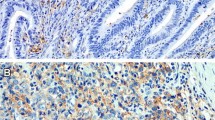
Abstract
Introduction
The progressive growth of malignancies is accompanied by a decline in the immune response through mechanisms which are poorly understood. Apoptosis and induction of inflammation by tumor released cytokines as tumor escape mechanisms have been proposed to play an important role in colorectal carcinogenesis.
Methods
Expression of Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) was analyzed in colorectal cancer specimen and the cancer cell line HT-29 by immunohistochemistry and RT-PCR. TNF-α expression on protein and mRNA level were correlated with clinical characteristics and impact on survival. TNFR-1 was co-labelled with TNF-α and CD8+ cytotoxic T cells in immunofluorescence double staining experiments. Results: 94% (n = 98/104) of the patients with CRC expressed TNF-α. High TNF-α expression was significantly associated with positive lymph node stage and recurrence of the tumor. Multivariate analysis revealed high TNF-α expression as an independent prognostic factor. Immunohistochemistry was correlated with RT-PCR results (т = 0.794). Immunofluorescence double staining experiments revealed increased TNFR-1 expression by CD8+ cells.
Conclusions
TNF-α expression by tumor cells may be an efficient immunological escape mechanism by inflammation-enhanced metastases and probably by induction of apoptosis in tumor-infiltrating CD8+ immune cells resulting in a down regulation of the tumoral immune response. Our data support the role of tumor-derived TNF-α expression as an important promoter of tumoral immune escape mechanisms and malignant progression, and suggest that analysis on either protein (immunohistochemistry) or RNA level (RT-PCR) can be used effectively in this respect. Targeting TNF-α may be a promising option, especially in cases with high TNF-α expression and positive lymph node metastases.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CRC:
-
colorectal carcinoma
References
F. Adami, A. Guarini, M. Pini, F. Siviero, R. Sancetta, M. Massaia, L. Trentin, R. Foa, G. Semenzato, Serum levels of tumour necrosis factor-alpha in patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Eur J Cancer 30A(9), 1259–1263 (1994)
B.B. Aggarwal, Signalling pathways of the TNF superfamily: a double-edged sword. Nat Rev Immunol 3(9), 745–756 (2003)
A. Ashkenazi, V.M. Dixit, Death receptors: signalling and modulation. Science 281(5381), 1305–1308 (1998)
S.J. Baker, E.P. Reddy, Modulation of life and death by the TNF receptor superfamily. Oncogene 17(25), 3261–3270 (1998)
F. Balkwill, Tumor necrosis factor or tumor promoting factor? Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 13(2), 135–141 (2002)
F. Balkwill, A. Mantovani, Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow? Lancet 357(9255), 539–545 (2001)
F. Balkwill, L.M. Coussens, Cancer: an inflammatory link. Nature 431(7007), 405–406 (2004)
T.D. Brown, P. Goodman, T. Fleming, J.S. Macdonald, E.M. Hersh, T.J. Braun, A phase II trial of recombinant tumor necrosis factor in patients with adenocarcinoma of the pancreas: a Southwest Oncology Group study. J Immunother 10(5), 376–378 (1991)
M. Bueter, M. Gasser, N. Schramm, T. Lebedeva, G. Tocco, C. Gerstlauer, M. Grimm, E. Nichiporuk, A. Thalheimer, A. Thiede, D. Meyer, G. Benichou, A.M. Waaga-Gasser, T-cell response to p53 tumor-associated antigen in patients with colorectal carcinoma. Int J Oncol 28(2), 431–438 (2006)
F. Colotta, P. Allavena, A. Sica, C. Garlanda, A. Mantovani, Cancer-related inflammation, the seventh hallmark of cancer: links to genetic instability. Carcinogenesis 30(7), 1073–1081 (2009)
C.C. Compton, L.P. Fielding, L.J. Burgart, B. Conley, H.S. Cooper, S.R. Hamilton, M.E. Hammond, D.E. Henson, R.V. Hutter, R.B. Nagle, M.L. Nielsen, D.J. Sargent, C.R. Taylor, M. Welton, C. Willett, Prognostic factors in colorectal cancer. College of American Pathologists Consensus Statement 1999. Arch Pathol Lab Med 124(7), 979–994 (2000)
D.R. Cox, Regression models and life tables. J R Stat Soc 34, 1987–2001 (1972)
E.T. Creagan, J.S. Kovach, C.G. Moertel, S. Frytak, L.K. Kvols, A phase I clinical trial of recombinant human tumor necrosis factor. Cancer 62(12), 2467–2471 (1988)
S. Cubillos, B. Scallon, M. Feldmann, P. Taylor, Effect of blocking TNF on IL-6 levels and metastasis in a B16-BL6 melanoma/mouse model. Anticancer Res 17(3C), 2207–2211 (1997)
J. Finke, S. Ferrone, A. Frey, A. Mufson, A. Ochoa, Where have all the T cells gone? Mechanisms of immune evasion by tumors. Immunol Today 20(4), 158–160 (1999)
A.B. Frey, N. Monu, Signalling defects in anti-tumor T cells. Immunol Rev 222, 192–205 (2008)
W.L. Furman, D. Strother, K. McClain, B. Bell, B. Leventhal, C.B. Pratt, Phase I clinical trial of recombinant human tumor necrosis factor in children with refractory solid tumors: a Pediatric Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol 11(11), 2205–2210 (1993)
P. Geborek, A. Bladstrom, C. Turesson, A. Gulfe, I.F. Petersson, T. Saxne, H. Olsson, L.T. Jacobsson, Tumour necrosis factor blockers do not increase overall tumour risk in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, but may be associated with an increased risk of lymphomas. Ann Rheum Dis 64(5), 699–703 (2005)
F.L. Greene, TNM staging for malignancies of the digestive tract: 2003 changes and beyond. Semin Surg Oncol 21(1), 23–29 (2003)
Grimm M, Kim M, von Rahden B, Meier E, Tsaur I, Rosenwald A, Germer CT, Gasser M and W.-G. AM., Tumour-mediated TRAIL-Receptor expression indicates effective apoptotic depletion of infiltrating CD8+ immune cells in clinical colorectal cancer, Eur J Cancer accepted (2010).
Grimm M, Gasser M, Bueter M, Otto C, Strehl J, Wang J, Nichiporuk E, Germer CT, Meyer D, Waaga-Gasser AM and T. A., Immunological escape mechanisms of colorectal hepatic metastases, BMC Cancer accepted (2010).
A.L. Hamilton SR, Pathology and genetics of tumours of the digestive system. Tumours of small intestine (IARC, Lyon, 2000), pp. 69–91
D. Hanahan, R.A. Weinberg, The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100(1), 57–70 (2000)
D. Holzel, J. Engel, U. Lohrs, Elective lymph node dissections–still a standard in cancer surgery? Zentralbl Chir 133(6), 582–589 (2008)
D. Holzel, R. Eckel, J. Engel, Colorectal cancer metastasis. Frequency, prognosis, and consequences. Chirurg 80(4), 331–340 (2009)
A.G. Jarnicki, J. Lysaght, S. Todryk, K.H. Mills, Suppression of antitumor immunity by IL-10 and TGF-beta-producing T cells infiltrating the growing tumor: influence of tumor environment on the induction of CD4+ and CD8+ regulatory T cells. J Immunol 177(2), 896–904 (2006)
E.L. Kaplan, P. Meier, Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 75, 457–487 (1958)
S. Lankiewicz, E. Rother, S. Zimmermann, C. Hollmann, F. Korangy, T.F. Greten, Tumour-associated transcripts and EGFR deletion variants in colorectal cancer in primary tumour, metastases and circulating tumour cells. Cell Oncol 30(6), 463–471 (2008)
S.T. Malik, M.S. Naylor, N. East, A. Oliff, F.R. Balkwill, Cells secreting tumour necrosis factor show enhanced metastasis in nude mice. Eur J Cancer 26(10), 1031–1034 (1990)
A. Mantovani, Cancer: Inflaming metastasis. Nature 457(7225), 36–37 (2009)
W.E. Mesker, G.J. Liefers, J.M. Junggeburt, G.W. van Pelt, P. Alberici, P.J. Kuppen, N.F. Miranda, K.A. van Leeuwen, H. Morreau, K. Szuhai, R.A. Tollenaar, H.J. Tanke, Presence of a high amount of stroma and downregulation of SMAD4 predict for worse survival for stage I-II colon cancer patients. Cell Oncol 31(3), 169–178 (2009)
V. Michalaki, K. Syrigos, P. Charles, J. Waxman, Serum levels of IL-6 and TNF-alpha correlate with clinicopathological features and patient survival in patients with prostate cancer. Br J Cancer 90(12), 2312–2316 (2004)
D.W. Miles, L.C. Happerfield, M.S. Naylor, L.G. Bobrow, R.D. Rubens, F.R. Balkwill, Expression of tumour necrosis factor (TNF alpha) and its receptors in benign and malignant breast tissue. Int J Cancer 56(6), 777–782 (1994)
C.P. Morales, R.F. Souza, S.J. Spechler, Hallmarks of cancer progression in Barrett’s oesophagus. Lancet 360(9345), 1587–1589 (2002)
J.R. Muppidi, J. Tschopp, R.M. Siegel, Life and death decisions: secondary complexes and lipid rafts in TNF receptor family signal transduction. Immunity 21(4), 461–465 (2004)
J. Nakashima, M. Tachibana, M. Ueno, A. Miyajima, S. Baba, M. Murai, Association between tumor necrosis factor in serum and cachexia in patients with prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 4(7), 1743–1748 (1998)
M.S. Naylor, G.W. Stamp, W.D. Foulkes, D. Eccles, F.R. Balkwill, Tumor necrosis factor and its receptors in human ovarian cancer. Potential role in disease progression. J Clin Invest 91(5), 2194–2206 (1993)
P. Orosz, B. Echtenacher, W. Falk, J. Ruschoff, D. Weber, D.N. Mannel, Enhancement of experimental metastasis by tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med 177(5), 1391–1398 (1993)
Z. Qin, S. Kruger-Krasagakes, U. Kunzendorf, H. Hock, T. Diamantstein, T. Blankenstein, Expression of tumor necrosis factor by different tumor cell lines results either in tumor suppression or augmented metastasis. J Exp Med 178(1), 355–360 (1993)
S. Rajput, A. Wilber, Roles of inflammation in cancer initiation, progression, and metastasis. Front Biosci (Schol Ed) 2, 176–183 (2010)
J.C. Reed, Apoptosis-targeted therapies for cancer. Cancer Cell 3(1), 17–22 (2003)
M.J. Sack, S.A. Roberts, Cytokeratins 20 and 7 in the differential diagnosis of metastatic carcinoma in cytologic specimens. Diagn Cytopathol 16(2), 132–136 (1997)
H.I. Sati, M. Greaves, J.F. Apperley, R.G. Russell, P.I. Croucher, Expression of interleukin-1beta and tumour necrosis factor-alpha in plasma cells from patients with multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol 104(2), 350–357 (1999)
P. Selby, S. Hobbs, C. Viner, E. Jackson, A. Jones, D. Newell, A.H. Calvert, T. McElwain, K. Fearon, J. Humphreys et al., Tumour necrosis factor in man: clinical and biological observations. Br J Cancer 56(6), 803–808 (1987)
P.E. Shrout, J.L. Fleiss, Intraclass correlations: uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychol Bull 86(2), 420–428 (1979)
J.S. Smolen, D. Aletaha, Developments in the clinical understanding of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 11(1), 204 (2009)
Sobin LH and W. Ch., UICC. TNM Classification of Malignant Tumors, 6th edition (2002).
L.A. Tartaglia, D.V. Goeddel, Two TNF receptors. Immunol Today 13(5), 151–153 (1992)
S. Trompet, A.J. de Craen, S. Mooijaart, D.J. Stott, I. Ford, N. Sattar, W. Jukema, R.G. Westendorp, High innate production capacity of proinflammatory cytokines increases risk for death from cancer: results of the PROSPER study. Clin Cancer Res 15(24), 7744–7748 (2009)
P. Vandenabeele, W. Declercq, R. Beyaert, W. Fiers, Two tumour necrosis factor receptors: structure and function. Trends Cell Biol 5(10), 392–399 (1995)
L.M. Veenendaal, O. Kranenburg, N. Smakman, A. Klomp, I.H. Borel Rinkes, P.J. van Diest, Differential Notch and TGFbeta signalling in primary colorectal tumors and their corresponding metastases. Cell Oncol 30(1), 1–11 (2008)
K. Warzocha, P. Ribeiro, N. Renard, J. Bienvenu, C. Charlot, B. Coiffier, G. Salles, Expression of genes coding for the tumor necrosis factor and lymphotoxin ligand-receptor system in non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. Cancer Immunol Immunother 49(9), 469–475 (2000)
Y. Wu and B. P. Zhou, TNF-alpha/NF-kappaB/Snail pathway in cancer cell migration and invasion, Br J Cancer.
I. Zidi, S. Mestiri, A. Bartegi, N. B. Amor, TNF-alpha and its inhibitors in cancer, Med Oncol (2009).
K. Zins, D. Abraham, M. Sioud, S. Aharinejad, Colon cancer cell-derived tumor necrosis factor-alpha mediates the tumor growth-promoting response in macrophages by up-regulating the colony-stimulating factor-1 pathway. Cancer Res 67(3), 1038–1045 (2007)
C.C. Zouboulis, K. Schroder, C. Garbe, K. Krasagakis, S. Kruger, C.E. Orfanos, Cytostatic and cytotoxic effects of recombinant tumor necrosis factor-alpha on sensitive human melanoma cells in vitro may result in selection of cells with enhanced markers of malignancy. J Invest Dermatol 95(6 Suppl), 223S–230S (1990)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the assistance of Mrs. Mariola Dragan and Mrs. Sabine Mueller for their technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper is a reprint from ‘Tumor necrosis factor-α is associated with positive lymph node status in patients with recurrence of colorectal cancer indications for anti-TNF-α agents in cancer treatment, M. Grimm, M. Lazariotou, S. Kircher, A. Hfelmayr, C.T. Germer, B.H.A. von Rahden, A.M. Waaga-Gasser and M. Gasser’ originally published in Analytical Cellular Pathology/Cellular Oncology, Volume 33, number 3-4, 2010, pp. 151-163, IOS Press.
M. Grimm and M. Lazariotou contributed equally to this work.
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s13402-011-0057-1
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grimm, M., Lazariotou, M., Kircher, S. et al. Tumor necrosis factor-α is associated with positive lymph node status in patients with recurrence of colorectal cancer—indications for anti-TNF-α agents in cancer treatment. Cell Oncol. 34, 315–326 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-011-0027-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-011-0027-7