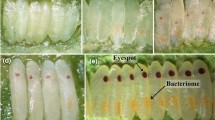
Abstract
Tetrastichus howardi (Olliff) (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) parasitizes the diamond back moth Plutella xylostella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae), but not much is known about its potential as a biocontrol agent. A rearing protocol has been established for this parasitoid on pupae of the factitious host Tenebrio molitor (L.) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae), with the aim of releasing it in the field to manage several lepidopteran species. The potential population growth of a parasitoid can be measured through fertility life tables and provide supporting information for using T. howardi in the management of P. xylostella. Also, the fitness and behavior of T. howardi reared on a factitious host can be indicators of its potential to control P. xylostella. Thus, in this study, the fertility life table parameters of T. howardi parasitizing P. xylostella were determined, as well as the effects of the natal host on the behavior of T. howardi towards host volatiles and parasitism rate. The results showed that net reproduction rate (Ro) and the intrinsic rate of population growth (rm) of T. howardi parasitizing P. xylostella were 13.6 (♀/♀) and 0.124 (♀/♀*day), respectively, whereas the mean generation time was 20.9 days. Moreover, the natal host (T. molitor or P. xylostella) did not affect the fitness, parasitism rate, or olfactory response of T. howardi. In general, regardless of the natal host, parasitoid females responded to volatiles of both host species and exhibited the same rate of parasitism on P. xylostella. Therefore, T. howardi reared on the factitious host maintains its attraction and potential to parasitize P. xylostella, and can contribute to the biological control of this pest.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data from this research might be available upon request.
References
Agritempo (2020) Sistema de Monitoramento Agrometeorológico. https://www.agritempo.gov.br/agritempo/jsp/PesquisaClima/index.jsp?siglaUF=PE. Accessed 08 Jan 2021
Alvarenga TM (2020) Hospedeiros alternativos para a criação em massa do parasitoide Tetrastichus howardi (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae). Dissertação de mestrado, Universidade Federal de Viçosa, Viçosa, MG 23
Barros R, Vendramim JD (1999) Efeito de cultivares de repolho, utilizadas para criação de Plutella xylostella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae), no desenvolvimento de Trichogramma pretiosum Riley (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Anais da Sociedade Entomológica do Brasil 28: 3
Bodino N, Ferracini C, Tavella L (2016) Is host selection influenced by natal and adult experience in the parasitoid Necremnus tutae (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae)? Anim Behav 112:221–228
Carey JR (1993) Applied demography for biologists with special emphasis on insects. Oxford University Press, New York, p 33
Corbet SA (1985) Insect chemosensory responses: a chemical legacy hypothesis. Ecol Entomol 10:143–153
Deyrup LD, Rivers DB, Matthews RW (2006) Venom from the ectoparasitic wasp Melittobia digitata (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) induces paralysis and developmental delay in natural and factitious hosts. Ann Entomol Soc Am 99:1199–1205
Di Stefano J (2005) Effect size estimates and confidence intervals: an factitious focus for the presentation and interpretation of ecological data. In: Burk AR (ed) New trends in ecology research. Nova Science, pp 71–102
Favero K, Pereira FF, Torres JB, Oliveira HN, Kassab SO, Zanuncio JC (2015) Reproduction of Tetrastichus howardi (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) in Diatraea saccharalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) pupae at different temperatures. Entomol da Flórida 98(3):865–869
Favoreto AL, Pavani RF, Ribeiro MF, Zanuncio AJV, Soares MA, Zanuncio JC, Wilcken CF (2020) Tetrastichus howardi (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae): first report of parasitism in Oxydia vesulia (Lepidoptera: Geometridae). Braz J Biol 81:406–410
Fernandes EC, Souza MM, Nava DE, Silva JG, Araujo EL (2021) Fertility life table and biology of Tetrastichus giffardianus (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) in the larvae of Ceratitis capitata (Diptera: Tephritidae). Bull Entomol Res 111:182–189
Ferreira SWJ, Barros RB, Torres JB (2003) Exigências Térmicas e Estimativa do Número de Gerações de Oomyzus sokolowskii (Kurdjumov) (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae), Para Regiões Produtoras de CrucÌferas em Pernambuco. Neot Entomol 32:407–411
Ferreira NGP, Pereira FF, Borges FLG, Rossoni C, Silva AS, Kassab SO (2016) Multiplicar Tetrastichus howardi (Hymenoptera: ¿Eulophidae) en la oruga de la seda afecta su biología? Acta Biol Colombiana 21:189–193
Floriano ET, Fagundes FP, Oliveira SK, Hidalgo BR, Garcia CRC, Zanuncio J (2018) Biological quality of Tetrastichus howardi (Hym: Eulophidae) reared with Tenebrio molitor (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) pupae after storage at low temperatures for different periods. PeerJ Preprints 6:2686
Giunti G, Benelli G, Messing RH, Canale A (2016) Early adult learning affects host preferences in the tephritid parasitoid Psyttalia concolor (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). J Pest Sci 89:529–537
Golizadeh A, Kamali K, Fathupour Y, Abbasipour H (2009) Effect of temperature on life table parameters of Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) on two brassicaceous host plants. J Asia-Pacific Entomol 12:207–212
González JFA (2004) Estudios Bioecológicos, Reproducción Artificial y Liberación de Tetrastichus howardi (Olliff) (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae), Parasitoide Pupal de Diatraea saccharalis (Fab.) en Cuba. Tese (Doutorado em Ciências Agrícolas). Universidad Central de Las Villas. Santa Clara, Cuba, 179
Gutiérrez-Ibáñez C, Vilagra CA, Niemeyer HM (2007) Pre-pupation behaviour of the aphid parasitoid Aphidius ervi (Haliday) and its consequences for pre-imaginal learning. Naturwissenschaften 94:595–600
Heimpel GE (2019) Linking parasitoid nectar feeding and dispersal in conservation biological control. Biol Control 132:36–41
Hoffmann Schlesener DC, Wollmann J, Kruger AP, Nunes AM, Bernardi D, Garcia FRM (2018) Biology and fertility life table of Drosophila suzukii on artificial diets. Entomol Exp Appl 166:932–936
Hondo T, Koike A, Sugimoto T (2006) Comparison of thermal tolerance of seven native species of parasitoids (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) as biological control agents against Liriomyza trifolii (Diptera: Agromyzidae) in Japan. Appl Entomol Zool 41:73–82
Institute SAS (2001) SAS users guide, Version 8 for Windows. SAS Institute, Cary, NC
Jaenike J (1983) Induction of host preference in Drosophila melanogaster. Oecologia 58:320–325
Kessler A, Heil M (2011) The multiple faces of indirect defences and their agents of natural selection. Funct Ecol 25:348–357
Kfir R, Gouws J, Moore SD (1993) Biology of Tetrastichus howardi (Olliff) (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae): a facultative hyperparasitoid of stem borers. Biocontrol Sci Tech 3:149–159
Kher SV, Cárcamo HA, Evenden ML, Dosdall LM (2017) Olfactory host-finding behaviour of Oulema melanopus (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) and its parasitoid, Tetrastichus julis (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae). J Appl Entomol 141:740–750
Lins J, Caldeira J, Bueno VHP, Silva DB, Sampaio MV, Van Lenteren JC (2011) Praon volucre (Hymenoptera: Braconidae: Aphidiinae), a natural enemy of Macrosiphum euphorbiae (Hemiptera: Aphididae): life table and intrinsic rate of population increase. Eur J Entomol 108(4):573–580
Lira R, Nascimento DV, Torres JB, Siqueira HAA (2019) Predation on diamondback moth larvae and aphid by resistant and susceptible lady beetle, Eriopis connexa. Neo Entomol 48:909–918
Lucchetta JT (2016) Parasitismo e desenvolvimento de Tetrastichus howardi (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) em lagartas e pupas de Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Dissertação de mestrado. Universidade Federal de Grande Dourados, Dourados, MS 16–17
Magalhães DM, Borges M, Laumann RA, Sujii ER, Mayon P, Caulfield JC, Midega CA, Khan ZR, Pickett JA, Birkett MA, Blassioli-Moraes MC (2012) Semiochemicals from herbivory induced cotton plants enhance the foraging behavior of the cotton boll weevil, Anthonomus grandis. J Chem Ecol 38:1528–1538
Maia ADH, Luiz AJ, Campanhola C (2000) Statistical inference on associated fertility life table parameters using jackknife technique: computational aspects. J Econ Entomol 93:511–518
Morris RJ, Fellowes MDE (2002) Learning and natal host influence host preference, handling time and sex allocation behaviour in a pupal parasitoid. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 51:386–393
Pedigo LP & Zeiss RM (1996) Constructing life table for insect populations, Analyses in insect ecology and management. Iowa, Iowa State University Press. 75–105
Pedro L, Tormos J, Asís JD, Sabater-Muñoz B, Beitia F (2018) Biology of Aganaspis daci (Hymenoptera: Figitidae), parasitoid of Ceratitis capitata (Diptera: Tephritidae): mode of reproduction, biological parameters and superparasitism. Crop Prot 108:54–61
Pereira FF, Kassab SO, Vargas EL, Calado VRF, Oliveira HN, Zanuncio JC (2015) Parasitism and emergence of Tetrastichus howardi (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) on the caterpillars’ pupae and adults of Diatraea saccharalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). Fla Entomol 95:384–387
Pereira FF, Pastori PL, Kassab SO, Torres JB, Cardoso CRG, Fernandes VC, Oliveira NH, Zanuncio JC (2021) Uso de eulofídeos no controle biológico de pragas. In: Parra JRP, Pinto AS, Nava DE, Oliveira RC, Diniz AJF (Org.). Controle Biológico com parasitoides e predadores na agricultura brasileira. 1ed.Piracicaba: FEALQ, 1 317–361
Piñeyro NG, Pereira FF, Borges FLG, Rossoni C, Silva AS, Kassab SO (2016) Does multiplying Tetrastichus howardi (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) in the silkworm affect its biology? Acta Biol Colomb 21:189–193
Pires PDDS, Sant'Ana J, Redaelli LR, Leite NA (2022) Chemotaxis and parasitism of the Neotropical fruit fly parasitoid Ganaspis pelleranoi can be altered by pre‐imaginal and imaginal conditioning to fruit volatiles. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 170:419–426
Poelman EH, Ruinsman M, Zhu F, Weldegergis BT, Boursault AE, Jongema Y, Dicke M (2012) Hyperparasitoids use herbivore-induced plant volatiles to locate their parasitoid host. PLoS Biol 10:e1001435
Prasad KS, Aruna AS, Kumar V, Kariappa BK (2007) Feasibility of mass production of Tetrastichus howardi (Olliff) a parasitoid of leaf roller (Diaphania pulverulentalis) on Musca domestica (L.). Indian J Seric 46(404):89–91
Rodrigues A, Pereira FF, Barbosa PR, Silva-Torres CS, Torres JB (2021) Parasitism behavior of Tetrastichus howardi (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) on larvae and pupae of sugarcane borers. J Insect Behav 34:71–81
Silva-Torres CS, Matthews RM, Ruberson JR, Lewis WJ (2005) Role of chemical cues and natal rearing effect on host recognition by the parasitic wasp Melittobia digitata. Entomol Sci 8:355–362
Silva-Torres CS, Barros R, Torres JB (2009) Efeito da idade, fotoperíodo e disponibilidade de hospedeiro no comportamento de parasitismo de Oomyzus sokolowskii Kurdjumov (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae). Neotrop Entomol 38:512–519
Silva-Torres CS, Pontes IV, Torres JB, Barros R (2010a) New records of natural enemies of Plutella xylostella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) in Pernambuco. Brazil Neotrop Entomol 39:835–838
Silva-Torres CSA, Torres JB, Barros R, Pallini A (2010b) Parasitism of diamondback moth by Oomyzus sokolowskii. Pesq Agropecu Bras 45:638–645
Simonato J, Oliveira HN, Grigolli JF, Grigolli MMK, Silva IF (2020) Potential of the parasitoid Tetrastichus howardi (Olliff, 1893) (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) on the control of Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner, 1805) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J Agri Sci 12:7
Soufbaf M, Talebi AA, Tazerouni Z, Fathipour Y (2018) Bottom-up effect of two host plants on life table parameters of Aphis gossypii (Hemiptera: Aphididae). J Agric 18:179–190
Southwood TRE, Henderson PA (2000) Ecological methods. Blackwell, Oxford, United Kingdom, p 592p
Stenberg JA, Sundh I, Becher PG, Bjorkman C, Dube M, Egan PA, Viketoft M (2021) When is it biological control? A framework of definitions, mechanisms, and classifications. J Pest Sci 94:665–676
Thorpe WH (1939) Further studies on pre-imaginal olfactory conditioning in insects. Proc R Soc Lond 127:424–433
Tiago EF, Pereira FF, Kassab SO, Barbosa RH, Cardoso CRG, Sanomia WY, Pereira HC, Silva RMMF, Zanuncio JC (2019) Biological quality of Tetrastichus howardi (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) reared with Tenebrio molitor (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) pupae after cold storage. Fla Entomol 102:571–576
Vinson SB (1976) Host selection by insect parasitoids. Ann Rev Entomol 21:109–133
Yan S, Su H, Lyu B, Lu H, Tang J, Zhuo Z, Yang F (2021) Effects of temperature and supplementary food on the development and fecundity of the Eulophid parasitoid Tetrastichus howardi on Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), Int J Pest Manag. https://doi.org/10.1080/09670874.2021.1968535
Zamperline B, Zanuncio JC, Leite JEM, Bragança MAL (1992) Influence of Tenebrio molitor L. 1758 (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) feeding on nymphal development of Podisus connexivus Bergroth, 1891 (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). Tree Magazine 16:224–230
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Dr. Jaimie Kenney from the University of California Riverside (UCR) for editing this manuscript.
Funding
The present research was supported by Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—CAPES Foundation, granted to R. J. S. S. Moraes through the CAPES/PROEX, financial code 001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RJSSM collected, analyzed the data, and wrote earlier version of the manuscript. CSAST, PRRB and JBT conceived the idea and conceptualization, wrote-review and edited the manuscript. CSAST conceived supervision and funding acquisition. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Edited by Adeney de Freitas Bueno
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Moraes, R.J.S.S., Silva-Torres, C.S.A., Barbosa, P.R.R. et al. Olfaction Response and Fertility Life Table Parameters of Tetrastichus howardi (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) Parasitizing Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) and the factitious host Tenebrio molitor (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). Neotrop Entomol 52, 921–931 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13744-023-01068-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13744-023-01068-8