Abstract
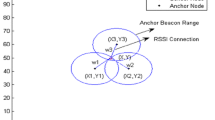
The aim of this paper is to propose a localization algorithm in which nodes are able to estimate their speeds, directions and motion types. By this way, node’s next state can be estimated and the particles can be distributed closer to the predicted locations. Hence, accuracy and the precision of the localization are increased considerably. Sequential Monte Carlo method is used to represent the posterior distribution of a node’s possible locations with a set of weighted samples. The developed algorithm is designed for a general network where no restrictions are made on the densities and the distributions of the nodes. Eight localization algorithms, namely Centroid, APIT, Amorphous, DV-Hop, MCL, SMCL, MCB and the developed algorithm SMCLA are implemented and compared for different parameters and mobility models. Simulation results show that the developed algorithm performs best for each of the simulation comparisons.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abusaimeh H., Shkoukani M., Alshrouf F.: Balancing the network clusters for the lifetime enhancement in dense wireless sensor networks. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 39(5), 3771–3779 (2014)
Zoghi M.R., Kahaei M.H.: Sensor management under tracking accuracy and energy constraints in wireless sensor networks. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 37(3), 721–734 (2012)
Doherty L., Pister K.S.J., El Ghaoui L.: Convex position estimation in wireless sensor networks. IEEE INFOCOM 3, 1655–1663 (2001)
Shang, Y.; Fromherz, M.P.J.; Ruml, W.; Zhang, Y.: Localization from mere connectivity. In: Proceedings of the International Symposium on Mobile Ad Hoc Networking and Computing, pp. 201–212 (2003)
Wellenho B.H., Lichtenegger H., Collins J.: Global Positioning System. Theory and Practice, 4th edn. Springer, Berlin (1997)
Bahl, P.; Padmanabhan, V.N.: RADAR: an in-building RF-based user location and tracking system. IEEE InfoCom, Mar (2000)
Patwari, N.; Hero, III, A.O.: Using proximity and quantized RSS for sensor localization in wireless networks. Workshop on Wireless Sensor Networks and Applications, Sept (2003)
Savvides, A.; Han, C.; Strivastava, M.B.: Dynamic fine grained localization in ad-hoc networks of sensors. MobiCom (2001)
Niculescu, D.; Nath, B.: Ad hoc positioning system (APS) using AoA. IEEE InfoCom (2003)
Bulusu, N.; Heidemann, J.; Estrin, D.: GPS-less low cost outdoor localization for very small devices. IEEE Personal Communications Magazine, Oct (2000)
He, T.; Huang, C.; Blum, B.M.; Stankovic, J.A.; Abdelzaher, T.: Range-free localization schemes for large scale sensor networks. MobiCom (2003)
Niculescu D., Nath B.: DV based positioning in ad hoc networks. J. Telecommun. Syst. 22, 267–280 (2003)
Nagpal, R.; Shrobe, H.; Bachrach, J.: Organizing a global coordinate system from local information on an ad hoc sensor network. In: 2nd International Workshop on Information Processing in Sensor Networks, Apr (2003)
Hu, L.; Evans, D.: Localization for mobile sensor networks. In: 10th International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, USA, pp. 45–57, Sept (2004)
Wang W., Zhu Q.: Sequential Monte Carlo localization in mobile sensor networks. Wirel. Netw. 15, 481–495 (2009)
Baggio, A.; Langendoen, K.: Monte Carlo localization for mobile wireless sensor networks. In: 2nd International Conference on Mobile Adhoc and Sensor Networks, Dec (2006)
Yang, Z.; Wang, X.: Joint mobility tracking and hard handoff in cellular networks via sequential Monte Carlo Filtering. IEEE INFOCOM, pp. 968–975 (2002)
Pourvoyeur, K.; Stelzer, A.; Gahleitner, T.; Schuster, S.; Gassenbauer, G.: Effects of motion models and sensor data on the accuracy of the LPM positioning system. In: 9th International Conference on Information Fusion, pp. 1–7 (2006)
Arulampalam S., Maskell S., Gordon N., Clapp T.: A tutorial on particle filters for on-line non-linear/non-Gaussian bayesian tracking. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 50, 174–188 (2001)
Yang N., Tian W., Jin Z.: An interacting multiple model particle filter for manoeuvring target location. Meas. Sci. Technol. 17, 1307–1311 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alaybeyoglu, A. An Efficient Monte Carlo-Based Localization Algorithm for Mobile Wireless Sensor Networks. Arab J Sci Eng 40, 1375–1384 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1614-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1614-0