Abstract
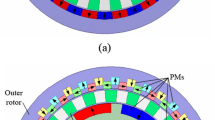
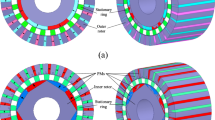
Concentric magnetic gear (CMG) can achieve a torque density of more than 150 kN m/m3 through several modifications of the original structure and the removal of material volume. However, the complexity of such a system may be impractical to assemble and realize. CMG with an alternative condition where the pole piece acts as the outer rotor can deliver higher torque instead of outer pole pair on the same structure. This unconventional condition was known since CMG inception, but it inherits the problem similar to the reluctance machine of high torque ripple. In this paper, a considerably high torque density rotating pole piece magnetic gear is proposed. Several pole pair combinations were evaluated that could yield the highest torque density at lower torque ripple. The best pole pair combination was then optimized through the width reduction of three elements, namely the pole piece, the inner yoke and the outer yoke. By enhancing the structure with the best pole pair combination, the highest torque density achieved was 364.5 kNm/m3. At the same time, the torque ripple was ably kept at below 15%. Unlike other complex structures that yield high torque density, the proposed structure is simpler, easier to assemble and hence should be more cost effective to be produced.






















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mcgilton, B.; Mueller, P.M.; Mcdonald, A.: Review of magnetic gear technologies and their applications in marine energy. In: 5th IET International Conference on Renewable Power Generation (RPG) 2016. pp. 1–6 (2016).
Aiso, K.; Akatsu, K.; Aoyama, Y.: Reluctance magnetic gear and flux switching magnetic gear for high speed motor system. In: 2017 IEEE Energy Convers. Congr. Expo. ECCE 2017. 2017-Janua, 2445–2452 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/ECCE.2017.8096470.
Huang, C.C.; Tsai, M.C.; Dorrell, D.G.; Lin, B.J.: Development of a magnetic planetary gearbox. IEEE Trans. Magn. 44, 403–412 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2007.914665
Perez-Diaz, J.L.; Diez-Jimenez, E.; Alvarez-Valenzuela, M.A.; Sanchez-García-Casarrubios, J.; Cristache, C.; Valiente-Blanco, I.: Magnetic gearboxes for aerospace applications. Aerosp. Mech. Symp. 365–374 (2014)
Rasmussen, P.O.; Andersen, T.O.; Jørgensen, F.T.; Nielsen, O.: Development of a high-performance magnetic gear. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 41, 764–770 (2005)
Neves, C.G.C.; Figueiredo, D.L.; Nunes, A.S.: Magnetic gear: a review. In: 2014 11th IEEE/IAS Int. Conf. Ind. Appl. 1–6 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/INDUSCON.2014.7059417.
Rasmussen, P.O.; Andersen, T.O.; Joergensen, F.T.: Development of a high performance magnetic gear. In: Industry Applications Society Annual Meeting (IAS). pp. 1696–1702 (2003).
Furlani, E.P.: A two-dimensional analysis for the coupling of magnetic gears. IEEE Trans. Magn. 33, 2317–2321 (1997)
Kikuchi, S.; Tsurumoto, K.: Design and characteristics of a new magnetic worm gear using permanent magnet. IEEE Trans. Magn. 29, 2923–2925 (1993)
Howe, K.D.: A novel high-performance linear magnetic gear. IEEE Trans. Magn. 37, 2844–2846 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1541/ieejias.126.1352
Li, K.; Bird, J.; Kadel, J.; Williams, W.: A flux-focusing cycloidal magnetic gearbox. IEEE Trans. Magn. 51, 30–33 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2015.2440218
Jing, L.; Gong, J.U.N.; Huang, Z.: A new structure for the magnetic gear. IEEE Access 7, 75550–75555 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2919679
Jing, L.; Zhang, T.; Gao, Y.; Qu, R.: A novel HTS modulated coaxial magnetic gear with eccentric structure and Halbach arrays. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 29, 1–5 (2019)
Yin, H.; WongBird, J.Z.; Barnett, D.; Williams, W.; David Bird, J.Z.; Williams, W.: A high torque density Halbach rotor coaxial magnetic gear. In: IEEE International Electric Machines & Drives Conference (IEMDC) (2019).
Aiso, K.; Akatsu, K.; Aoyama, Y.: A novel reluctance magnetic gear for high-speed motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 55, 2690–2699 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2019.2900205
Li, K.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, P.: A reluctance magnetic gear for high speed and vibration motor systems. In: Proceedings of the 2018 25th International Conference on Mechatronics and Machine Vision in Practice, M2VIP 2018. pp. 1–5. IEEE (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/M2VIP.2018.8600905.
Li, X.; Cheng, M.; Wang, Y.: Analysis, design and experimental verification of a coaxial magnetic gear using stationary permanent-magnet ring. IET Electr. Power Appl. 12, 231–238 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-epa.2017.0382
da Costa Neves, C.G.; Flores Filho, A.F.; Goettems, M.F.; Borges, P.A.M.: Pseudo direct drive simulation and analysis. COMPEL Int. J. Comput. Math. Electr. Electron. Eng. 37, 1722–1731 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1108/COMPEL-01-2018-0008
Jing, L.; Huang, Z.; Chen, J.; Qu, R.: Design, analysis, and realization of a hybrid-excited magnetic gear during overload. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 56, 4812–4819 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2020.3004425
Halim, M.F.M.A.; Sulaiman, E.; Othman, R.N.F.K.R.: Flux modulated rotating pole piece magnetic gear. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. 11, 1731–1736 (2020). https://doi.org/10.11591/ijpeds.v11.i4.pp1731-1736
Nachimowicz, J.; Rafałowski, S.: Modelling the meshing of cycloidal gears. Acta Mechanica et Automatica. 10(2), 137–140 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1515/ama-2016-0022
Sim, M.S.; Ro, J.S.: Semi-analytical modeling and analysis of Halbach array. Energies. 13(5), 1252 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/en13051252
Jang, D.; Chang, J.: Influences of winding MMF harmonics on torque characteristics in surface-mounted permanent magnet vernier machines. Energies (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/en10040580
Atallah, K.; Calverley, S.D.; Howe, D.: High-performance magnetic gears. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 272–276, 1727–1729 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2003.12.520
Neves, C.G.C.; Filho, A.F.F.: Magnetic gearing electromagnetic concepts. J. Microwaves Optoelectron. Electromagn. Appl. 16, 108–119 (2017)
Gerber, S.: Evaluation and design aspects of magnetic gears and magnetically geared electrical machines, (2015).
Mohd Ab Halim, M.F.; Sulaiman, E.; Othman, R.N.F.K.R.; Rahman, A.A.: A new speed multiplier coaxial magnetic gear. Prog. Electromagn. Res. M. 93, 145–154 (2020). https://doi.org/10.2528/pierm20040103
Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Chen, Z.: Analysis and design optimization of a coaxial surface-mounted permanent-magnet magnetic gear. Energies 7, 8535–8553 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3390/en7128535
Wang, Y.; Filippini, M.; Bacco, G.; Bianchi, N.: Parametric design and optimization of magnetic gears with differential evolution method. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 55, 3445–3452 (2018)
Ometto, A., Rotondale, A., Rotondale, N.: Analysis and optimization of coaxial magnetic gears. In: 2016 International Symposium on Power Electronics, Electrical Drives, Automation and Motion. pp. 843–848. IEEE (2016).
Array, P., Fajri, S.N., Siswanto, I., Khoiron, A.M.: Design and analysis of coaxial magnetic gear mechanism with halbach design and analysis of coaxial magnetic gear mechanism with Halbach permanent-magnet array. In: Journal of Physics: Conference Series. pp. 1–6 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1273/1/012062.
Zhu, X.; Shu, Z.; Quan, L.; Xiang, Z.; Pan, X.: Multi-objective optimization of an outer-rotor V-shaped permanent magnet flux switching motor based on multi-level design method. IEEE Trans. Magn. 52, 1–8 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2016.2581767
Omar, M.F.: Design of segmental rotor and nonoverlap windings in single-phase FEFSM for low torque high-speed applications, PhD Thesis, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn (2019)
Frank, N.W.; Toliyat, H.A.: Gearing Ratios of a Magnetic Gear for Wind Turbines. In: 2009 IEEE International Electric Machines and Drives Conference. pp. 1224–1230. IEEE (2009).
Al-qarni, A.; Wu, F.: High-Torque-Density Low-Cost Magnetic Gear Utilizing Hybrid Magnets and Advanced Materials. In: 2019 IEEE International Electric Machines & Drives Conference (IEMDC). pp. 225–232. IEEE (2019).
Johnson, M.; Gardner, M.C.; Toliyat, H.A.: Design comparison of NdFeB and ferrite radial flux magnetic gears. In: 2016 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE). IEEE (2016).
Benarous, M.; Trezieres, M.: Design of a cost-effective magnetic gearbox for an aerospace application. J. Eng. 2019, 4081–4084 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1049/joe.2018.8238
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Centre for Research and Innovation Management, Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka (UTeM) and Universiti Tun Hussein Onn for the technical and financial support provided for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Halim, M.F.M.A., Sulaiman, E., Aziz, R. et al. Torque Density Design Optimization of Rotating Pole Piece Concentric Magnetic Gear. Arab J Sci Eng 47, 2797–2806 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05812-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05812-3