Abstract
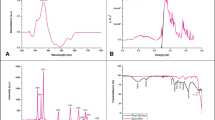
The study evaluated the antidiabetic potentials of green-synthesized iron oxide (Fe2O3) nanoparticles using stem extract of Securidaca longipedunculata. Fe2O3 nanoparticles were synthesized via green route and characterized using different analytical tools. Diabetes was induced in albino Wister rats by a single dose intraperitoneal injection of 90 mg/kg bodyweight of alloxan monohydrate and treated for 21 days. Lipid profiles, biochemical parameters and histopathological study of the liver and kidney were also examined. The characterization results confirmed formation of spherical, hematite phase of iron oxide with crystallite size of 4.07 nm and maximum wavelength of 372.27 nm. There was a significant (p < 0.05) decrease in blood glucose level of the diabetic rats from 409.50 ± 5.50 to 199.1550 ± 9.33 mg/dL in Fe2O3 nanoparticle group compared to the diabetic and extract control groups. Group treated with Fe2O3 nanoparticle shows an increase in bodyweight throughout the treatment period and is significantly different (p < 0.05) with the other groups. There is a significant difference (p < 0.05) in serum alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST) and alanine phosphatase (ALP) of the Fe2O3 nanoparticles treated group with Glibenclamide and diabetic control group. The histopathology of the liver and kidney shows normal histoarchitecture with no features of acute or chronic damage in all groups. The green-synthesized Fe2O3 nanoparticles have the potential of treating hyperglycemia and could serve as drug lead in the treatment of diabetes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali, L.M.A., Shaker, S.A., Pinol, R., Millan, A., Hanafy, M.Y., Helmy, M.H., Kamel, M.A., Mahmoud, S.A.: Effect of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles on glucose homeostasis on type 2 diabetes experimental model. Life Sci. 245, 117361 (2020)
Simcox, J.A., McClain, D.A.: Iron and diabetes risk. Cell Metab. 17(3), 329–341 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2013.02.007
Ovais, M., Khalil, A.T., Islam, N.U., Ahmad, I., Ayaz, M., Saravanan, M., Shinwari, Z.K., Mukherjee, S.: Role of plant phytochemicals and microbial enzymes inbiosynthesis of metallic nanoparticles. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 102(16), 6799–6814 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9146-7
El-Boubbou, K.: Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as drug carriers: preparation, conjugation and delivery. Nanomedicine 13, 929–952 (2017)
Ponnaiah, S., Rajan, J.: A review on iron oxide nanoparticles and their biomedical applications. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 31, 3397–3413 (2018)
Demirer, G.S., Okur, A.C., Kizilel, S.: Synthesis and design of biologically inspired biocompatible iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 3, 7831–7849 (2015)
Parka, J., Kadasala, N.R., Abouelmagd, S.A., Castanares, M.A., Collins, D.S., Wei, A., Yeo, Y.: Polymer–iron oxide composite nanoparticles for EPR-independent drug delivery. Biomaterials 101, 285–295 (2016)
Banerji, B., Pramanik, S.K., Mandal, S., Maiti, N.C., Chaudhuri, K.: Synthesis, characterization and cytotoxicity study of magnetic (Fe3O4) nanoparticles and their drug conjugate. RSC Adv. 2, 2493–2497 (2012)
Vasantharaj, S., Sathiyavimal, S., Senthilkumar, P., LewisOscar, F., Pugazhendhi, A.: Biosynthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using leaf extract of Ruellia tuberosa: antimicrobial properties and their applications in photocatalytic degradation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 192, 74–82 (2019)
Devi HS, Boda MA, Shah MA, Parveen S, Wani AH.: Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using Platanus orientalis leaf extract for antifungal activity. Green Process. Synth. 8(1), 38–45 (2019)
Muthukumar, H., Mohammed, S.N., Chandrasekaran, N.I., Sekar, A.D., Pugazhendhi, A., Matheswaran, M.: Effect of iron doped zinc oxide nanoparticles coating in the anode on current generation in microbial electrochemical cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 44, 2407–2416 (2019)
Ahmed, E.M.: Hydrogel: preparation, characterization, and applications: a review. J. Adv. Res. 6(2), 105–121 (2015)
Khalil, A.T., Ovais, M., Ullah, I., Ali, M., Shinwari, Z.K., Maaza, M.: Biosynthesis of iron oxide (Fe2O3) nanoparticles via aqueous extracts of Sageretia thea (Osbeck.) and their pharmacognostic properties. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 10, 186–201 (2017)
Ovais, M., Khalil, A.T., Raza, A., Khan, M.A., Ahmad, I., Islam, N.U., Saravanan, M., Ubaid, M.F., Ali, M., Shinwari, Z.K.: Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles via plant extracts: beginning a new era in cancer theranostics. Nanomedicine 12, 3157–3177 (2016)
Khalil, A.T., Ovais, M., Ullah, I., Ali, M., Shinwari, Z.K., Hassan, D., Maaza, M.: Sageretia thea (Osbeck.) modulated biosynthesis of NiO nanoparticles and their in vitro pharmacognostic, antioxidant and cytotoxic potential. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 46, 1–15 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2017.1345928
Khalil, A.T., Ovais, M., Ullah, I., Ali, M., Shinwari, Z.K., Khamlich, S., Maaza, M.: Sageretia thea (Osbeck.) mediated synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles and its biological applications. Nanomedicine 12, 1767–1789 (2017)
Ovais, M., Raza, A., Naz, S., Islam, N.U., Khalil, A.T., Ali, S., Khan, M.A., Shinwari, Z.K.: Current state and prospects of the phytosynthesized colloidal gold nanoparticles and their applications in cancer theranostics. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 101, 3551–3565 (2017)
Kasithevar, M., Saravanan, M., Prakash, P., Kumar, H., Ovais, M., Barabadi, H., Shinwari, Z.K.: Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Alysicarpus monilifer leaf extract and its antibacterial activity against MRSA and CoNS isolates in HIV patients. J. Interdiscip. Nanomed. 2, 131–141 (2017)
Khan, M.A., Raza, A., Ovais, M., Sohail, M.F., Ali, S.: Current state and prospects of nano-delivery systems for sorafenib. Int. J. Polym. Mater. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/00914037.2018.1429434
Alkaladi, A., Abdelazim, A.M., Afifi, M.: Antidiabetic activity of zinc oxide and silver nanoparticles on streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 15, 2015–2023 (2015)
Shaheen, T.I., El-Naggar, M.E., Hussein, J.S., El-Bana, M., Emara, E., El-Khayat, Z.: Antidiabetic assessment; in vivo study of gold and core–shell silver–gold nanoparticles on streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 83, 865–887 (2016)
Sharifi, S., Daghighi, S., Motazacker, M.M., Badlou, B., Sanjabi, B., Akbarkhanzadeh, A.: Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles alter expression of obesity and T2 associated risk genes in human adipocytes. Sci. Rep. 3, 2173 (2013)
Tshisikhawe M.P, Baloyi O, Maanda HL-M.: Ecología poblacional de Securidaca longepedunculata Fresen. en la Reserva Natural Nylsvley, Provincia Limpopo, Sudáfric. Phyton (Buenos Aires) 81, 51–58 (2012)
Tikisa, T., Abdissa, D., Abdissa, N.: Chemical constituents of Securidaca longipedunculata root bark and evaluation of their antibacterial activities. Ethiop. J. Educ. Sci. 14, 2 (2019)
Mongalo, N.I., McGaw, L.J., Finnie, J.F., Van Staden, J.: Securidaca longipedunculata Fresen (Polygalaceae): a review of its ethnomedicinal uses, phytochemistry, pharmacological properties and toxicology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 165, 215–226 (2015)
Simeon, K.A., ImohImeh, J., Gbola, O.: Plants in respiratory disorders I antiasthmatics, a review. Br. J. Pharm. Res. 16, 1–22 (2017)
Keay, R.W.J., Onochie, C.F.A., Stanfield, D.P.: Nigerian trees. Department of Forest Research Publishers, Ibadan (1964)
Ejikeme, C.M., Ezeonu, C.S., Eboatu, A.N.: Determination of physical and phytochemical constituents of some tropical timbers indigenous to Niger Delta Area of Nigeria. Eur. Sci. J. 10(18), 247–270 (2014)
Hikino, H., Kiso, Y., Wagner, H., Fiebig, M.: Antihepatotoxic actions of flavonolignans from Silybum marianum fruits. Planta Med. 50(3), 248–250 (1984)
Bibi, I., Nazar, N., Ata, S., Sultan, M., Ali, A., Abbas, A., Jilani, K., Kamal, S., Sarim, F.M., Khan, I., Jalal, F., Iqbal, M.: Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using pomegranate seEDX extract and photocatalytic activity evaluation for the degradation of textile dye. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 8(6), 6115–6124 (2019)
Ojiako, A.O., Chikezie, P.C., Ogbuji, C.A.: Histopathological studies of renal and hepatic tissues of hyperglycemic rats administered with traditional herbal formulations. Int. J. Green Pharm. 9, 184–191 (2015)
Belayneh, Y.M., Birru, E.M., Ambikar, D.: Evaluation of hypoglycemic, antihyperglycemic and antihyperlipidemic activities of 80% methanolic seed extract of Calpurnia aurea (Ait.) Benth. (Fabaceae) in mice. J. Exp. Pharmacol. 11, 73–83 (2019). https://doi.org/10.2147/JEP.S212206
Friedewald, W., Levy, R., Fredrickson, D.: Estimation of concentration of low-density lipoprotein in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin. Chem. 18, 499–502 (1972)
Oluba, O.M., Olusola, A.O., Eidangbe, G.O., Babatola, L.J., Onyeneke, E.C.: Modulation of lipoprotein cholesterol levels in Plasmodium berghei malarial infection by crude aqueous extract of Ganoderma lucidum. Cholesterol 6, 53–63 (2012)
Burnstein, M.A., Sammaille, J.A.: rapid determination of cholesterol bound to A and B lipoprotein. Clin. Chem. Acta 5, 601–609 (1960)
Bhuiyan, S.H., Miah, M.Y., Paul, S.C., Aka, T.D., Saha, O., Rahaman, M., Habiba, J.I.O., Ashaduzzaman, M.D.: Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticle using Carica papaya leaf extract: application for photocatalytic degradation of remazol yellow RR dye and antibacterial activity. Heliyon (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04603
Behera, S.S., Patra, J.K., Pramanik, K., Panda, N., Thatoi, H.: Characterization and evaluation of antibacterial activities of chemically synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles. World J. Nanosci. Eng. 2, 196 (2012)
Fouad, D.F., Zhang, C., El-Didamony, H., Yingnan, L., Mekuria, T.D., Shah, A.H.: Improved size, morphology and crystallinity of hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles synthesized via the precipitation route using ferric sulfate precursor. Results Phys. 12, 1253–1261 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2019.01.005
Ahmmad, B., Leonard, K., Islam, S., Kurawaki, J., Muruganandham, M.: Green synthesis of mesoporous hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles and their photocatalytic activity. Adv. Powder Technol. 24(1), 160–167 (2013)
Suresh, S., Karthikeyan, S., Jayamoorthy, K.: Effect of bulk and nano-Fe2O3 particles on peanut plant leaves studied by Fourier transform infrared spectral studies. J. Adv. Res. 7, 739–747 (2016)
Lassoued, A., Lassoued, M.S., Dkhil, B., Ammar, S., Gadri, A.: Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye by iron oxide (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles under visible irradiation. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 8142–8152 (2018)
Lamiaa, M.A.A., Sara, A.S., Rafael, P., Millan, A., Mervat, Y.H., Madiha, H.H., Maher, A.K., Shimaa, A.M.: Effect of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles on glucose homeostasis on type 2 diabetes experimental model. Life Sci. 245, 117361 (2020)
Liu, J., Li, Q., Yang, Y., Ma, L.: Iron metabolism and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis and systematic review. J. Diabetes Investig. 11, 946–955 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1111/jdi.13216
Carlos, A.R., Weis, S., Soares, M.P.: Cross-talk between iron and glucose metabolism in the establishment of disease tolerance. Front. Immunol. 9, 2498 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.02498
Bhardwaj, M., Yadav, P., Vashishth, D., Sharma, K., Kumar, A., Chahal, J., Dalal, S., Kataria, S.K.: A review on obesity management through natural compounds and a green nanomedicine-based approach. Molecules 26(11), 3278 (2021)
Balan, K., Qing, W., Wang, Y., Liu, X., Palvannan, T., Wang, Y., Ma, F., Zhang, Y.: Antidiabetic activity of silver nanoparticles from green synthesis using Lonicera japonica leaf extract. RSC Adv. 6(46), 40162–40168 (2016)
Najafabadi, R.E., Kazemipour, N., Esmaeili, A., Beheshti, S., Nazifi, S.: Quercetin prevents body weight loss due to the using of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in rat. Adv. Biomed. Res. 7(8), 14–17 (2018). https://doi.org/10.4103/abr.abr_141_17
Szalay, B., Tátrai, E., Nyírő, G., Vezér, T., Dura, G.: Potential toxic effects of iron oxide nanoparticles in in vivo and in vitro experiments. J. Appl. Toxicol. 32, 446–453 (2012)
Zhu, M.T., Wang, Y., Feng, W.Y., Wang, B., Wang, M., Ouyang, H.: Oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by iron oxide nanoparticles in cultured human umbilical endothelial cells. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 10, 8584–8590 (2012)
Khan, M.I., Mohammad, A., Patil, G., Naqvi, S.A., Chauhan, L.K., Ahmad, I.: Induction of ROS, mitochondrial damage and autophagy in lung epithelial cancer cells by iron oxide nanoparticles. Biomaterials 33, 1477–1488 (2012)
Alarifi, S., Ali, D., Alkahtani, S., Alhader, M.S.: Iron oxide nanoparticles induce oxidative stress, DNA damage, and caspase activation in the human breast cancer cell line. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 159, 416–424 (2014)
Ikewuchi, J.C., Onyeike, E.N., Uwakwe, A.A., Ikewuchi, C.C.: Effect of aqueous extract of the leaves of Acalypha wilkesiana ‘Godseffiana’ Muell Arg (Euphorbiaceae) on the hematology, plasma biochemistry and ocular indices of oxidative stress in alloxan induced diabetic rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 137(3), 1415–1424 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2011.08.015
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study protocol was approved by the Ethical Committee of the Federal University Technology, Minna Nigeria and assigned number: 000022.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Daniel, A.I., Umar, M.B., Tijani, O.J. et al. Antidiabetic potentials of green-synthesized alpha iron oxide nanoparticles using stem extract of Securidaca longipedunculata. Int Nano Lett 12, 281–293 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40089-022-00377-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40089-022-00377-x