Abstract
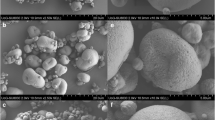
The use of lipids as taste-masking excipients in paracetamol sachets and chewable tablets without compromising drug release was investigated. Twelve paracetamol granule formulations were prepared by melt granulation, using Precirol® (glyceryl palmitostearate), cetyl alcohol and stearic acid, at different paracetamol-lipid ratios. Based on efficient taste-masking results coupled with minimum retardation of drug release, paracetamol-Precirol (1:1), paracetamol-cetyl alcohol (1:2) and paracetamol-stearic acid (1:2) granules were selected for preparation of chewable tablets and sachets. Formulations were evaluated for the effect of storage, at 40 °C and 75 % RH for 6 months, on their performance. Results inferred that paracetamol sachets, after reconstitution in 100 ml water, showed efficient taste-masking compared to control sachets (without lipids). The sachets released more than 90 % of their drug content in 30 min, when tested in 900 ml of phosphate buffered saline, pH 5.8. Chewable tablets exhibited comparable taste-masking effect to a reference product, Tylenol® 80 mg chewable tablets, and yielded similar drug dissolution profiles (similarity factor f 2 > 50). Differential scanning calorimetry indicated the absence of interaction between paracetamol and lipids. Scanning electron micrographs supported the obtained results. Upon storage at 40 °C and 75 % RH for 6 months, all the prepared sachets and chewable tablets were found to be stable except cetyl alcohol-based tablets that showed decrease in the efficiency of taste masking with increase in release rate. In conclusion, selected lipids, Precirol®, cetyl alcohol and stearic acid, could be efficiently used in formulation of taste masked paracetamol sachets and chewable tablets without adversely delaying drug release.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahire S, Bankar V et al (2012) A review: taste masking techniques in pharmaceuticals. Pharm Sci Monitor 3(3):68–82
Albertini B, Cavallari C et al (2004) Characterization and taste-masking evaluation of acetaminophen granules: comparison between different preparation methods in a high-shear mixer. Eur J Pharm Sci 21(2):295–303
Arun P, Sandip C et al (2011) Evaluation of hot melt coating as taste masking tool. IRJP 2(8):169–172
Bladh N, Blychert E et al (2007) A new esomeprazole packet (sachet) formulation for suspension: in vitro characteristics and comparative pharmacokinetics versus intact capsules/tablets in healthy volunteers. Clin Ther 29(4):640–649
Costa P, Sousa Lobo JM (2001) Modeling and comparison of dissolution profiles. Eur J Pharm Sci 13(2):123–133
Cram A, Breitkreutz J et al (2009) Challenges of developing palatable oral paediatric formulations. Int J Pharm 365(1):1–3
El-Massik M (2006) Development of Cetirizine chewable tablets with inhibited bitterness using liquid solid compact technology. Alex J Pharm Sci 20(1):11–16
El-Massik M (2007) Preparation and evaluation of extended-release doxazosin lipid matrix granules. Alex J Pharm Sci 21(2):111–117
Gowan WG, Bruce RD (1993) Aliphatic esters as solventless coating pharmaceuticals. Can Pat Appl 11:CA2082137
Hejaz H, Karaman R et al (2012) Computer-assisted design for paracetamol masking bitter taste prodrugs. J Mol Model 18(1):103–114
Hulse WL, Grimsey IM et al (2008) The impact of low-level inorganic impurities on key physicochemical properties of paracetamol. Int J Pharm 349(1):61–65
Kamble R, Maheshwari M et al (2004) Melt solidification technique: incorporation of higher wax content in ibuprofen beads. AAPS PharmSciTech 5(4):75–83
Kaushik D, Dureja H (2014) Recent patents and patented technology platforms for pharmaceutical taste masking. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul 8(1):37–45
Kulkarni RB, Amin PD (2008) Masking of unpleasant gustatory sensation by cross-linking of dehydrated paracetamol alginate pellets produced by extrusion-spheronization. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 34(2):199–205
Kumar KS, Bhowmik D et al (2013) Recent trends in taste masking of bitter drugs. J Drug Deliv Res 1:1–11
Lindley M (2002) Composition comprising paracetamol and a bitterness masking component, US Patent App. 10/492,809
Maniruzzaman M, Boateng JS et al (2013) A review on the taste masking of bitter APIs: hot-melt extrusion (HME) evaluation. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 40(2):1–12
Özyazıcı M, Gökçe EH et al (2006) Release and diffusional modeling of metronidazole lipid matrices. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 63(3):331–339
Reitz C, Strachan C et al (2008) Solid lipid extrudates as sustained-release matrices: the effect of surface structure on drug release properties. Eur J Pharm Sci 35(4):335–343
Rowe RC, Sheskey PJ et al (2003) Handbook of pharmaceutical excipients. Pharmaceutical Press, London
Savolainen M, Khoo C et al (2002) Evaluation of controlled-release polar lipid microparticles. Int J Pharm 244(1):151–161
Shiino K, Iwao Y et al (2010) Optimization of a novel wax matrix system using amino alkyl methacrylate copolymer E and ethylcellulose to suppress the bitter taste of acetaminophen. Int J Pharm 395(1):71–77
Sohi H, Sultana Y et al (2004) Taste masking technologies in oral pharmaceuticals: recent developments and approaches. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 30(5):429–448
Suzuki H, Onishi H et al (2003) Development of oral acetaminophen chewable tablets with inhibited bitter taste. Int J Pharm 251(1):123–132
Suzuki H, Onishi H et al (2004) Acetaminophen-containing chewable tablets with suppressed bitterness and improved oral feeling. Int J Pharm 278(1):51–61
Tripathi A, Parmar D et al (2011) Taste masking: a novel approach for bitter and obnoxious drugs. JPSBR 1(3):36–142
Venkatesan P, Manavalan R et al (2009) Microencapsulation: a vital technique in novel drug delivery system. J Pharm Sci Res 1(4):26–35
Wu Z, Patel A et al (2010) Development of acetaminophen proline prodrug. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20(13):3851–3854
Yoshida T, Tasaki H et al (2009) Salting-out taste-masking system generates lag time with subsequent immediate release. Int J Pharm 365(1):81–88
Acknowledgments
This article does not contain any studies with animal subjects performed by any of the authors. All authors (W.M. El-Refaie, M.A. El-Massik, O.Y. Abdallah, and N.M. Khalafallah) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Refaie, W.M., El-Massik, M.A., Abdallah, O.Y. et al. Formulation and evaluation of taste-masked paracetamol-lipid sachets and chewable tablets. Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation 44, 431–442 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-014-0137-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-014-0137-0