Abstract
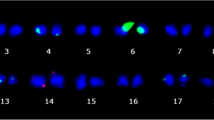
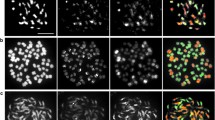
Chrysanthemum is a globally important crop associated with a variety of ornamental products including cut flowers, potted plants, and garden varieties, and high demand for such products has facilitated the development of higher-performing varieties that better meet customer and market requirements. However, chrysanthemum breeding is challenging owing to its complex genetic background and limited knowledge of its genetics and ploidy. To provide more information for breeding material identification in chrysanthemum, we performed both morphological and cytogenetic analysis of 11 chrysanthemum cultivars from Korea. Morphological evaluation of the 11 cultivars revealed that cultivar ‘Green Diamond’ had the tallest plants, ‘Orange Pangpang’ produced the longest cauline leaves, ‘Woonbaek’ had the broadest inflorescences, and ‘Snow Pop’ produced the highest number of ligulate flowers. Cytogenetic investigation suggested that seven of the cultivars (63.6%) were hexaploid (2n = 6× = 54), and the remaining four cultivars (36.4%) were hexaploid-based aneuploids. The cultivars also differed in total chromosome length and in the number 18S rDNA signals, which were located at terminal sites of the short arms. However, all 11 cultivars possessed three pairs of 5S rDNA loci, and those signals were located at interstitial locations of the long arms. These findings will be useful for breeding stock selection, cultivar identification, global communication of new cultivars, and germplasm enhancement.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd El-Twab MH, Kondo K (2006) FISH physical mapping of 5S, 45S and Arabidopsis-type telomere sequence repeats in Chrysanthemum zawadskii showing intra-chromosomal variation and complexity in nature. Chromosome Bot 1:1–5. https://doi.org/10.3199/iscb.1.1
Abd El-Twab MH, Kondo K (2007) FISH physical mapping of 5S rDNA and telomere sequence repeats identified a peculiar chromosome mapping and mutation in Leucanthemella linearis and Nipponanthemum nipponicum in Chrysanthemum sensu lato. Chromosome Bot 2:11–17. https://doi.org/10.3199/iscb.2.11
Abd El-Twab MH, Kondo K (2009) GISH identification of ancestor or closely related genome to Chrysanthemum grandiflorum cv. “Happy Gold.” Chromosome Bot 4:47–51. https://doi.org/10.3199/iscb.4.47
Abd El-Twab MH, Kondo K (2012a) Genome mutation revealed by artificial hybridization between Chrysanthemum yoshinaganthum and Chrysanthemum vestitum assessed by FISH and GISH. J Bot 2012:480310. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/480310
Abd El-Twab MH, Kondo K (2012b) Physical mapping of 5S and 45S rDNA in Chrysanthemum and related genera of the Anthemideae by FISH, and species relationships. J Genet 91:245–249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-012-0177-z
Abd El-Twab MH, Mekawy AM, El-Katatny MS (2008) Karyomorphological studies of some species of Chrysanthemum sensu lato in Egypt. Chromosome Bot 3:41–47. https://doi.org/10.3199/iscb.3.41
Anderson NO (2006) Chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum x grandiflora Tzvelv). In: Anderson NO (ed) Flower breeding and genetics issues, challenges and opportunities for the 21st century. Springer, New York, pp 389–437. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-4428-1
Bhat TA, Wani AA (2017) Chromosome structure and aberrations. Springer, New Delhi
Bhattacharya A, da Silva JAT (2006) Molecular systematics in Chrysanthemum × grandiflorum (Ramat.) Kitamura. Sci Hortic 109:379–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2006.06.004
Brasileiro-Vidal A, dos Santos-Serejo J, Soares Filho WDS, Guerra M (2007) A simple chromosomal marker can reliably distinguish Poncirus from Citrus species. Genetica 129:273–279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-006-0007-4
Chang L, Chen S-M, Chen F-D, Zhen L, Fang W-M (2009) Karyomorphological studies on Chinese pot chrysanthemum cultivars with large inflorescences. Agric Sci China 8:793–802. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1671-2927(08)60280-1
Dai S, Wang W, Huang J (2002) Advances of researches on phylogeny of Dendranthema and origin of chrysanthemum. J Beijing For Univ 24:230–234. https://doi.org/10.13332/j.1000-1522.2002.z1.046
Dai SL, Wang WK, Li MX, Xu YX (2005) Phylogenetic relationship of Dendranthema (DC.) Des Moul. revealed by fluorescent in situ hybridization. J Integr Plant Biol 47:783–791. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7909.2005.00068.x
Datta S, Janakiram T (2015) Breeding and genetic diversity in Chrysanthemum morifolium in India: a review. Indian J Agric Sci 85:1379–1395
Dorwick G (1953) The chromosomes of Chrysanthemum II: garden varieties. Heredity 7:59–72. https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.1953.5
Embassy of the Kingdom of the Netherlands in Seoul (2019) Report 2019 Korean Flower Market. Agroberichten Buitenland. https://www.agroberichtenbuitenland.nl/documenten/rapporten/2019/06/26/report-2019-korean-flower-marketfocusing-on-cut-flower. Accessed 11 Jan 2019
Guo HB, Ke WD, Li SM (2010) Morphological diversity of flower lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn. ssp. nucifera) germplasms. Bull Bot Res 30:70–80. https://doi.org/10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2010.01.014
Guo X, Luo C, Wu Z, Zhang X, Cheng X, Huang C (2012) Polyploidy levels of Chinese large-flower chrysanthemum determined by flow cytometry. Afr J Biotech 11:7789–7794. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB11.3600
Hanks G (2018) A review of production statistics for the cut flower and foliage sector 2015 (part of AHDB horticulture funded project PO BOF 002a). https://docplayer.net/44149734-A-review-of-production-statistics-for-the-cut-flower-and-foliage-sector-2015-part-of-ahdb-horticulture-funded-project-po-bof-002a.html. Accessed 24 June 2020
Haouas D, Halima-Kamel MB, Hamouda M (2008) Insecticidal activity of flower and leaf extracts from Chrysanthemum species against Tribolium confusum. Tunis J Plant Prot 3:87
Hejazi SH (2011) Karyological study on three Cicer L. species (Fabaceae) in Iran. Asian J Cell Biol 6:97–104. https://doi.org/10.3923/ajcb.2011.97.104
Heslop-Harrison J, Schwarzacher T (2011) Organisation of the plant genome in chromosomes. Plant J 66:18–33. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04544.x
Huang J, Ma L, Yang F, Fei S-Z, Li L (2008) 45S rDNA regions are chromosome fragile sites expressed as gaps in vitro on metaphase chromosomes of root-tip meristematic cells in Lolium spp. PLoS ONE 3:e2167. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0002167
Hwang Y-J, Younis A, Ryu KB, Lim K-B, Eun C-H, Lee J, Sohn S-H, Kwon S-J (2013) Karyomorphological analysis of wild Chrysanthemum boreale collected from four natural habitats in Korea. Flower Res J 21:182–189. https://doi.org/10.11623/frj.2013.21.4.34
Inafuku J, Nabeyama M, Kikuma Y, Saitoh J, Kubota S, Kohno S-I (2000) Chromosomal location and nucleotide sequences of 5S ribosomal DNA of two cyprinid species (Osteichthyes, Pisces). Chromosome Res 8:193–199. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009292610618
Jara-Seguel P, Urrutia J (2012) Cytogenetics of Chilean angiosperms: advances and prospects. Rev Chil Hist Nat 85:1–12. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0716-078X2012000100001
Jo YK, Mazharul IM, Kim C-K, Kim HY, Lim K-B (2019) Morphological characteristics and FISH analysis of Hibiscus F1 hybrids and parental lines. Hort Sci Technol 37:630–639. https://doi.org/10.7235/HORT.20190063
Kim JS, Pak J-H, Seo B-B, Tobe H (2003) Karyotypes of metaphase chromosomes in diploid populations of Dendranthema zawadskii and related species (Asteraceae) from Korea: diversity and evolutionary implications. J Plant Res 116:47–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-002-0067-1
Kim SJ, Lee CH, Kim J, Kim KS (2014) Phylogenetic analysis of Korean native Chrysanthemum species based on morphological characteristics. Sci Hortic 175:278–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2014.06.018
Law C, Snape J, Worland A (1987) Aneuploidy in wheat and its uses in genetic analysis. In: Lupton FGH (ed) Wheat breeding. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 71–108
Li C, Chen S, Chen F, Li J, Fang W (2011a) Cytogenetic study of three edible Chrysanthemum cultivars. Russ J Genet 47:176–181. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795411010054
Li J, Chen S-M, Chen F-D, Fang W-M (2008) Karyotype and meiotic analyses of six species in the subtribe Chrysantheminae. Euphytica 164:293–301. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-008-9734-1
Li X, Zhu C, Lin Z, Wu Y, Zhang D, Bai G, Song W, Ma J, Muehlbauer GJ, Scanlon MJ (2011b) Chromosome size in diploid eukaryotic species centers on the average length with a conserved boundary. Mol Biol Evol 28:1901–1911. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msr011
Lim JH, Shim MS, Sim S-C, Oh KH, Seo JY (2014) Genetic variation of flower characteristics in a population derived from a cross between the chrysanthemum cultivars ‘Falcao’ and ‘Frill Green.’ Hortic Environ Biotechnol 55:322–328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-014-0140-4
Liu G, Lan Y, Xin H, Hu F, Wu Z, Shi J, Xi M (2016) Cytogenetic analysis of Lilium rosthornii. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 141:444–448. https://doi.org/10.21273/JASHS03757-16
Liu P-L, Wan Q, Guo Y-P, Yang J, Rao G-Y (2012) Phylogeny of the genus Chrysanthemum L.: evidence from single-copy nuclear gene and chloroplast DNA sequences. PLoS ONE 7:e48970. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0048970
Lopez MG, Wulff AF, Poggio L, Xifreda CC (2008) South African fireweed Senecio madagascariensis (Asteraceae) in Argentina: relevance of chromosome studies to its systematics. Bot J Linn Soc 158:613–620. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8339.2008.00865.x
MacDonald J, Hackett M, Mirmak B (2017) Handbook on chrysanthemum classification. http://www.mums.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/2017-Classification-Handbook.pdf. Accessed 11 June 2020
Mártonfiová L (2013) A method of standardization of chromosome length measurement. Caryologia 66:304–312. https://doi.org/10.1080/00087114.2013.854565
Matoba H, Uchiyama H (2009) Physical mapping of 5S rDNA, 18S rDNA and telomere sequences in three species of the genus Artemisia (Asteraceae) with distinct basic chromosome numbers. Cytologia 74:115–123. https://doi.org/10.1508/cytologia.74.115
Mehes-Smith M, Nkongolo K, Kim N (2011) A comparative cytogenetic analysis of five pine species from North America, Pinus banksiana, P. contorta, P. monticola, P. resinosa, and P. strobus. Plant Syst Evol 292:153–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-010-0401-3
Mekapogu M, Kwon OK, Lee KJ, Ahn MS, Park JT, Jung JA (2020) Identification of standard type cultivars in Chrysanthemum (Dendranthema grandiflorum) using SSR markers. Hortic Environ Biotechnol 61:153–161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-019-00201-0
Mekki L, Badr A, Fekry M (2007) Cytogenetic studies on nine genotypes of Phaseolus vulgaris L. cultivated in Egypt in relation to zinc efficiency. Pak J Biol Sci 10:4230–4235. https://doi.org/10.3923/pjbs.2007.4230.4235
Nakata M (1992) Cytogenetic studies on wild Chrysanthemum sensu lato in China II. A natural hybrid between Dendranthema indicum (2n = 36) and D. vestitum (2n = 54) from Hubei Province. J Jpn Bot 67:92–100
National Chrysanthemum Society USA (2020) Chrysanthemum classifications. http://www.mums.org/chrysanthemum-classes/. Accessed 12 June 2020
Oberprieler C, Himmelreich S, Vogt R (2007) A new subtribal classification of the tribe Anthemideae (Compositae). Willdenowia 37:89–115. https://doi.org/10.3372/wi.37.37104
Park SK, Lim JH, Shin HK, Jung JA, Kwon YS, Kim MS, Kim KS (2014) Identification of chrysanthemum genetic resources resistant to white rust caused by Puccinia horiana. Plant Breed Biotechnol 2:184–193. https://doi.org/10.9787/PBB.2014.2.2.184
Pellerin RJ, Waminal NE, Kim HH (2019) FISH mapping of rDNA and telomeric repeats in 10 Senna species. Hortic Environ Biotechnol 60:253–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-018-0115-y
Poczai P, Hyvönen J (2010) Nuclear ribosomal spacer regions in plant phylogenetics: problems and prospects. Mol Biol Rep 37:1897–1912. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-009-9630-3
Qi X, Zhang F, Guan Z, Wang H, Jiang J, Chen S, Chen F (2015) Localization of 45S and 5S rDNA sites and karyotype of Chrysanthemum and its related genera by fluorescent in situ hybridization. Biochem Syst Ecol 62:164–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2015.08.006
Roa F, Guerra M (2012) Distribution of 45S rDNA sites in chromosomes of plants: structural and evolutionary implications. BMC Evol Biol 12:225. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-12-225
Song SH, Kim YB, Lee SD, Choi KJ, Yang MH, An CH, Shin HK (2000) Guide-lines for the Conduct of Tests for New Variety Examination (Chrysanthemum). National Seed Management Office
Speicher MR, Ballard SG, Ward DC (1996) Karyotyping human chromosomes by combinatorial multi-fluor FISH. Nat Genet 12:368–375. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0496-368
Su J, Jiang J, Zhang F, Liu Y, Ding L, Chen S, Chen F (2019) Current achievements and future prospects in the genetic breeding of chrysanthemum: a review. Hortic Res 6:109. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41438-019-0193-8
Sun C-Q, Chen F-D, Teng N-J, Liu Z-L, Fang W-M, Hou X-L (2010) Interspecific hybrids between Chrysanthemum grandiflorum (Ramat.) Kitamura and C. indicum (L.) Des Moul. and their drought tolerance evaluation. Euphytica 174:51–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-009-0117-z
Tanaka N, Uchiyama H, Matoba H, Koyama T (2009) Karyological analysis of the genus Canna (Cannaceae). Plant Syst Evol 280:45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-009-0165-9
Tang F, Chen F, Chen S, Wang XE, Zhao H (2010) Molecular cytogenetic identification and relationship of the artificial intergeneric hybrid between Dendranthema indica and Crossostephium chinense by GISH. Plant Syst Evol 289:91–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-010-0337-7
Union Internationale pour la Protection des Obtentions Végétales (2008) Guidelines for the conduct of tests for distinctness, uniformity and stability (Chrysanthemum). UPOV, Geneva
Vaio M, Speranza P, Valls JF, Guerra M, Mazzella C (2005) Localization of the 5S and 45S rDNA sites and cpDNA sequence analysis in species of the Quadrifaria group of Paspalum (Poaceae, Paniceae). Ann Bot 96:191–200. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mci168
Waminal NE, Pellerin RJ, Kim N-S, Jayakodi M, Park JY, Yang T-J, Kim HH (2018) Rapid and efficient FISH using pre-labeled oligomer probes. Sci Rep 8:8224. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-26667-z
Zhang A, Li N, Gong L, Gou X, Wang B, Deng X, Li C, Dong Q, Zhang H, Liu B (2017) Global analysis of gene expression in response to whole-chromosome aneuploidy in hexaploid wheat. Plant Phys 175:828–847. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.00819
Zhang M, Huang H, Wang Q, Dai S (2018) Cross breeding new cultivars of early-flowering multiflora chrysanthemum based on mathematical analysis. HortScience 53:421–426. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTSCI12769-17
Zhang Y, Luo XY, Zhu J, Wang C, Hong Y, Lu J, Liu QQ, Li BQ, Zhu ML, Wang ZF (2014) A classification study for chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum × grandiflorum Tzvelv.) cultivars based on multivariate statistical analyses. J Syst Evol 52:612–628. https://doi.org/10.1111/jse.12104
Zhang Y, Zhu ML, Dai SL (2013) Analysis of karyotype diversity of 40 Chinese chrysanthemum cultivars. J Syst Evol 51:335–352. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1759-6831.2012.00235
Acknowledgements
This work was conducted with the support of the “Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science and Technology Development (Project No. PJ012804)” Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YW carried out the FISH experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. JAJ and WHK performed morphological data acquisition and analysis. KBL provided technical support. YJH supervised the project, designed the experiments, and conceived the original idea. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by So-Young Park, Ph.D.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Jung, J.A., Kim, W.H. et al. Morphological and rDNA fluorescence in situ hybridization analyses of chrysanthemum cultivars from Korea. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 62, 917–925 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-021-00361-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-021-00361-y