Abstract
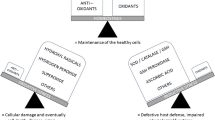
Interest in medicinal plant research and usage has risen due to many reported side effects of synthetic drugs and their relatively higher cost. Ocimum americanum (family Lamiaceae) is a commonly used spice in Ghana with the aqueous extracts of leaves, flowers and stem been rich in saponins, alkaloids, flavonoids, and tannins. The aim of the study was to evaluate the nephroprotective potential of the aqueous extracts of O. americanum parts on gentamicin- and cisplatin-induced toxicity in rats. In a ten-day experiment, nephrotoxicity was induced with gentamicin (GM; 100 mg/kg b.wt. for 8 days) and cisplatin (Cisp; 6 mg/kg b.wt. for 1 day) after pre-treatment with 250 mg/kg b.wt. of the leaves, stem, and flower extracts of O. americanum and standard drug, silymarin (100 mg/kg b.wt.) for 10 days. The nephroprotective activity was evaluated by assaying the activity of serum kidney function parameter, kidney oxidative stress parameters, kidney inflammatory cytokines (NF-κB and IL-1) and histopathology. The activities of kidney function parameters of animals were significantly increased following Cisp and GM treatment with resultant alteration is kidney microarchitecture, over-expressions of NF-κB and IL1 and kidney oxidative stress markers. Extract pre-treatment restored kidney function to near-normal, downregulating the expressions of IL-1 and NF-κB and improved levels of reduced GSH contents, GPx and SOD activities. However, leaves extract showed the best protection against GM while all extracts showed improved protection (> 50%) against Cisp. Extract of Ocimum americanum exhibit nephroprotective activity and could be developed as a potent kidney protector.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adewuyi A, Otuechere CA, Adebayo OL, Anazodo C, Pereira FV (2018) Renal toxicological evaluations of sulphonated nanocellulose from Khaya sengalensis seed in Wistar rats. Chem Biol Interact 284:56–68
Alsalame HAA, Al-Aameli MH, Al-Taee RAM, Al-Bazii WGH (2018) Protective role of alcoholic extract of fennel seed in nephrotoxicity induced by cisplatin in male rabbits. Biochem Cell Arch 18(Suppl 1):1–6
Berhow MA, Affum AO, Gyan BA (2012) Rosmarinic acid content in antidiabetic aqueous extract of Ocimum canum Sims grown in Ghana. J Med Food 15(7):611–620
Beutler E, Duron O, Kelly BM (1963) Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J Lab Clin Med 61:882–888
Chatterjee P, Mukherjee A, Nandy S (2012) Protective effects of the aqueous leaf extract of Aloe barbadensis on gentamicin and cisplatin-induced nephrotoxic rats. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 2(3):S1754–S1763
Edelstein CL (2008) Biomarkers of acute kidney injury. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 15(3):222–234
Endale M, Park SC, Kim S, Yang Y, Cho JY, Rhee MH (2013) Quercetin disrupts tyrosine-phosphorylated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and myeloid differentiation factor-88 association, and inhibits MAPK/AP-1 and IKK/NF-κB-induced inflammatory mediators production in RAW 264.7 cells. Immunobiology 218(12):1452–1467
Genfi AKA, Larbie C, Emikpe BO, Oyagbemi AA, Firempong CK, Adjei CO (2020) Modulation of oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines as therapeutic mechanisms of Ocimum americanum L. extract in carbon tetrachloride and acetaminophen-induced toxicity in rats. J Evid Based Integr Med 25:1–13
Ghane Shahrbaf F, Assadi F (2015) Drug-induced renal disorders. J Renal Inj Prev 4(3):57–60
Ghaznavi H, Fatemi I, Kalantari H, Hosseini Tabatabaei S, Mehrabani M, Gholamine B, Kalantar M, Mehrzadi S, Goudarzi M (2018) Ameliorative effects of gallic acid on gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. J Asian Nat Prod Res 20(12):1182–1193. https://doi.org/10.1080/10286020.2017.1384819
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB (1974) Glutathione S-transferases, the first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem 249(22):7130–7139
Hanigan MH, Devarajan P (2003) Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: molecular mechanisms. Cancer Ther 1:47–61
Ilić S, Stojiljković N, Veljković M, Veljković S, Stojanović G (2015) Protective effect of quercetin on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Med Biol 16(2):71–75
Jarikre TA, Emikpe BO (2017) First report of immunohistochemical detection of Peste des petit ruminants, parainfluenza 3 and respiratory syncytial viral antigens in lungs of Nigerian goats. J Immunoassay Immunochem 38(5):555–568
Jobin C, Bradham CA, Russo MP, Juma B, Narula AS, Brenner DA, Sartor RB (1999) Curcumin blocks cytokine-mediated NF-kappa B activation and proinflammatory gene expression by inhibiting inhibitory factor I-kappa B kinase activity. J Immunol 163(6):3474–3483
Jollow DJ, Mitchell JR, Zampaglione N, Gillette JR (1974) Bromobenzene-induced liver necrosis. Protective role of glutathione and evidence for 3,4-bromobenzene oxide as the hepatotoxic metabolite. Pharmacology 11(3):151–169
Karasawa T, Steyger PS (2015) An integrated view of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity. Toxicol Lett 237(3):219–227
Karimi A, Majlesi M, Rafieian-Kopaei M (2015) Herbal versus synthetic drugs; beliefs and facts. J Nephropharmacol 4(1):27–30
Kirst HA, Allen NE (2007) Aminoglycosides antibiotics. In: Comprehensive medicinal chemistry II, vol 7, pp 629–652
Kovacic P, Sacman A, Wu-Weis M (2002) Nephrotoxins: widespread role of oxidative stress and electron transfer. Curr Med Chem 9(8):823–847
Kundu JK, Shin YK, Kim SH, Surh YJ (2006) Resveratrol inhibits phorbol ester-induced expression of COX-2 and activation of NF-kappaB in mouse skin by blocking IkappaB kinase activity. Carcinogenesis 27(7):1465–1474
Larbie C, Owusu Nyarkoh C, Owusu Adjei C (2019) Phytochemical and safety evaluation of hydroethanolic leaf extract of Tecoma stans (L.) Juss. ex Kunth. Evid Based Complementary Altern Med 2019:1–12
Liyanage T, Ninomiya T, Jha V et al (2015) Worldwide access to treatment for end-stage kidney disease: a systematic review. Lancet 385(9981):1975–1982
Martínez-Salgado C, López-Hernández FJ, López-Novoa JM (2007) Glomerular nephrotoxicity of aminoglycosides. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 223(1):86–98
Mehmood RK (2014) Review of Cisplatin and oxaliplatin in current immunogenic and monoclonal antibody treatments. Oncol Rev 8(2):256
Mihai S, Codrici E, Popescu ID, Enciu AM, Albulescu L, Necula LG, Mambet C, Anton G, Tanase C (2018) Inflammation-related mechanisms in chronic kidney disease prediction, progression, and outcome. J Immunol Res 2018:2180373
Murray CJ, Barber RM et al (2015) Global, regional, and national disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 306 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 188 countries, 1990–2013: quantifying the epidemiological transition. Lancet 386(10009):2145–2191
Murthy RLN, Nataraj HN, Ramachandra SS (2011) Nephroprotective activity of Cyanotis fasiculata var fasiculata against cisplatin induced nephrotoxicity. Int Res J Pharm 2(9):137–142
National Research Council (2011) Guide for care and use of laboratory animal, 8th edn. National Academic Press, Washington, pp 43–45
Nyarko AK, Ofosuhene M, Addy ME (2002) Extract of Ocimum canum lowers blood glucose and facilitates insulin release by isolated pancreatic β-islet cells. Phytomedicine 9:346–351
Nyarko RA, Larbie C, Anning AK, Baidoo PK, Emikpe BO, Oyagbemi AA, Jarikre TA (2019) Griffonia simplicifolia (DC.) Baill. attenuates gentamicin and cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicty in rats. Comp Clin Path 28:1293–1304
Oboh G (2008) Antioxidative potential of Ocimum gratissimum and Ocimum canum leaf Polyphenols and protective effects on some pro-oxidants induced lipid peroxidation in rat brain: an in vitro study. Am J Food Technol 3(5):325–334
Ogundipe DJ, Akomolafe RO, Sanusi AA, Imafidon CE, Olukiran OS, Oladele AA (2017) Ocimum gratissimum ameliorates gentamicin-induced kidney injury but decreases creatinine clearance following sub-chronic administration in rats. J Evid Based Complementary Altern Med 22(4):592–602
Oyagbemi AA, Omobowale TO, Akinrinde AS, Saba AB, Ogunpolu BS, Daramola O (2015) Lack of reversal of oxidative damage in renal tissues of lead acetate-treated rats. Environ Toxicol 30(11):1235–1243
Oyebode O, Kandala NB, Chilton PJ, Lilford RJ (2016) Use of traditional medicine in middle-income countries: a WHO-SAGE study. Health Policy Plan 31(8):984–991
Ozkok A, Edelstein CL (2014) Pathophysiology of cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Biomed Res Int 2014:967826
Pabla N, Dong Z (2008) Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: mechanisms and renoprotective strategies. Kidney Int 73(9):994–1007
Rai S, Ghosh H, Basheer M (2016) Phytochemical characterization and antioxidative property of Ocimum canum: effect of ethanolic extract of leaves and seeds on basic immunologic and metabolic status of male rats. J Immunobiol 1(2):108–114
Saliou C, Rihn B, Cillard J, Okamoto T, Packer L (1998) Selective inhibition of NF-kappaB activation by the flavonoid hepatoprotector silymarin in HepG2. Evidence for different activating pathways. FEBS Lett 440(1–2):8–12
Sun C, Wu Z, Wang Z, Zhang H (2015) Effect of ethanol/water solvents on phenolic profiles and antioxidant properties of Beijing propolis extracts. Evid Based Complementary Altern Med 2015: Article ID 595393
Tsao R (2010) Chemistry and biochemistry of dietary polyphenols. Nutrients 2(12):1231–1246
Varshney R, Kale RK (1990) Effects of calmodulin antagonists on radiation-induced lipid peroxidation in microsomes. Int J Radiat Biol 58(5):733–743
World Health Organization (2017) Tackling NCDs: best buys and other recommended interventions for the prevention and control of noncommunicable diseases. Geneva. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/259232/WHO-NMH-NVI-17.9-eng.pdf?sequence=1 [cited 2018 Feb 27]
Yoon JH, Baek SJ (2005) Molecular targets of dietary polyphenols with anti-inflammatory properties. Yonsei Med J 46(5):585–596
Zhang H, Sun SC (2015) NF-κB in inflammation and renal diseases. Cell Biosci 5:63
Funding
This research did not receive any assistance from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or non-profit sectors. They were performed as part of the work duties of the research team.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement
All animal experiments were conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the Committee for the Purpose of Control and Supervision of Experiment on Animals (CPCSEA, New Delhi, India) and the guide for the care and use of laboratory animals (Washington, USA). Protocol for the animal study was approved by a veterinarian on the team.
Conflict of interest
Christopher Larbie has no conflict of interest. Ruby A. Nyarko has no conflict of interest. Ademola A. Oyagbemi has no conflict of interest. Theophilus A. Jarikre has no conflict of interest. Clement O. Adjei has no conflict of interest. Emmanuel B. Aseidu has no conflict of interest. Rosemond Mawuenyega has no conflict of interest. Benjamin O. Emikpe has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Larbie, C., Nyarko, R.A., Oyagbemi, A.A. et al. Biochemical and anti-inflammatory effect of Ocimum americanum Linn. extracts on gentamicin- and cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. ADV TRADIT MED (ADTM) 21, 747–758 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-020-00501-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-020-00501-2