Bussmann C, et al. Guidelines on eosinophilic esophagitis: evidence-based statements and recommendations for diagnosis and management in children and adults. United Eur Gastroenterol J. 2017;5:335–58.
Gonzales-Cervera J, Lucendo AJ. Eosinophilic esophagitis: an evidence-based approach to therapy. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2016;26:8–18.
Attwood SE, Smyrk TC, Demeester TR, Jones JB. Esophageal eosinophilia with dysphagia. A distinct clinicopathologic syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. 1993;38:109–16.
Navarro P, Arias Á, Arias-González L, Laserna-Mendieta EJ, Ruiz-Ponce M, Lucendo AJ. Systematic review with meta-analysis: the growing incidence and prevalence of eosinophilic oesophagitis in children and adults in population-based studies. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2019;49:1116–25.
Jensen ET, Hoffman K, Shaheen NJ, Genta RM, Dellon ES. Esophageal eosinophilia is increased in rural areas with low population density: results from a national pathology database. Am J Gastroenterol. 2014;109:668–75.
Jensen ET, Shah ND, Hoffman K, Sonnenberg A, Genta RM, Dellon ES. Seasonal variation in detection of oesophageal eosinophilia and eosinophilic oesophagitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015;42:461–9.
Dellon ES, Hirano I. Epidemiology and natural history of eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2018;154:319–32.
Lyles J, Rothenberg M. Role of genetics, environment, and their interactions in the pathogenesis of eosinophilic esophagitis. Curr Opin Immunol. 2019;60:46–53.
Alexander ES, Martin LJ, Collins MH, Kottyan LC, Sucharew H, He H, Mukkada VA, et al. Twin and family studies reveal strong environmental and weaker genetic cues explaining heritability of eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134:1084–92.
Allen-Brady K, Firszt R, Fang JC, Wong J, Smith KR, Peterson KA. Population-based familial aggregation of eosinophilic esophagitis suggests a genetic contribution. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;140:1138–43.
O’Shea KM, Aceves SS, Dellon ES, Gupta SK, Spergel JM, Furuta GT, et al. Pathophysiology of eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2018;154:333–45.
Kottyan LE, Rothenberg ME. Genetics of eosinophilic esophagitis. Mucosal Immunol. 2017;10:580–8.
Blanchard C, Wang N, Stringer KF, Mishra A, Fulkerson P, Abonia JP, et al. Eotaxin-3 and a uniquely conserved gene-expression profile in eosinophilic esophagitis. J Clin Invest. 2006;116:536–47.
Sleiman PM, Wang ML, Cianferoni A, Aceves S, Gonsalves N, Nadeau K, et al. GWAS identifies four novel eosinophilic esophagitis loci. Nat Commun. 2014;5:5593.
Litosh VA, Rochman M, Rymer JK, Porollo A, Kottyan LC, Rothenberg ME. Calpain-14 and its association with eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;139:1762–71.
Blanchard C, Mingler MK, McBride M, Putnam PE, Collins MH, Chang G, et al. Periostin facilitates eosinophil tissue infiltration in allergic lung and esophageal responses. Mucosal Immunol. 2008;1:289–96.
Wong CK, Hu S, Cheung PF, Lam CW. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin induces chemotactic and prosurvival effects in eosinophils: implications in allergic inflammation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Bio. 2010;43:305–15.
Allakhverdi Z, Comeau MR, Jessup HK, Yoon BR, Brewer A, Chartier S, et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin is released by human epithelial cells in response to microbes, trauma, or inflammation and potently activates mast cells. J Exp Med. 2007;204:253–8.
Noti M, Wojno ED, Kim BS, Siracusa MC, Giacomin PR, Nair MG, et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin-elicited basophil responses promote eosinophilic esophagitis. Nat Med. 2013;19:1005–133.
Rajavelu P, Rayapudi M, Moffitt M, Mishra A. Significance of para-esophageal lymph nodes in food or aeroallergen-induced iNKT cell-mediated experimental eosinophilic esophagitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012;302:G645–G654654.
Rayapudi M, Mavi P, Zhu X, Pandey AK, Abonia JP, Rothenberg ME, et al. Indoor insect allergens are potent inducers of experimental eosinophilic esophagitis in mice. J Leukoc Biol. 2010;88:337–46.
Benitez AJ, Hoffman C, Muir AB, Dods KK, Spergel JM, Bushman FD, et al. Inflammation-associated microbiota in pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis. Microbiome. 2015;1(3):23.
Harris JK, Fang R, Wagner BD, Choe HN, Kelly CJ, Schroeder S, et al. Esophageal microbiome in eosinophilic esophagitis. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0128346.
Von Armin U, Wex T, Link A, Messerschmidt M, Venerito M, Miehlke S, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection is associated with a reduced risk of developing eosinophilic esophagitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016;43:825–30.
Jensen ET, Dellon ES. Environmental factors and eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018;142:32–40.
Guajardo JR, Zegarra-Bustamante MA, Brooks EG. Does aeroallergen sensitization cause or contribute to eosinophilic esophagitis? Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2018;55:65–9.
Lucendo AJ, Sanchez-Cazalilla M. Adult versus pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis: important differences and similarities for the clinician to understand. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2012;8:733–45.
Lucendo AJ, Arias-González L, Molina-Infante J, Arias Á. Systematic review: health-related quality of life in children and adults with eosinophilic oesophagitis—measure instruments and determinant factors. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2017;46:401–9.
Shaheen NJ. A phenotypic analysis shows that eosinophilic esophagitis is a progressive fibrostenotic disease. Gastrointest Endosc. 2014;79:577–85.
Lipka S, Kumar A, Richter JE. Impact of diagnostic delay and other risk factors on eosinophilic esophagitis phenotype and oesophageal diameter. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2016;50:134–40.
Runge TM, Dellon ES. Do we know what causes eosinophilic esophagitis? A mechanistic update. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2015;17:33.
Dellon ES, Kim HP, Sperry SL, Rybnicek DA, Woosley JT, Shaheen NJ. A phenotypic analysis shows that eosinophilic esophagitis is a progressive fibrostenotic disease. Gastrointest Endosc. 2014;79(577–585):e4.
Schoepfer AM, Safroneeva E, Bussmann C, Kuchen T, Portmann S, Simon H-U, et al. Delay in diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis increases risk for stricture formation in a time dependent manner. Gastroenterology. 2013;145:1230–6.
Schoepfer AM, Straumann A, Panczak R, Coslovsky M, Kuehni CE, Maurer E, et al. Development and validation of a symptom-based activity index for adults with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2014;147:1255–66.
Martin LJ, Franciosi JP, Collins MH, Abonia JP, Lee JJ, Hommel KA, et al. Pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis symptom scores (PEESS v2.0) identify histologic and molecular correlates of the key clinical features of disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;135(6):1519–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2015.03.004.
Dellon ES, Speck O, Woodward K, Covey S, Rusin S, Shaheen NJ, et al. Distribution and variability of esophageal eosinophilia in patients undergoing upper endoscopy. Mod Pathol. 2015;28:383–90.
Kim HP, Vance RB, Shaheen NJ, Dellon ES. The prevalence and diagnostic utility of endoscopic features of eosinophilic esophagitis: a meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;10:988–96.
Hirano I, Moy N, Heckman MG, Thomas CS, Gonsalves N, Achem SR. Endoscopic assessment of the oesophageal features of eosinophilic oesophagitis: validation of a novel classification and grading system. Gut. 2013;62:489–95.
Collins MH. Histopathologic features of eosinophilic esophagitis and eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2014;43:257–68.
Kagalwalla AF, Akhtar N, Woodruff SA, Rea BA, Masterson JC, Mukkada V, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: epithelial mesenchymal transition contributes to esophageal remodeling and reverses with treatment. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;129:1387–96.
Min SB, Nylund CM, Baker TP, Ally M, Reinhardt B, Chen YJ, et al. Longitudinal evaluation of noninvasive biomarkers for eosinophilic esophagitis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2017;51(2):127–35.
Rao GS, Mitchell L, Ohnuki JF, Fitzgerald J, Gleich GJ, Corkins M, et al. Can eosinophil derived neurotoxin (EDN) act as a surrogate marker of disease activity in children with allergic eosinophilic esophagitis (AEE)? Gastrointest Endosc. 2004;59:P103.
Dellon ES, Rusin S, Gebhart JH, Covey S, Higgins LL, Beitia R, et al. Utility of a noninvasive serum biomarker panel for diagnosis and monitoring of eosinophilic esophagitis: a prospective study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015;110:821–7.
Furuta GT, Kagalwalla AF, Lee JJ, Alumkal P, Maybruck BT, Fillon S, et al. The oesophageal string test: a novel, minimally invasive method measures mucosal inflammation in eosinophilic oesophagitis. Gut. 2013;62:1395–405.
Katzka DA, Geno DM, Ravi A, Smyrk TC, Lao-Sirieix P, Miremadi A, et al. Accuracy, safety, and tolerability of tissue collection by Cytosponge vs endoscopy for evaluation of eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;13:77–83.
Rosen R, Amirault J, Johnston N, Haver K, Khatwa U, Rubinstein E, et al. The utility of endoscopy and multichannel intraluminal impedance testing in children with cough and wheezing. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2014;49(11):1090–6.
Menard-Katcher C, Swerdlow MP, Mehta P, Furuta GT, Fenton LZ. Contribution of esophagram to the evaluation of complicated pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2015;61(5):541–6.
Nelson MJ, Miller FH, Moy N, Zalewski A, Gonsalves N, Gregory DL, et al. Comparison of endoscopy and radiographic imaging for detection of esophageal inflammation and remodeling in adults with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018;87:962–8.
Straumann A, Katzka DA. Diagnosis and treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2018;154:346–59.
Molina-Infante J, Lucendo AJ. Dietary therapy for eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018;142:41–7.
Kelly KJ, Lazenby AJ, Rowe PC, Yardley JH, Perman JA, Sampson HA, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis attributed to gastroesophageal reflux: improvement with an amino acid-based formula. Gastroenterology. 1995;109:1503–12.
Arias A, Gonzalez-Cervera J, Tenias JM, Lucendo AJ. Efficacy of dietary interventions for inducing histologic remission in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. 2014;146:1639–48.
Spergel JM, Beausoleil JL, Mascarenhas M, Liacouras CA. The use of skin prick tests and patch tests to identify causative foods in eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002;109:363–8.
Spergel JM, Brown-Whitehorn TF, Cianferoni A, Shuker M, Wang ML, Verma R, et al. Identification of causative foods in children with eosinophilic esophagitis treated with an elimination diet. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;130:461–7.
Molina-Infante J, Martin-Noguerol E, Alvarado-Arenas M, Porcel-Carreno SL, Jimenez-Timon S, Hernandez-Arbeiza FJ. Selective elimination diet based on skin testing has suboptimal efficacy for adult eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;130:1200–2.
Wolf WA, Jerath MR, Sperry SLW, Shaheen NJ, Dellon ES. Dietary elimination therapy is an effective option for adults with eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;12:1272–9.
Philpott H, Nandurkar S, Royce SG, Thien F, Gibson PR. Allergy tests do not predict food triggers in adult patients with eosinophilic oesophagitis. A comprehensive prospective study using five modalities. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016;44:223–33.
Kagalwalla AF, Sentongo TA, Ritz S, Hess T, Nelson SP, Emerick KM, et al. Effect of six-food elimination diet on clinical and histologic outcomes in eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;4:1097–102.
Philpott H, Nandurkar S, Royce SG, Thien F, Gibson PR. A prospective open clinical trial of a proton pump inhibitor, elimination diet and/or budesonide for eosinophilic oesophagitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016;43:985–93.
Hoofien A, Dias JA, Malamisura M, Rea F, Chong S, Oudshoorn J, et al. Pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis: results of the European retrospective pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis registry (RetroPEER). J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2019;68(4):552–8.
Lucendo AJ, Arias A, Gonzalez-Cervera J, Yague-Compadre JL, Guagnozzi D, Angueira T, et al. Empiric 6-food elimination diet induced and maintained prolonged remission in patients with adult eosinophilic esophagitis: a prospective study on the food cause of the disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;131:797–804.
Kagalwalla AF, Wechsler JB, Amsden K, Schwartz S, Makhija M, Olive A, et al. Efficacy of a 4-food elimination diet for children with eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;15:1698–707.
Molina-Infante J, Arias A, Alcedo J, Garcia-Romero R, Casabona-Frances S, Prieto-Garcia A, et al. Step-up empiric elimination diet for pediatric and adult eosinophilic esophagitis: the 2-4-6 study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018;141(4):1365–72.
Kagalwalla AF, Shah A, Li BU, Sentongo TA, Ritz S, Manuel-Rubio M, et al. Identification of specific foods responsible for inflammation in children with eosinophilic esophagitis successfully treated with empiric elimination diet. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2011;53:145–9.
Reed CC, Fan C, Koutlas NT, Shaheen NJ, Dellon ES. Food elimination diets are effective for long-term treatment of adults with eosinophilic oesophagitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2017;46:836–44.
Dellon ES, Gonsalves N, Hirano I, Furuta GT, Liacouras CA, Katzka DA, American College of Gastroenterology. ACG clinical guideline: evidenced based approach to the diagnosis and management of esophageal eosinophilia and eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE). Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108:679–92.
Dellon ES, Liacouras CA, Molina-Infante J, Furuta GT, Spergel JM, Zevit N, et al. Updated international consensus diagnostic criteria for eosinophilic esophagitis: proceedings of the AGREE conference. Gastroenterology. 2018;155(4):1022–33.e10.
Vazquez-Elizondo G, Ngamruengphong S, Khrisna M, Devault KR, Talley NJ, Achem SR. The outcome of patients with oesophageal eosinophilic infiltration after an eight-week trial of a proton pump inhibitor. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2013;38:1312–9.
Dellon ES, Speck O, Woodward K, Gebhart JH, Madanick RD, Levinson S, et al. Clinical and endoscopic characteristics do not reliably differentiate PPI-responsive esophageal eosinophilia and eosinophilic esophagitis in patients undergoing upper endoscopy: a prospective cohort study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108:1854–60.
Moawad FJ, Veerappan GR, Dias JA, Baker TP, Maydonovitch CL, Wong RK. Randomized controlled trial comparing aerosolized swallowed fluticasone to esomeprazole for esophageal eosinophilia. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108:366–72.
Peterson KA, Thomas KL, Hilden K, Emerson LL, Wills JC, Fang JC. Comparison of esomeprazole to aerosolized, swallowed fluticasone for eosinophilic esophagitis. Dig Dis Sci. 2010;55:1313–9.
Lucendo AJ, Arias A, Molina-Infante J. Efficacy of proton pump inhibitor drugs for inducing clinical and histologic remission in patients with symptomatic esophageal eosinophilia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;4:13–22.
Molina-Infante J, Ferrando-Lamana L, Ripoll C, Hernandez-Alonso M, Mateos JM, Fernandez-Bermejo M, et al. Esophageal eosinophilic infiltration responds to proton pump inhibition in most adults. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;9:110–7.
Gutierrez-Junquera C, Fernandez-Fernandez S, Cilleruelo ML, Rayo A, Echeverría L, Quevedo S, et al. High revalence of response to proton-pump inhibitor treatment in children with esophageal eosinophilia. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2016;62:704–10.
Liacouras CA, Furuta GT, Hirano I, Atkins D, Attwood SE, Bonis PA, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: updated consensus recommendations for children and adults. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;128:3–20.
Molina-Infante J, Rodriguez-Sanchez J, Martinek J, van Rhijn BD, Krajciova J, Rivas MD, et al. Long-term loss of response in proton pump inhibitor-responsive esophageal eosinophilia is uncommon and influenced by CYP2C19 genotype and rhinoconjunctivitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015;110:1567–75.
Gómez Torrijos E, García-Rodríguez R, Castro-Jiménez A, Rodríguez-Sanchez J, Méndez Díaz Y, Molina-Infante J. The efficacy of step-down therapy in adult patients with proton pump inhibitorresponsive oesophageal eosinophilia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016;43:534–40.
Dellon ES, Liacouras CA. Advances in clinical management of eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2014;147:1238–54.
Cotton CC, Durban R, Dellon ES. Illuminating elimination diets: controversies regarding dietary treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis. Dig Dis Sci. 2019;64(6):1401–8.
Dranove JE, Horn DS, Davis MA, Kernek KM, Gupta SK. Predictors of response to proton pump inhibitor therapy among children with significant esophageal eosinophilia. J Pediatr. 2009;154:96–100.
Rea F, Caldaro T, Tambucci R, Romeo EF, Caloisi C, Torroni F, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: is it also a surgical disease? J Pediatr Surg. 2013;48:304–8.
Moledina DG, Perazella MA. PPIs and kidney disease: from AIN to CKD. J Nephrol. 2016;29(5):611–6.
Ye X, Liu H, Wu C, Qin Y, Qin Y, Zang J, Gao Q, et al. Proton pump inhibitors therapy and risk of hip fracture: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;23(9):794–800.
Aceves SS, Newbury RO, Chen D, Mueller J, Dohil R, Hoffman H, et al. Resolution of remodeling in eosinophilic esophagitis correlates with epithelial response to topical corticosteroids. Allergy. 2010;65(1):109–16.
Van Rhijn BD, Verheij J, van den Bergh Weerman MA, Verseijden C, van den Wijngaard RM, de Jonge WJ, et al. Histological response to fluticasone propionate in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis is associated with improved functional esophageal mucosal integrity. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015;110(9):1289–97.
Richter JE. Endoscopic treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2018;28:97–110.
Molina Infante J, Rivas MD, Hernandez-Alonso M, Vinagre-Rodríguez G, Mateos-Rodríguez JM, Dueñas-Sadornil C, et al. Proton pump inhibitor-responsive oesophageal eosinophilia correlates with downregulation of eotaxin-3 and Th2 cytokines overexpression. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014;40:955–96.
Zhang X, Cheng E, Huo X, Yu C, Zhang Q, Pham TH, et al. Omeprazole blocks STAT6 binding to the eotaxin-3 promoter in eosinophilic esophagitis cells. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e50037.
Liacouras CA, Wenner WJ, Brown K, Ruchelli E. Primary eosinophilic esophagitis in children: successful treatment with oral corticosteroids. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1998;26(4):380–5.
Schaefer ET, Fitzgerald JF, Molleston JP, Croffie JM, Pfefferkorn MD, Corkins MR, et al. Comparison of oral prednisone and topical fluticasone in the treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis: a randomized trial in children. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;6:165–73.
Chuang MYA, Chinnaratha MA, Hancock DG, Woodman R, Wong GR, Cock C, et al. Topical steroid therapy for the treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2015;6:e82.
Murali AR, Gupta A, Attar BM, Ravi V, Koduru P. Topical steroids in eosinophilic esophagitis: systematic review and metaanalysis of placebo-controlled randomized clinical trials. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;31:1111–9.
Sawas T, Dhalla S, Sayyar M, Pasricha PJ, Hernaez R. Systematic review with meta-analysis: pharmacological interventions for eosinophilic oesophagitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015;41:797–806.
Tan ND, Xiao YL, Chen MH. Steroids therapy for eosinophilic esophagitis: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Dig Dis. 2015;16:431–42.
De Rooij WE, Dellon ES, Parker CE, Feagan BG, Jairath V, Ma C, et al. Pharmacotherapies for the treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis: state of the art review. Drugs. 2019;79(13):1419–34.
Oliva S, Rossetti D, Papoff P, Tiberti A, Rossi P, Isoldi S, et al. A New formulation of oral viscous budesonide in treating paediatric eosinophilic oesophagitis: a pilot study. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2017;64(2):218–24.
Eusebi LH, Rabitti S, Artesiani ML, et al. Proton pump inhibitors: risks of long-term use. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;32(7):1295–302.
De Bruyne P, Ito S. Toxicity of long-term use of proton pump inhibitors in children. Arch Dis Child. 2018;103(1):78–82.
Liacouras CA, Furuta GT, Hirano I, Atkins D, Attwood SE, Bonis PA, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: updated consensus rec-ommendations for children and adults. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;128:3–20.
Dellon ES, Woosley JT, Arrington A, McGee SJ, Covington J, Moist SE, et al. Efficacy of budesonide vs fluticasone for initial treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis in a randomized controlled trial. Gastroenterology. 2019;157:65.
Lindberg GM, Van Eldik R, Saboorian MH. A case of her-pes esophagitis after fluticasone propionate for eosinophilicesophagitis. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;5:527–30.
Machicado JD, Younes M, Wolf DS. An unusual cause ofodynophagia in a patient with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2014;147:37–8.
European Medicines Agency. New medicine for rare inflammatory condition of the oesophagus: Jorveza approved under accelerated assessment. 9 November 2017. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/new-medicine-rare-inflammatory-condition-oesophagus.
Oliva S, Rossetti D, Papoff P, Tiberti A, Mallardo S, Volpe D, et al. A 12-week maintenance therapy with a new prepared viscous budesonide in pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis. Dig Dis Sci. 2019;64(6):1571–8.
Butz BK, Wen T, Gleich GJ, Furuta GT, Spergel J, King E, et al. Efficacy, dose reduction, and resistance to high-dose fluticasone in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2014;147:324–33.
Wolf WA, Cotton CC, Green DJ, Hughes JT, Woosley JT, Shaheen NJ, et al. Predictors of response to steroid therapy for eosinophilic esophagitis and treatment of steroid-refractory patients. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;13:452.
Philpott H, Dellon ES. The role of maintenance therapy in eosinophilic esophagitis: who, why, end how? J Gastroenterol. 2018;53:165–71.
Liacouras CA, Spergel JM, Ruchelli E, Verma R, Mascarenhas M, Semeao E, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: a 10-year experience in 381 children. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005;3:1198–206.
Harel S, Hursh B, Chan E, Avinashi V, Panagiotopoulos C. Adrenal suppression in children treated with oral viscous budesonide for eosinophilic esophagitis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2015;61:190–3.
Ahmet A, Benchimol E, Goldbloom E, Barkey JL. Adrenal suppression in children treated with swallowed fluticasone and oral viscous budesonide for eosinophilic esophagitis. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2016;12:49.
Philpott H, Dougherty MK, Reed CC, Caldwell M, Kirk D, Torpy DJ, et al. Systematic review: adrenal insufficiency secondary to swallowed topical corticosteroids in eosinophilic oesophagitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2018;47:1071–8.
Stein ML, Collins MH, Villanueva JM, Kushner JP, Putnam PE, Buckmeier BK, et al. Anti-IL-5 (mepolizumab) therapy for eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;118:1312–9.
Straumann A, Conus S, Grzonka P, Kita H, Kephart G, Bussmann C, et al. Anti-interleukin-5 antibody treatment (mepolizumab) in active eosinophilic oesophagitis: a randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial. Gut. 2010;59:21–30.
Assaad AH, Gupta SK, Collins MH, Thomson M, Heath AT, Smith DA, et al. An antibody against IL-5 reduces numbers of esophageal intraepithelial eosinophils in children with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2011;141:1593–604.
Spergel JM, Rothenberg ME, Collins MH, Furuta GT, Markowitz JE, Fuchs G, et al. Reslizumab in children and adolescents with eosinophilic esophagitis: results of a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;129(456–463):463.e1–.e3.
Markowitz JE, Jobe L, Miller M, Frost C, Laney Z, Eke R. Safety and efficacy of reslizumab for children and adolescents with eosinophilic esophagitis treated for 9 years. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2018;66:893–7.
Clayton F, Fang JC, Gleich GJ, Lucendo AJ, Olalla JM, Vinson LA, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis in adults is associated with IgG4 and not mediated by IgE. Gastroenterology. 2014;147:602–9.
Rothenberg ME, Wen T, Greenberg A, Alpan O, Enav B, Hirano I, et al. Intravenous anti-IL-13 mAb QAX576 for the treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;135:500–7.
Hirano I, Collins MH, Assouline-Dayan Y, Evans L, Gupta S, Schoepfer A, et al. Anti-Interleukin-13 monoclonal antibody (RPC4046) in adult patients with active Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2019;156(3):592–603.
Hirano I, Dellon ES, Hamilton JD, Collins MH, Peterson K, Chehade M, et al. Efficacy of dupilumab in a phase 2 randomized trial of adults with active eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2019;158:111–22.
Venturelli N, Lexmond WS, Ohsaki A, Nurko S, Karasuyama H, Fiebiger E, et al. Allergic skin sensitization promotes eosinophilic esophagitis through the IL-33-basophil axis in mice. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016;138:1367–80.
De Souza HS, Tortori CA, Lintomen L, Figueiredo RT, Bernardazzi C, Leng L, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor promotes eosinophil accumulation and tissue remodeling in eosinophilic esophagitis. Mucosal Immunol. 2015;8:1154–65.
Attwood SEA, Lewis CJ, Bronder CS, Morris CD, Armstrong GR, Whittam J. Eosinophilic oesophagitis: a novel treatment using Montelukast. Gut. 2003;52:181–5.
Lucendo AJ, de Rezende LC, Jimenez-Contreras S, Yagüe-Compadre JL, González-Cervera J, Mota-Huertas T, et al. Montelukast was inefficient in maintaining steroid-induced remission in adult eosinophilic esophagitis. Dig Dis Sci. 2011;56:3551–8.
Alexander JA, Ravi K, Enders FT, Geno DM, Kryzer LA, Mara KC, et al. Montelukast does not maintain symptom remission after topical steroid therapy for eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;15:214–21.
Netzer P, Gschossmann JM, Straumann A, Sendensky A, Weimann R, Schoepfer AM. Corticosteroid-dependent eosinophilic oesophagitis: azathioprine and 6-mercaptopurine can induce and maintain long-term remission. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;19:865–9.
Lieberman JA, Zhang J, Whitworth J, Cavender C. A randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled study of the use of viscous oral cromolyn sodium for the treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018;120(5):527–31.
Runge TM, Eluri S, Woosley JT, Shaheen NJ, Dellon ES. Control of inflammation decreases the need for subsequent esophageal dilation in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Dis Esophagus. 2017;30:1–7.
Dougherty M, Runge TM, Eluri S, Dellon ES. Esophageal dilation with either bougie or balloon technique as a treatment for eosinophilic esophagitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;86(4):581–591.e3.
Moawad FJ, Molina-Infante J, Lucendo AJ, Cantrell SE, Tmanova L, Douglas KM. Systematic review with meta-analysis: endoscopic dilation is highly effective and safe in children and adults with eosinophilic oesophagitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2017;46(2):96–105.
Kavitt RT, Ates F, Slaughter JC, Higginbotham T, Shepherd BD, Sumner EL, et al. Randomized controlled trial comparing esophageal dilation to no dilation among adults with esophageal eosinophilia and dysphagia. Dis Esophagus. 2016;29(8):983–91.
Menard-Katcher C, Furuta GT, Kramer RE. Dilation of pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis: adverse events and short-term outcomes. J Ped Gastroenterol Nutr. 2017;64:701–6.
Prasad GA, Alexander JA, Schleck CD, Zinsmeister AR, Smyrk TC, Elias RM, et al. Epidemiology of eosinophilic esophagitis over three decades in Olmsted County. Minnesota Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;7:1055–61.
Müller S, Pühl S, Vieth M, Stolte M. Analysis of symptoms and endoscopic findings in 117 patients with histological diagnoses of eosinophilic esophagitis. Endoscopy. 2007;39:339–44.
Henderson CJ, Abonia JP, King EC, Putnam PE, Collins MH, Franciosi JP, et al. Comparative dietary therapy effectiveness in remission of pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;129:1570–8.
Kuang FL, Kumar S, Powers A, Quezado M, Wang Z, Ware JA, et al. Benralizumab (anti-IL5Ra) depletes gut tissue eosinophilia and improves symptoms in hypereosinophilic syndrome with gastrointestinal involvement. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018;141:196.
Oliva S, Laudadio I, Fulci V, Rossetti D, Isoldi S, Stronati L, et al. SERPINB12 as a possible marker of steroid dependency in children with eosinophilic esophagitis: a pilot study. Dig Liver Dis. 2020;52:158–63.
Oliva S, Azouz NP, Stronati L, Rothenberg ME. Recent advances in potential targets for eosinophilic esophagitis treatments. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2020;16(4):421–8.
Funding
No sources of funding were used to conduct this study or prepare this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Danilo Rossetti, Sara Isoldi, and Salvatore Oliva have no conflicts of interest that are directly relevant to the content of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rossetti, D., Isoldi, S. & Oliva, S. Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Update on Diagnosis and Treatment in Pediatric Patients. Pediatr Drugs 22, 343–356 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40272-020-00398-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40272-020-00398-z