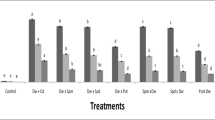
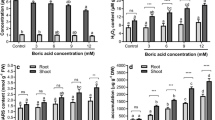
Abstract
Heavy metal pollution, which is one of the most important environmental problems, has a significant effect on plant productivity. Vanadium (V) is considered one of the most important elements of the twenty-first century due to its high consumption in industries. Morphological and physiological measurements have been performed in V studies, but there are deficiencies in molecular studies. The purpose of the present work was to elucidate the effects of V on enzymes activity, DNA damage levels and genomic template stability (GTS%) in Triticum aestivum L., as well as to investigate whether boric acid (BA) has preventive effects on these changes. Antioxidant enzyme activities were determined by SOD (superoxide dismutase), POD (peroxidase) and MDA (malondialdehyde) level. The inter-simple sequence repeats polymerase chain reaction (ISSR-PCR) assay was used to determine the genotoxic effects of V on DNA. According to the obtained results, while V stress increased MDA level and POD enzyme activity, SOD enzyme activity decreased. When V and BA were applied together, MDA level decreased and SOD and POD enzyme activities increased. All doses of V (4.4, 6.6, 8.8 mM) resulted in DNA damage and decreased GTS%. On the other hand, different concentrations of BA (4 and 8 mM) combined with V decreased the toxic effects of V. The results suggested that V could also have negative effects on wheat plants by increasing DNA damage and lipid peroxidation, and BA has an antagonistic effect against V toxicity. BA may be an alternative to reduce genetic damage in plants.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BA:
-
Boric acid
- CTAB:
-
Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide
- GTS:
-
Genomic template stability
- ISSR:
-
Inter-simple sequence repeat
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- POD:
-
Peroxidase
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- V:
-
Vanadium
References
Shyam, R.; Aery, N.C.: Effect of cerium on growth, dry matter production, biochemical constituents and enzymatic activities of cowpea plants. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 12(1), 1–14 (2012)
Anke, M.: Vanadium: an element both essential and toxic to plants, animals and humans? Anales de la Real Academia Nacional de Farmacia 70, 961–999 (2004)
Amorim, F.A.; Welz, B.; Costa, A.C.; Lepri, F.G.; Vale, M.G.R.; Ferreira, S.L.: Determination of vanadium in petroleum and petroleum products using atomic spectrometric techniques. Talanta 72(2), 349–359 (2007)
Kar, B.B.; Datta, P.; Misra, V.N.: Spent catalyst: secondary source for molybdenum recovery. Hydrometallurgy 72(1–2), 87–92 (2004)
Bhatt, K.H.; Anwar, S.; Nawaz, K.; Hussain, K.; Siddiqi, E.H.; Sharif, R.U.; Talat, A.; Khalid, A.: Effect of heavy metal lead (PB) stress of different concentration on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Middle East J. Sci. Res. 14(2), 148–154 (2013). https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.mejsr.2013.14.2.19560
Lamhamdi, M.; El Galiou, O.; Bakrim, A.; Novoa-Munoz, J.C.; Arias-Estevez, M.; Aarab, A.; Lafont, R.: Effect of lead stress on mineral content and growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum) and spinach (Spinacia oleracea) seedlings. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 20(1), 29–36 (2013)
Mahajan, S.; Tuteja, N.: Cold, salinity and drought stresses: an overview. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 444(2), 139–158 (2005)
Imtiaz, M.; Rizwan, M.S.; Xiong, S.; Li, H.; Ashraf, M.; Shahzad, S.M.; Shahzad, M.; Rizwan, M.: Vanadium, recent advancements and research prospects. Environ. Int. 80, 79–88 (2015)
Gill, S.S.; Tuteja, N.: Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 48(12), 909–930 (2010)
Tang, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Yao, Y.; Ying, H.; Xiong, J.; Bai, J.: Production of cytidine 5′-diphosphorylcholine with high utilization of ATP by whole cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Bioresour. Technol. 101(22), 8807–8813 (2010)
IARC (International Agency for Research on Cancer): Cobalt in Hard Metals and Cobalt Sulfate, Gallium Arsenide, Indium Phosphide and Vanadium Pentoxide. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, vol. 86, pp. 1–294 (2006)
Mailhes, J.B.; Hilliard, C.; Fuseler, J.W.; London, S.N.: Vanadate, an inhibitor of tyrosine phosphatases, induced premature anaphase in oocytes and aneuploidy and polyploidy in mouse bone marrow cells. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 538(1), 101–107 (2003)
Ramirez, P.; Eastmond, D.A.; Laclette, J.P.; Ostrosky-Wegman, P.: Disruption of microtubule assembly and spindle formation as a mechanism for the induction of aneuploid cells by sodium arsenite and vanadium pentoxide. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 386(3), 291–298 (1997)
Evangelou, A.M.: Vanadium in cancer treatment. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 42(3), 249–265 (2002)
Rodríguez-Mercado, J.J.; Mateos-Nava, R.A.; Altamirano-Lozano, M.A.: DNA damage induction in human cells exposed to vanadium oxides in vitro. Toxicol. In Vitro 25(8), 1996–2002 (2011)
Shireen, F.; Nawaz, M.A.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Sohail, H.; Sun, J.Y.; Cao, H.S.; Huang, Y.; Bie, Z.: Boron: functions and approaches to enhance its availability in plants for sustainable agriculture. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19(7), 1856 (2018)
Camacho-Cristóbal, J.J.; Martín-Rejano, E.M.; Herrera-Rodríguez, M.B.; Navarro-Gochicoa, M.T.; Rexach, J.; González-Fontes, A.: Boron deficiency inhibits root cell elongation via an ethylene/auxin/ROS-dependent pathway in Arabidopsis seedlings. J. Exp. Bot. 66, 3831–3840 (2015)
Hänsch, R.; Mendel, R.R.: Physiological functions of mineral micronutrients (Cu, Zn, Mn, Fe, Ni, Mo, B, Cl). Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 12, 259–266 (2009)
Turkez, H.; Geyikoglu, F.; Tatar, A.; Keles, M.S.; Kaplan, İ.: The effects of some boron compounds against heavy metal toxicity in human blood. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 64(1–2), 93–101 (2012)
Erturk, F.A.; Agar, G.; Arslan, E.; Nardemir, G.; Sahin, Z.: Determination of genomic instability and DNA methylation effects of Cr on maize (Zea mays L.) using RAPD and CRED-RA analysis. Acta Physiol. Plant. 36(6), 1529–1537 (2014)
Nawaz, M.A.; Jiao, Y.; Chen, C.; Shireen, F.; Zheng, Z.; Imtiaz, M.; Huang, Y.: Melatonin pretreatment improves vanadium stress tolerance of watermelon seedlings by reducing vanadium concentration in the leaves and regulating melatonin biosynthesis and antioxidant-related gene expression. J. Plant Physiol. 220, 115–127 (2018)
Çatav, Ş.S.; Genç, T.O.; Oktay, M.K.; Küçükakyüz, K.: Effect of boron toxicity on oxidative stress and genotoxicity in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 100(4), 502–508 (2018)
Yildirim, N.; Agar, G.; Taspinar, M.S.; Turan, M.; Aydin, M.; Arslan, E.: Protective role of humic acids against dicamba-induced genotoxicity and DNA methylation in Phaseolus vulgaris L. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B Soil Plant Sci. 64, 141–148 (2014)
Imtiaz, M.; Tu, S.; Xie, Z.; Han, D.; Ashraf, M.; Rizwan, M.S.: Growth, V uptake, and antioxidant enzymes responses of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) genotypes under vanadium stress. Plant Soil 390(1–2), 17–27 (2015)
Goc, A.: Biological activity of vanadium compounds. Cent. Eur. J. Biol. 1(3), 314–332 (2006)
Gokul, A.; Cyster, L.F.; Keyster, M.: Efficient superoxide scavenging and metal immobilization in roots determines the level of tolerance to Vanadium stress in two contrasting Brassica napus genotypes. S. Afr. J. Bot. 119, 17–27 (2018)
Liu, F.; Grundke-Iqbal, I.; Iqbal, K.; Gong, C.X.: Contributions of protein phosphatases PP1, PP2A, PP2B and PP5 to the regulation of tau phosphorylation. Eur. J. Neurosci. 22(8), 1942–1950 (2005)
Pessoa, J.C.; Etcheverry, S.; Gambino, D.: Vanadium compounds in medicine. Coord. Chem. Rev. 301, 24–48 (2015)
Usende, I.L.; Alimba, C.G.; Emikpe, B.O.; Bakare, A.A.; Olopade, J.O.: Intraperitoneal sodium metavanadate exposure induced severe clinicopathological alterations, hepato-renal toxicity and cytogenotoxicity in African giant rats (Cricetomys gambianus, Waterhouse, 1840). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 25(26), 26383–26393 (2018)
Samira, M.; Mounira, T.; Kamel, K.; Yacoubi, M.T.; Ben Rhouma, K.; Sakly, M.; Tebourbi, O.: Hepatotoxicity of vanadyl sulfate in nondiabetic and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 96(11), 1076–1083 (2018)
Poschenrieder, C.; Gunsé, B.; Corrales, I.; Barceló, J.: A glance into aluminum toxicity and resistance in plants. Sci. Total Environ. 400(1–3), 356–368 (2008)
Yu, M.; Shen, R.; Liu, J.; Chen, R.; Xu, M.; Yong, Y.: The role of root border cells in aluminum resistance of pea (Pisum sativum) grown in mist culture. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 172, 528–534 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bakir, O., Agar, G. Ameliorating Effect of Boric Acid Against Vanadium Toxicity in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Arab J Sci Eng 45, 113–120 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-04109-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-04109-w