Abstract
Purpose
In this study, the prevalence of diabetes and pre-diabetes (pre-DM) has been estimated; also, some factors related to diabetes and pre-diabetes in the city of Kharameh, southern Iran, were investigated.
Methods
This cross-sectional study was conducted on a total of 10,474 subjects aged 40–70 years who participated in phase one of PERSIAN Kharameh cohort carried out between 2015 and 2016. Eligible individuals were included in the study by census method.
Results
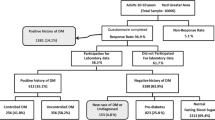
Prevalence of diabetes is 20.17% (95% CI: 19.95–20.39) and that of pre-diabetes is 15.74% (95% CI 15.54–15.93). Multivariate logistic regression results showed that the prevalence of diabetes had a direct relationship with increasing age (p < 0.001), being single (p = 0.005), family history of diabetes (p < 0.001), abdominal obesity (p < 0.001), hypertension (p: < 0.001), and high triglycerides (p: < 0.001); also, it had an inverse relationship with residence in rural areas (p < 0.001), education (p < 0.001), and employment (p < 0.001).
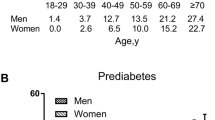
Also, the prevalence of pre-diabetes showed a direct relationship with increasing age (60–70 years p = 0.010), being single (p = 0.004), living in rural areas (P < 0.001), having a family history of diabetes ( both P = 0.023), abdominal obesity (P < 0.001), hypertension (P < 0.001), high cholesterol (P < 0.001) and high triglycerides (P < 0.001), and an inverse relationship with female gender (P < 0.001), education (high school P = 0.022), employment (P = 0.010), and smoking habit (P = 0.019). These results were all statistically significant.
Conclusion
The present study shows the high prevalence of diabetes and pre- diabetes in the city of Kharameh. Diabetes prevention policies should be developed and implemented for the public.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hunter DJ, Reddy KS. Noncommunicable diseases. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(14):1336–43. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1109345.
Bennett JE, Stevens GA, Mathers CD, Bonita R, Rehm J, Kruk ME, et al. NCD Countdown 2030: worldwide trends in non-communicable disease mortality and progress towards Sustainable Development Goal target 3.4. Lancet. 2018;392(10152):1072–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31992-5.
Zheng Y, Ley SH, Hu FB. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018;14(2):88–98. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2017.151.
Zhou B, Lu Y, Hajifathalian K, Bentham J, Di Cesare M, Danaei G, et al. Worldwide trends in diabetes since 1980: a pooled analysis of 751 population-based studies with 4· 4 million participants. The Lancet. 2016;387(10027):1513–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00618-8.
Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019;157: 107843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843.
Akbarzadeh A, Salehi A, Vardanjani HM, Poustchi H, Gandomkar A, Fattahi MR, et al. Epidemiology of adult diabetes mellitus and its correlates in pars cohort study in Southern Iran. Arch Iran Med. 2019;22(11):633–9.
Widyahening I, Kayode G, Wangge G, Grobbee D. Country Characteristics and Variation in Diabetes Prevalence among Asian Countries–an Ecological Study. Journal of the ASEAN Federation of Endocrine Societies. 2019;34(1):80.
Peykari N, GHAJARIEH SS, Djalalinia S, Kasaeian A, Parsaeian M, Ahmadvand A, et al. National and sub-national prevalence, trend, and burden of metabolic risk factors (MRFs) in Iran: 1990–2013, study protocol. 2014. https://doi.org/10.15605/jafes.034.01.12
Javanbakht M, Mashayekhi A, Baradaran HR, Haghdoost A, Afshin A. Projection of diabetes population size and associated economic burden through 2030 in Iran: evidence from micro-simulation Markov model and Bayesian meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(7): e0132505. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0132505.
Esteghamati A, Larijani B, Aghajani MH, Ghaemi F, Kermanchi J, Shahrami A, et al. Diabetes in Iran: prospective analysis from first nationwide diabetes report of National Program for Prevention and Control of Diabetes (NPPCD-2016). Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-13379-z.
Huang Y, Cai X, Mai W, Li M, Hu Y. Association between prediabetes and risk of cardiovascular disease and all cause mortality: systematic review and meta-analysis. Bmj. 2016;355. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.i5953
Edwards CM, Cusi K. Prediabetes: a worldwide epidemic. Endocrinol Metab Clin. 2016;45(4):751–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecl.2016.06.007.
Hostalek U. Global epidemiology of prediabetes-present and future perspectives. Clinical diabetes and endocrinology. 2019;5(1):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40842-019-0080-0.
Zhao M, Lin H, Yuan Y, Wang F, Xi Y, Wen LM, et al. Prevalence of pre-diabetes and its associated risk factors in rural areas of Ningbo, China. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2016;13(8):808. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13080808.
Mirahmadizadeh A, Fathalipour M, Mokhtari AM, Zeighami S, Hassanipour S, Heiran A. The prevalence of undiagnosed type 2 diabetes and prediabetes in Eastern Mediterranean region (EMRO): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020;160: 107931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107931.
Association AD. Standards of medical care in diabetes—2018 abridged for primary care providers. Clinical diabetes: a publication of the American Diabetes Association. 2018;36(1):14. https://doi.org/10.2337/cd17-0119.
Wu Y, Ding Y, Tanaka Y, Zhang W. Risk factors contributing to type 2 diabetes and recent advances in the treatment and prevention. Int J Med Sci. 2014;11(11):1185. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.10001.
Soewondo P, Pramono LA. Prevalence, characteristics, and predictors of pre-diabetes in Indonesia. Medical Journal of Indonesia. 2011;20(4):283–94. https://doi.org/10.13181/mji.v20i4.465
Danaei G, Lu Y, Singh GM, Carnahan E, Stevens GA, Cowan MJ, et al. Cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, and diabetes mortality burden of cardiometabolic risk factors from 1980 to 2010: a comparative risk assessment. Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology. 2014. http://observatorio.fm.usp.br/handle/OPI/16024
Kaiser A, Vollenweider P, Waeber G, Marques-Vidal P. Prevalence, awareness and treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Switzerland: the CoLaus study. Diabet Med. 2012;29(2):190–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-5491.2011.03422.x.
Poustchi H, Eghtesad S, Kamangar F, Etemadi A, Keshtkar A-A, Hekmatdoost A, et al. Prospective epidemiological research studies in Iran (the PERSIAN Cohort Study): rationale, objectives, and design. Am J Epidemiol. 2018;187(4):647–55. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwx314.
Organization WH. Waist circumference and waist-hip ratio: report of a WHO expert consultation, Geneva, 8–11 December 2008. 2011. http://www.who.int/about/licensing/copyright_form/en/index.html
Hirshkowitz M, Whiton K, Albert SM, Alessi C, Bruni O, DonCarlos L, et al. National Sleep Foundation’s sleep time duration recommendations: methodology and results summary. Sleep Health. 2015;1(1):40–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleh.2014.12.010.
Expert Panel on Detection E. Executive summary of the third report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (adult treatment panel III). Jama. 2001;285(19):2486–97. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.285.19.2486
Hosseini Z, Whiting SJ, Vatanparast H. Type 2 diabetes prevalence among Canadian adults—dietary habits and sociodemographic risk factors. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2019;44(10):1099–104. https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2018-0567.
Hu M, Wan Y, Yu L, Yuan J, Ma Y, Hou B, et al. Prevalence, awareness and associated risk factors of diabetes among adults in Xi’an. China Scientific reports. 2017;7(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-10797-x.
Shin J-Y. Trends in the prevalence and management of diabetes in Korea: 2007–2017. Epidemiology and health. 2019;41. https://doi.org/10.4178/2Fepih.e2019029
Barreto M, Kislaya I, Gaio V, Rodrigues AP, Santos AJ, Namorado S, et al. Prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of diabetes in Portugal: Results from the first National Health examination Survey (INSEF 2015). Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018;140:271–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2018.03.052.
Alkandari A, Longenecker JC, Barengo NC, Alkhatib A, Weiderpass E, Al-Wotayan R, et al. The prevalence of pre-diabetes and diabetes in the Kuwaiti adult population in 2014. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018;144:213–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2018.08.016.
Selçuk KT, Sözmen MK, Toğrul BÜ. Diabetes prevalence and awareness in adults in the Balçova district in Turkey. Turkish journal of medical sciences. 2015;45(6):1220–7. https://doi.org/10.3906/sag-1312-62.
Rashedi V, Asadi-Lari M, Delbari A, Fadayevatan R, Borhaninejad V, Foroughan M. Prevalence of diabetes type 2 in older adults: Findings from a large population-based survey in Tehran, Iran (Urban HEART-2). Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2017;11:S347–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2017.03.014.
Ebrahimi H, Emamian MH, Shariati M, Hashemi H, Fotouhi A. Diabetes mellitus and its risk factors among a middle-aged population of Iran, a population-based study. International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries. 2016;36(2):189–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-015-0397-x.
Safari-Faramani R, Rajati F, Tavakol K, Hamzeh B, Pasdar Y, Moradinazar M, et al. Prevalence, awareness, treatment, control, and the associated factors of diabetes in an Iranian Kurdish population. Journal of diabetes research. 2019;2019. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/5869206
Yazdanpanah L, Shahbazian H, Aleali AM, Jahanshahi A, Ghanbari S, Latifi S. Prevalence, awareness and risk factors of diabetes in Ahvaz (South West of Iran). Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2016;10(2):S114–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2016.03.007.
Katibeh M, Hosseini S, Soleimanizad R, Manaviat M, Kheiri B, Khabazkhoob M, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of diabetes mellitus in a central district in Islamic Republic of Iran: a population-based study on adults aged 40–80 years. EMHJ-Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal. 2015;21(6):412–9. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/255112
Endris T, Worede A, Asmelash D. Prevalence of diabetes mellitus, prediabetes and its associated factors in Dessie Town, Northeast Ethiopia: a community-based study. Diabetes, metabolic syndrome and obesity: targets and therapy. 2019;12:2799. https://doi.org/10.2147/2FDMSO.S225854.
Mirzaei M, Rahmaninan M, Mirzaei M, Nadjarzadeh A. Epidemiology of diabetes mellitus, pre-diabetes, undiagnosed and uncontrolled diabetes in Central Iran: results from Yazd health study. BMC Public Health. 2020;20(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-020-8267-y.
Abas AH. Prevalence and associated risk factors for type 2 diabetes mellitus among adults (>= 40 years of age) in jigjiga City, Somali region, Eastern Ethiopia. 2019.
Hammami S, Mehri S, Hajem S, Koubaa N, Souid H, Hammami M. Prevalence of diabetes mellitus among non institutionalized elderly in Monastir City. BMC Endocr Disord. 2012;12(1):1–7.
Zafar J, Nadeem D, Khan SA, Jawad Abbasi M, Aziz F, Saeed S. Prevalence of diabetes and its correlates in urban population of Pakistan: A Cross-sectional survey. J Pak Med Assoc. 2016;66(8):922–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6823-12-15.
Wu H, Meng X, Wild SH, Gasevic D, Jackson CA. Socioeconomic status and prevalence of type 2 diabetes in mainland China, Hong Kong and Taiwan: a systematic review. Journal of global health. 2017;7(1). https://doi.org/10.7189/2Fjogh.07.011103
Li M, Huang Y, Liu Z, Shen R, Chen H, Ma C, et al. The association between frailty and incidence of dementia in Beijing: findings from 10/66 dementia research group population-based cohort study. BMC Geriatr. 2020;20(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-020-01539-2.
Muche AA, Olayemi OO, Gete YK. Prevalence and determinants of gestational diabetes mellitus in Africa based on the updated international diagnostic criteria: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Archives of Public Health. 2019;77(1):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13690-019-0362-0.
Lee Y-H, Shin M-H, Nam H-S, Park K-S, Choi S-W, Ryu S-Y, et al. Effect of family history of diabetes on hemoglobin A1c levels among individuals with and without diabetes: the dong-gu study. Yonsei Med J. 2018;59(1):92–100. https://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2018.59.1.92.
Vornanen M, Konttinen H, Kääriäinen H, Männistö S, Salomaa V, Perola M, et al. Family history and perceived risk of diabetes, cardiovascular disease, cancer, and depression. Prev Med. 2016;90:177–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ypmed.2016.06.027.
Bennet L, Franks PW, Zöller B, Groop L. Family history of diabetes and its relationship with insulin secretion and insulin sensitivity in Iraqi immigrants and native Swedes: a population-based cohort study. Acta Diabetol. 2018;55(3):233–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-017-1088-5.
Zhao X, Zhu X, Zhang H, Zhao W, Li J, Shu Y, et al. Prevalence of diabetes and predictions of its risks using anthropometric measures in southwest rural areas of China. BMC Public Health. 2012;12(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-12-821.
Aynalem SB, Zeleke AJ. Prevalence of diabetes mellitus and its risk factors among individuals aged 15 years and above in Mizan-Aman town, Southwest Ethiopia, 2016: a cross sectional study. Int J Endocrinol. 2018;2018.https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9317987
Won JC, Lee JH, Kim JH, Kang ES, Won KC, Kim DJ, et al. Diabetes fact sheet in Korea, 2016: an appraisal of current status. Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(5):415–24. https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0017.
Babazadeh T, Dianatinasab M, Daemi A, Nikbakht HA, Moradi F, Ghaffari-Fam S. Association of self-care behaviors and quality of life among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Chaldoran County. Iran Diabetes & metabolism journal. 2017;41(6):449–56. https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.6.449.
Mirahmadizadeh A, Khorshidsavar H, Seif M, Sharifi MH. Adherence to medication, diet and physical activity and the associated factors amongst patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Therapy. 2020;11(2):479–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-019-00750-8.
Aung WP, Htet AS, Bjertness E, Stigum H, Chongsuvivatwong V, Kjøllesdal MKR. Urban–rural differences in the prevalence of diabetes mellitus among 25–74 year-old adults of the Yangon Region, Myanmar: Two cross-sectional studies. BMJ Open. 2018;8(3): e020406. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2017-020406.
Funding
Shiraz University of Medical Sciences financially supported this study. (Grant number: 99–12-05–21892).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest to the publication of this article.
Ethics approval
The study protocol was reviewed and approved by the ethical committee of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences (approval number: IR.SUMS.REC.1399.1266).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johari, M.G., Jokari, K., Mirahmadizadeh, A. et al. The prevalence and predictors of pre-diabetes and diabetes among adults 40–70 years in Kharameh cohort study: A population-based study in Fars province, south of Iran. J Diabetes Metab Disord 21, 85–95 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-021-00938-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-021-00938-5