Abstract
Purpose of Review
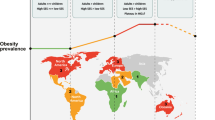
Rates of childhood obesity have been soaring in recent decades. The association between obesity in adulthood and excess morbidity and mortality has been readily established, whereas the association of childhood and adolescent obesity has not. The purpose of this review is to summarize existing data regarding the association of the presence of obesity in childhood/adolescence and early-onset adverse outcomes in adulthood, with specific focus on young adults under the age of 45 years.
Recent Findings
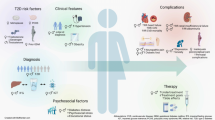
Diabetes, cancer, and cardiometabolic outcomes in midlife are closely linked to childhood and adolescent obesity.
Summary
Childhood and adolescent obesity confer major risks of excess and premature morbidity and mortality, which may be evident before age 30 years in both sexes. The scientific literature is mixed regarding the independent risk of illness, which may be attributed to childhood BMI regardless of adult BMI, and additional data is required to establish causality between the two. Nonetheless, the increasing prevalence of childhood and adolescent obesity may impose an increase of disease burden in midlife, emphasizing the need for effective interventions to be implemented at a young age.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance
Cockrell Skinner A, Ravanbakht SN, Skelton JA, Perrin EM, Armstrong SC, Skinner C. Prevalence of obesity and severe obesity in US children. Pediatrics. 1999;141:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2017-4078.
National Center for Health Statistics, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. [cited 2020 Dec 2] https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/hestat/obesity-child-17-18/obesity-child.htm#table2
Kumar S, Kelly AS. Review of childhood obesity: from epidemiology, etiology, and comorbidities to clinical assessment and treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. 2017;92:251–65. Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. Available from:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2016.09.017.
Lascar N, Brown J, Pattison H, Barnett AH, Bailey CJ, Bellary S. Type 2 diabetes in adolescents and young adults. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018;6:69–80. Available from:. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(17)30186-9.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ. 2009;339:332–6. Available from:. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.b2535.
American KR, Diabetes Association. Type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents: consensus conference report. Diabetes Care. 2000;105:671–80.
International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 9th edn. Brussels, Belgium: 2019. Available at: https://www.diabetesatlas.org, n.d.
• Twig G, Zucker I, Afek A, Cukierman-Yaffe T, Bendor CD, Derazne E, et al. Adolescent obesity and early-onset type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2020;43:1487–95 A nationwide study that assessed type 2 diabetes risk for different degrees of adolescent obesity during the third and fourth decades of life. It shows a substantial risk of incident diabetes for both sexes regardless socioeconomic status and other coexisting morbidities.
Tanamas SK, Reddy SP, Chambers MA, Clark EJ, Dunnigan DL, Hanson RL, et al. Effect of severe obesity in childhood and adolescence on risk of type 2 diabetes in youth and early adulthood in an American Indian population. Pediatr Diabetes. 2018;19:622–9.
Zimmermann E, Bjerregaard LG, Gamborg M, Vaag AA, Sørensen TIA, Baker JL. Childhood body mass index and development of type 2 diabetes throughout adult life—a large-scale danish cohort study. Obesity. 2017;25:965–71.
Twig G, Afek A, Derazne E, Tzur D, Cukierman-Yaffe T, Gerstein HC, et al. Diabetes risk among overweight and obese metabolically healthy young adults. Diabetes Care. 2014;37:2989–95.
Tirosh A, Shai I, Tekes-Manova D, Israeli E, Pereg D, Shochat T, et al. Normal fasting plasma glucose levels and type 2 diabetes in young men. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1454–62.
Magnussen CG, Koskinen J, Chen W, Thomson R, Schmidt MD, Srinivasan SR, et al. Pediatric metabolic syndrome predicts adulthood metabolic syndrome, subclinical atherosclerosis, and type 2 diabetes mellitus but is no better than body mass index alone: the Bogalusa Heart Study and the Cardiovascular Risk in Young Finns Study. Circulation. 2010;122:1604–11.
Hillier TA, Pedula KL. Characteristics of an adult population with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2001;24:1522–7.
Skinner AC, Perrin EM, Moss LA, Skelton JA. Cardiometabolic risks and severity of obesity in children and young adults. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:1307–17.
Zhang T, Xu J, Li S, Bazzano LA, He J, Whelton PK, et al. Trajectories of childhood BMI and adult diabetes : the Bogalusa Heart Study. Diabetologia. 2019;62:70–7.
Tirosh A, Shai I, Afek A, Dubnov-Raz G, Ayalon N, Gordon B, et al. Adolescent BMI trajectory and risk of diabetes versus coronary disease. N Engl J Med. 2011;55:296–7.
Juonala M, Magnussen CG, Berenson GS, Venn A, Burns TL, Sabin MA, et al. Childhood adiposity, adult adiposity, and cardiovascular risk factors. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:1876–85.
Bjerregaard LG, Jensen BW, Ängquist L, Osler M, Sørensen TIA, Baker JL. Change in overweight from childhood to early adulthood and risk of type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:1302–12.
The NS, Richardson AS, Gordon-Larsen P. Timing and duration of obesity in relation to diabetes: findings from an ethnically diverse, nationally representative sample. Diabetes Care. 2013;36:865–72.
Liang Y, Hou D, Zhao X, Wang L, Hu Y, Liu J, et al. Childhood obesity affects adult metabolic syndrome and diabetes. Endocrine. 2015;50:87–92. Available from:. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-015-0560-7.
• Geng T, Smith CE, Li C, Huang T. Childhood BMI and adult type 2 diabetes, coronary artery diseases, chronic kidney disease, and cardiometabolic traits: a Mendelian randomization analysis. Diabetes Care. 2018;41:dc172141 The first Mendelian randomization study that proves causality between obesity and deleterious cardiovascular metabolic comorbidities.
Viitasalo A, Schnurr TM, Pitkänen N, Hollensted M, Nielsen TRH, Pahkala K, et al. Abdominal adiposity and cardiometabolic risk factors in children and adolescents: a Mendelian randomization analysis. Am J Clin Nutr. 2019;110:1079–87.
Yuan S, Larsson SC. An atlas on risk factors for type 2 diabetes: a wide-angled Mendelian randomisation study. Diabetologia. 2020;63:2359–71.
Zhang T, Zhang H, Li Y, Li S, Fernandez C, Bazzano L, et al. Long-term impact of temporal sequence from childhood obesity to hyperinsulinemia on adult metabolic syndrome and diabetes: the Bogalusa Heart Study. Sci Rep. 2017;7:1–7.
Hillier TA, Pedula KL. Complications in young adults with early-onset type 2 diabetes: losing the relative protection of youth. Diabetes Care. 2003;26:2999–3005.
Pinhas-Hamiel O, Zeitler P. Acute and chronic complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents. Lancet. 2007;369:1823–31.
Bacha F. Progressive deterioration of β-cell function in obese youth with type 2 diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes. 2013;23:1–7 Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3624763/pdf/nihms412728.pdf.
Matthews DR, Cull CA, Stratton IM, Holman RR, Turner RC. UKPDS 26: sulphonylurea failure in non-insulin-dependent diabetic patients over six years. Diabet Med. 1998;15:297–303.
Gungor N, Bacha F, Saad R, Janosky J, Arslanian S. Youth type 2 diabetes: insulin resistance, β-cell failure, or both? Diabetes Care. 2005;28:638–44.
Constantino MI, Molyneaux L, Limacher-Gisler F, Al-Saeed A, Luo C, Wu T, et al. Long-term complications and mortality in young-onset diabetes: type 2 diabetes is more hazardous and lethal than type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2013;36:3863–9.
Twig G, Tirosh A, Leiba A, Levine H, Shor DBA, Derazne E, et al. BMI at age 17 years and diabetes mortality in midlife: a nationwide cohort of 2.3 million adolescents. Diabetes Care. 2016;39:1996–2003.
Iyengar NM, Hudis CA, Dannenberg AJ. Obesity and cancer: local and systemic mechanisms. Annu Rev Med. 2015;66:297–309.
WRCF. Body fatness and weight gain and the risk of cancer. Contin Updat Proj Expert Rep. 2018;2018:3–141 Available from: Available at dietcancerreport.org.
Cancer Research UK. When could overweight and obesity overtake smoking as the biggest cause of cancer in the UK? September, 2018. https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/sites/default/files/obesity_ tobacco_cross_over_report_final.pdf (accessed Dec 2, 2020).
• Furer A, Afek A, Sommer A, Keinan-Boker L, Derazne E, Levi Z, et al. Adolescent obesity and midlife cancer risk: a population-based cohort study of 2·3 million adolescents in Israel. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020;8:216–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30019-XA nationwide study that assessed cancer-specific risk for various groups of adolescent BMI. It shows a substantial risk of incident cancer among adolescents with overweight and obesity that was apparent before age 30 years. Cancer risk for the latter persisted when the study sample was limited to overweight and obese adolescents who had unimpaired health at baseline.
Baer HJ, Colditz GA, Rosner B, Michels KB, Rich-Edwards JW, Hunter DJ, et al. Body fatness during childhood and adolescence and incidence of breast cancer in premenopausal women: a prospective cohort study. Breast Cancer Res. 2005;7:R314–25.
Keinan-Boker L, Levine H, Derazne E, Molina-Hazan V, Kark JD. Measured adolescent body mass index and adult breast cancer in a cohort of 951,480 women. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016;158:157–67.
Levi Z, Kark JD, Shamiss A, Derazne E, Tzur D, Keinan-Boker L, et al. Body mass index and socioeconomic status measured in adolescence, country of origin, and the incidence of gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma in a cohort of 1 million men. Cancer. 2013;119:4086–93.
Keinan-Boker L, Levine H, Leiba A, Derazne E, Kark JD. Adolescent obesity and adult male breast cancer in a cohort of 1,382,093 men. Int J Cancer. 2018;142:910–8.
Leiba A, Kark JD, Afek A, Derazne E, Barchana M, Tzur D, et al. Adolescent obesity and paternal country of origin predict renal cell carcinoma: a cohort study of 1.1 million 16 to 19-year-old males. J Urol. 2013;189:25–9. Available from:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2012.08.184.
Zohar L, Rottenberg Y, Twig G, Katz L, Leiba A, Derazne E, et al. Adolescent overweight and obesity and the risk for pancreatic cancer among men and women: a nationwide study of 1.79 million Israeli adolescents. Cancer. 2019;125:118–26.
Levi Z, Kark JD, Twig G, Katz L, Leiba A, Derazne E, et al. Body mass index at adolescence and risk of noncardia gastric cancer in a cohort of 1.79 million men and women. Cancer. 2018;124:356–63.
Levi Z, Kark JD, Katz LH, Twig G, Derazne E, Tzur D, et al. Adolescent body mass index and risk of colon and rectal cancer in a cohort of 1.79 million Israeli men and women: a population-based study. Cancer. 2017;123:4022–30.
Leiba M, Leiba A, Keinan-Boker L, Avigdor A, Derazne E, Levine H, et al. Adolescent weight and height are predictors of specific non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtypes among a cohort of 2,352,988 individuals aged 16 to 19 years. Cancer. 2016;122:1068–77.
Kitahara CM, Gamborg M, De González AB, Sørensen TIA, Baker JL. Childhood height and body mass index were associated with risk of adult thyroid cancer in a large cohort study. Cancer Res. 2014;74:235–42.
Sommer A, Twig G. The impact of childhood and adolescent obesity on cardiovascular risk in adulthood: a systematic review. Curr Diab Rep. 2018;18:91.
Würtz P, Wang Q, Kangas AJ, Richmond RC, Skarp J, Tiainen M, et al. Metabolic signatures of adiposity in young adults: Mendelian randomization analysis and effects of weight change. PLoS Med. 2014;11:e1001765.
Mattsson N, Rönnemaa T, Juonala M, Viikari JSA, Raitakari OT. Childhood predictors of the metabolic syndrome in adulthood. The Cardiovascular Risk in Young Finns Study. Ann Med. 2008;40:542–52.
Morrison JA, Friedman LA, Gray-McGuire C. Metabolic syndrome in childhood predicts adult cardiovascular disease 25 years later: the Princeton lipid research clinics follow-up study. Pediatrics. 2007;120:340–5.
Sundaram MES, Berg RL, Economos C, Coleman LA. The relationship between childhood BMI and adult serum cholesterol, LDL, And ankle brachial index. Clin Med Res. 2014;12:33–9.
Rademacher ER, Jacobs DR, Moran A, Steinberger J, Prineas RJ, Sinaiko A. Relation of blood pressure and body mass index during childhood to cardiovascular risk factor levels in young adults. J Hypertens. 2009;27:1766–74.
Kelly RK, Magnussen CG, Sabin MA, Cheung M, Juonala M. Development of hypertension in overweight adolescents: a review. Adolesc Health Med Ther. 2015;6:171–87.
Movahed MR, Bates S, Strootman D, Sattur S. Obesity in adolescence is associated with left ventricular hypertrophy and hypertension. Echocardiography. 2011;28:150–3.
Twig G, Reichman B, Afek A, Derazne E, Hamiel U, Furer A, et al. Severe obesity and cardio-metabolic comorbidities: a nationwide study of 2.8 million adolescents. Int J Obes. 2019;43:1391–9. Available from:. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-018-0213-z.
Pereira PF, Serrano HMS, Carvalho GQ, Lamounier JA, Peluzio MDCG, Franceschini SDCC, et al. Body fat location and cardiovascular disease risk factors in overweight female adolescents and eutrophic female adolescents with a high percentage of body fat. Cardiol Young. 2012;22:162–9.
Sabo RT, Lu Z, Daniels S, SSS. Serial childhood body mass index and associations with adult hypertension and obesity: the Fels Longitudinal Study. Physiol Behav. 2017;176:139–48.
Chorin E, Hassidim A, Hartal M, Havakuk O, Flint N, Ziv-Baran T, et al. Trends in adolescents obesity and the association between BMI and blood pressure: a cross-sectional study in 714,922 healthy teenagers. Am J Hypertens. 2015;28:1157–63.
Park MH, Sovio U, Viner RM, Hardy RJ, Kinra S. Overweight in childhood, adolescence and adulthood and cardiovascular risk in later life: pooled analysis of three British birth cohorts. PLoS One. 2013;8:3–8.
Su TC, Liao CC, Chien KL, Hsu SHJ, Sung FC. An overweight or obese status in childhood predicts subclinical atherosclerosis and prehypertension/hypertension in young adults. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2014;21:1170–82.
Tirosh A, Afek A, Rudich A, Percik R, Gordon B, Ayalon N, et al. Progression of normotensive adolescents to hypertensive adults a study of 26 980 teenagers. Hypertension. 2010;56:203–9.
Twig G, Ben-Ami Shor D, Furer A, Levine H, Derazne E, Goldberger N, et al. Adolescent body mass index and cardiovascular disease-specific mortality by midlife. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017;102:3011–20.
Twig G, Gerstein HC, Shor DBA, Derazne E, Tzur D, Afek A, et al. Coronary artery disease risk among obese metabolically healthy young men. Eur J Endocrinol. 2015;173:305–12.
Williams MJA, Milne BJ, Ambler A, Theodore R, Ramrakha S, Caspi A, et al. Childhood body mass index and endothelial dysfunction evaluated by peripheral arterial tonometry in early midlife. Int J Obes. 2017;41:1355–60.
Hao G, Wang X, Treiber FA, Harshfield G, Kapuku G, Su S. Body mass index trajectories in childhood is predictive of cardiovascular risk: results from the 23-year longitudinal Georgia Stress and Heart study. Int J Obes. 2018;42:923–5.
Juonala M, Magnussen CG, Venn A, Dwyer T, Burns TL, Davis PH, et al. Influence of age on associations between childhood risk factors and carotid intima-media thickness in adulthood. Circulation. 2010;122:2514–20.
Yan Y, Hou D, Liu J, Zhao X, Cheng H, Xi B, et al. Childhood body mass index and blood pressure in prediction of subclinical vascular damage in adulthood: Beijing blood pressure cohort. J Hypertens. 2017;35:47–54.
Andersen LG, Ängquist L, Eriksson JG, Forsen T, Gamborg M, Osmond C, et al. Birth weight, childhood body mass index and risk of coronary heart disease in adults: combined historical cohort studies. PLoS One. 2010;5:20–2.
Falkstedt D, Hemmingsson T, Rasmussen F, Lundberg I. Body mass index in late adolescence and its association with coronary heart disease and stroke in middle age among Swedish men. Int J Obes. 2007;31:777–83.
Fang X, Zuo J, Zhou J, Cai J, Chen C, Xiang E, et al. Childhood obesity leads to adult type 2 diabetes and coronary artery diseases: a 2-sample Mendelian randomization study. Med (United States). 2019;98:e16825.
Must A, Jacques PF, Dallal GE, Bajema CJ, Dietz WH. Long-term morbidity and mortality of overweight adolescents. N Engl J Med. 1992;326:653–7.
Baker JL, Olsen LW, Sørensen TIA. Childhood body-mass index and the risk of coronary heart disease in adulthood. N Engl J Med. 2007:687–96.
• Twig G, Yaniv G, Levine H, Leiba A, Goldberger N, Derazne E, et al. Body-mass index in 2.3 million adolescents and cardiovascular death in adulthood. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:2430–40 A nationwide study that assessed the association between adolescent BMI and midlife mortality. It showed that the risk of mortality due to cardiovascular disease was nearly 2- and 4-fold among adolescents with overweight and obesity respectively and was evident before age 30 years. The mortality risk for the latter persisted with extensive sensitivity analyses including limiting the study sample to overweight and obese adolescents who had unimpaired health at baseline.
Furer A, Afek A, Orr O, Gershovitz L, Landau Rabbi M, Derazne E, et al. Sex-specific associations between adolescent categories of BMI with cardiovascular and non-cardiovascular mortality in midlife. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018;17:1–10. Available from:. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-018-0727-7.
Barasa A, Schaufelberger M, Lappas G, Swedberg K, Dellborg M, Rosengren A. Heart failure in young adults: 20-year trends in hospitalization, aetiology, and case fatality in Sweden. Eur Heart J. 2014;35:25–32.
Aune D, Sen A, Norat T, Janszky I, Romundstad P, Tonstad S, et al. Body mass index, abdominal fatness, and heart failure incidence and mortality: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. Circulation. 2016;133:639–49.
Rosengren A, Åberg M, Robertson J, Waern M, Schaufelberger M, Kuhn G, et al. Body weight in adolescence and long-term risk of early heart failure in adulthood among men in Sweden. Eur Heart J. 2017;38:1926–33.
Robertson J, Schaufelberger M, Lindgren M, Adiels M, Schiöler L, Torén K, et al. Higher body mass index in adolescence predicts cardiomyopathy risk in midlife: long-term follow-up among Swedish men. Circulation. 2019;140:117–25.
Mangner N, Scheuermann K, Winzer E, Wagner I, Hoellriegel R, Sandri M, et al. Childhood obesity: impact on cardiac geometry and function. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2014;7:1198–205.
Twig G, Vivante A, Bader T, Derazne E, Tsur AM, Levi M, et al. Body mass index and kidney disease-related mortality in midlife: a nationwide cohort of 2.3 million adolescents. Obesity. 2018;26:776–81.
Twig G, Geva N, Levine H, Derazne E, Goldberger N, Haklai Z, et al. Body mass index and infectious disease mortality in midlife in a cohort of 2.3 million adolescents. Int J Obes. 2018;42:801–7. Available from:. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2017.263.
Acknowledgements
This review is dedicated to prof. Arnon Afek for his continuous support of medical research in the Israel Defense Forces by facilitating seminal medical data linkage between various governmental agencies in Israel, making key longitudinal studies on adolescent obesity possible.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Adi Horesh, Avishai M. Tsur, Aya Bardugo, and Gilad Twig declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Childhood Obesity
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 54 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horesh, A., Tsur, A.M., Bardugo, A. et al. Adolescent and Childhood Obesity and Excess Morbidity and Mortality in Young Adulthood—a Systematic Review. Curr Obes Rep 10, 301–310 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13679-021-00439-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13679-021-00439-9