Abstract
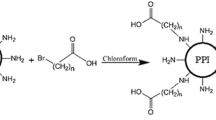
With high potency in treatment of various diseases, gene therapy is mainly hindered by lack of safe and efficient gene delivery vectors. The current study was aimed to develop an efficient non-viral vector with adequate cytotoxicity. To this end, alkylcarboxylate chains (6C, 10C, 16C) were exploited to ameliorate the characteristics of PEI 750 kDa. Briefly, alkylcarboxylate chains with three different lengths (6C, 10C, 16C) were chemically grafted to the primary amine groups of PEI 750 kDa in three percentages (10, 50, and 100%). After evaluating the physicochemical properties of prepared vectors including surface charge, size, buffering capacity, and DNA condensing, their transfection efficiency and cytotoxicity were investigated in Neuro2A cells. The polyplexes size were 158.9–264.5 nm and their zeta potentials were 14–30 mV, while their buffering capacity and DNA condensing were not significantly decreased. The highest transfection efficiency in term of C/P ratio was observed in PEI750-10C-68%, PEI750-10C-7%, and PEI750-6C-7% at C/P ratios of 2, 4, and 6, respectively. Altogether, the decanoylcarboxylate-modified PEI with medium grafting percentages showed promising results as gene delivery vector. To sum up, the modification of high molecular weight PEIs by alkylcarboxylate chains is an efficient approach for development of more efficient non-viral vectors.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akinc A, Thomas M, Klibanov AM, Langer R (2005) Exploring polyethylenimine-mediated DNA transfection and the proton sponge hypothesis. J Gene Med 7:657–663
Chen B, Le W, Wang Y, Li Z, Wang D, Ren L, Lin L, Cui S, Hu JJ, Hu Y et al (2016) Targeting negative surface charges of cancer cells by multifunctional nanoprobes. Theranostics 6:1887–1898
Creusat G, Rinaldi A-S, Weiss E, Elbaghdadi R, Remy J-S, Mulherkar R, Zuber G (2010) Proton sponge trick for pH-sensitive disassembly of polyethylenimine-based siRNA delivery systems. Bioconj Chem 21:994–1002
Dammeijer F, Lievense LA, Veerman GM, Hoogsteden HC, Hegmans JP, Arends LR, Aerts JG (2016) The efficacy of tumor vaccines and cellular immunotherapies in non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Oncol 34(26):3204–3212
Dehshahri A, Oskuee RK, Shier WT, Hatefi A, Ramezani M (2009) Gene transfer efficiency of high primary amine content, hydrophobic, alkyl-oligoamine derivatives of polyethylenimine. Biomaterials 30:4187–4194
Dehshahri A, Oskuee RK, Ramezani M (2012a) Plasmid DNA delivery into hepatocytes using a multifunctional nanocarrier based on sugarconjugated polyethylenimine. Gene Ther Mol Biol 14:62–71
Dehshahri A, Oskuee RK, Shier WT, Ramezani M (2012b) β-Galactosylated alkyl-oligoamine derivatives of polyethylenimine enhanced pDNA delivery into hepatic cells with reduced toxicity. Curr Nanosci 8:548–555
Dehshahri A, Sadeghpour H, Oskuee RK, Fadaei M, Sabahi Z, Alhashemi SH, Mohazabieh E (2014) Interleukin-12 plasmid DNA delivery using L-thyroxine-conjugated polyethylenimine nanocarriers. J Nanopart Res 16:2423
Doody AM, Korley JN, Dang KP, Zawaneh PN, Putnam D (2006) Characterizing the structure/function parameter space of hydrocarbon-conjugated branched polyethylenimine for DNA delivery in vitro. J Control Release 116:227–237
Erbacher P, Bettinger T, Brion E, Coll JL, Plank C, Behr JP, Remy JS (2004) Genuine DNA/polyethylenimine (PEI) complexes improve transfection properties and cell survival. J Drug Target 12:223–236
Fioretti D, Iurescia S, Fazio VM, Rinaldi M (2010) DNA vaccines: developing new strategies against cancer. Biomed Res Int
Kazemi Oskuee R, Zakeri V, Gholami L, Malaekeh-Nikouei B (2015) Preparation, characterization and transfection efficiency of nanoparticles composed of alkane-modified polyallylamine. Nanomed J 2:111–120
Komin A, Russell L, Hristova K, Searson P (2017) Peptide-based strategies for enhanced cell uptake, transcellular transport, and circulation: Mechanisms and challenges. Adv Drug Del Rev 110–111:52–64
Ma K, Hu M, Qi Y, Qiu L, Jin Y, Yu J, Li B (2009) Structure–transfection activity relationships with glucocorticoid–polyethyl-enimine conjugate nuclear gene delivery systems. Biomaterials 30:3780–3789
Malaekeh-Nikouei B, Rezaee M, Gholami L, Behzad M, Mohajeri M, Kazemi Oskuee R (2017) Dexamethasone conjugated polyallylamine: Synthesis, characterization, and in vitro transfection and cytotoxicity. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 40:172–179
Navarro SA, Carrillo E, Griñán-Lisón C, Martín A, Perán M, Marchal JA, Boulaiz H (2016) Cancer suicide gene therapy: a patent review. Expert Opin Ther Pat 26:1095–1104
Nguyen J, Xie X, Neu M, Dumitrascu R, Reul R, Sitterberg J, Bakowsky U, Schermuly R, Fink L, Schmehl T et al (2008) Effects of cell-penetrating peptides and pegylation on transfection efficiency of polyethylenimine in mouse lungs. J Gene Med 10:1236–1246
Nimesh S, Aggarwal A, Kumar P, Singh Y, Gupta KC, Chandra R (2007) Influence of acyl chain length on transfection mediated by acylated PEI nanoparticles. Int J Pharm 337:265–274
Oskuee RK, Dehshahri A, Shier WT, Ramezani M (2009) Alkylcarboxylate grafting to polyethylenimine: a simple approach to producing a DNA nanocarrier with low toxicity. J Gene Med 11:921–932
Oskuee RK, Philipp A, Dehshahri A, Wagner E, Ramezani M (2010) The impact of carboxyalkylation of branched polyethylenimine on effectiveness in small interfering RNA delivery. J Gene Med 12:729–738
Pack DW, Hoffman AS, Pun S, Stayton PS (2005) Design and development of polymers for gene delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discovery 4:581–593
Patnaik S, Gupta KC (2013) Novel polyethylenimine-derived nanoparticles for in vivo gene delivery. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 10:215–228
Paul-Smith MC, Bell RV, Alton WE, Alton EW, Griesenbach U (2016) Gene therapy for cystic fibrosis: recent progress and current aims. Expert Opin Orphan Drugs Drugs 4:649–658
Penacho N, Simões S, de Lima MCP (2009) Polyethylenimine of various molecular weights as adjuvant for transfection mediated by cationic liposomes. Mol Membr Biol 26:249–263
Pezzoli D, Tsekoura EK, Remant Bahadur KC, Candiani G, Mantovani D, Uludağ H (2017) Hydrophobe-substituted bPEI derivatives: boosting transfection on primary vascular cells. Sci China Mater 60:529–542
Rehman Z, Zuhorn IS, Hoekstra D (2013) How cationic lipids transfer nucleic acids into cells and across cellular membranes: recent advances. J Control Release 166:46–56
Rezaee M, Oskuee RK, Nassirli H, Malaekeh-Nikouei B (2016) Progress in the development of lipopolyplexes as efficient non-viral gene delivery systems. J Control Release 236:1–14
Sarisozen C, Pan J, Dutta I, Torchilin VP (2017) Polymers in the co-delivery of siRNA and anticancer drugs to treat multidrug-resistant tumors. J Pharm Investig 47:37–49
Shen ZL, Xia YQ, Yang QS, Tian WD, Chen K, Ma YQ (2017) Polymer–nucleic acid interactions. Top Curr Chem 375(2):44
Snyder SL, Sobocinski PZ (1975) An improved 2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid method for the determination of amines. Anal Biochem 64:284–288
Teo PY, Yang C, Hedrick JL, Engler AC, Coady DJ, Ghaem-Maghami S, George AJ, Yang YY (2013) Hydrophobic modification of low molecular weight polyethylenimine for improved gene transfection. Biomaterials 34:7971–7979
Thi EP, Lee AC, Geisbert JB, Ursic-Bedoya R, Agans KN, Robbins M, Deer DJ, Fenton KA, Kondratowicz AS, MacLachlan I (2016) Rescue of non-human primates from advanced Sudan ebolavirus infection with lipid encapsulated siRNA. Nat Microbiol 1:16142
Thomas T, Tajmir-Riahi H, Thomas T (2016) Polyamine–DNA interactions and development of gene delivery vehicles. Amino Acids 48:2423–2431
Verma IM, Somia N (1997) Gene therapy-promises, problems and prospects. Nature 389:239–242
von Harpe A, Petersen H, Li Y, Kissel T (2000) Characterization of commercially available and synthesized polyethylenimines for gene delivery. J Controlled Release 69:309–322
Yang Z, Jiang Z, Cao Z, Zhang C, Gao D, Luo X, Zhang X, Luo H, Jiang Q, Liu J (2014) Multifunctional non-viral gene vectors with enhanced stability, improved cellular and nuclear uptake capability, and increased transfection efficiency. Nanoscale 6:10193–10206
Zheng M, Zhong YA, Meng FH, Peng R, Zhong ZY (2011) Lipoic acid modified low molecular weight polyethylenimine mediates nontoxic and highly potent in vitro gene transfection. Mol Pharm 8:2434–2443
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Mashhad University of Medical Sciences (MUMS), Mashhad, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors (M. Rezaee, L. Gholami, M. Seddighi Gildeh, M. Ramezani and R. Kazemi Oskuee) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human and animal participants
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rezaee, M., Gholami, L., Gildeh, M.S. et al. Charge reduction: an efficient strategy to reduce toxicity and increase the transfection efficiency of high molecular weight polyethylenimine. J. Pharm. Investig. 49, 105–114 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-018-0388-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-018-0388-2