Abstract
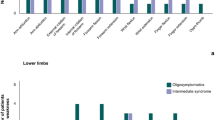
This was a cross-sectional prospective study. We performed a multivariate statistical analysis of the neurological signs and symptoms of patients infected with human T cell lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) in an attempt to separate them into distinct groups and identify clinical-neurological manifestations that could differentiate the various profiles. The study was performed in the city of Belém (state of Pará), located in the Amazon region of Brazil, from 2014 to 2016. We determined muscle strength and tone, reflexes, sensations, sphincter function, gait, and the Expanded Disability Status Scale score among individuals with HTLV-I. We then used exploratory statistical methods in an attempt to find different profiles and establish distinct groups. We analyzed 60 patients with HTLV-1. The filtering of the data, performed with mixed PCA, gave rise to a streamlined database with the most informative data and suggested the formation of three statistically distinct groups: asymptomatic carriers (AC), mono/oligosymptomatic (MOS), and HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSPd), AC and MOS (p = 0.002), AC and HAM/TSPd (p < 0.001), and HAM/TSPd and MOS (p = 0.001). The subsequent cluster analysis confirmed the formation of three clusters. The classification and regression tree demonstrated that altered gait was the most important variable for the classification of an individual with HAM/TSPd and that, in the absence of this impairment, hyperreflexia characterized MOS. The present study was able to separate patients infected by HTLV-1 into three clinical groups (AC, HAM/TSPd, and MOS) and identify clinical manifestations that could differentiate the various patient groups.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biswas HH, Engstrom JW, Kaidarova Z, Garratty G, Gibble JW, Newman BH, Smith JW, Ziman A, Fridey JL, Sacher RA, Murphy EL (2009) Neurologic abnormalities in HTLV-I- and HTLV-II-infected individuals without overt myelopathy. Neurology 73(10):781–789. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181b6bba9
Campbell WW, Dejong RN (2013) Dejong’s the neurologic examination, 7th edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Caskey MF, Morgan DJ, Porto AF, Giozza SP, Muniz AL, Orge GO, Travassos MJ, Barrón Y, Carvalho EM, Glesby MJ (2007) Clinical manifestations associated with HTLV type I infection: a cross-sectional study. AIDS Res Hum Retrovir 23(3):365–371
Champs AP, Passos VM, Barreto SM, Vaz LS, Ribas JG (2010) HTLV-1 associated myelopathy: clinical and epidemiological profile in a 10-year case series study. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop 43(6):668–672
De Castro-Costa CM, Araújo AQ, Barreto MM, Takayanagui OM, Sohler MP, da Silva EL, de Paula SM, Ishak R, Ribas JG, Rovirosa LC, Carton H, Gotuzzo E, Hall WW, Montano S, Murphy EL, Oger J, Remondegui C, Taylor GP (2006) Proposal for diagnostic criteria of tropical spastic paraparesis/HTLV-I-associated myelopathy (TSP/HAM). AIDS Res Hum Retrovir 22(10):931–935
Dias GA, Yoshikawa GT, Koyama RV, Fujihara S, Martins LC, Medeiros R, Quaresma JA, Fuzii HT (2016) Neurological manifestations in individuals with HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis in the Amazon. Spinal Cord 54(2):154–157. https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2015.112
Dray S, Dufour AB (2007) The ade4 package: implementing the duality diagram for ecologists. J Stat Softw 22(4):1–20
Franzoi AC, Araújo AQ (2007) Disability and determinants of gait performance in tropical spastic paraparesis/HTLV-I associated myelopathy (HAM/TSP). Spinal Cord 45(1):64–68
Gessain A, Barin F, Vernant JC, Gout O, Maurs L, Calender A, de Thé G (1985) Antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type-I in patients with tropical spastic paraparesis. Lancet 2(8452):407–410
Gotuzzo E, Cabrera J, Deza L, Verdonck K, Vandamme AM, Cairampoma R, Vizcarra D, Cabada M, Narvarte G, De las Casas C (2004) Clinical characteristics of patients in Peru with human T cell lymphotropic virus type 1-associated tropical spastic paraparesis. Clin Infect Dis 39(7):939–944
Hill MO, Smith AJE (1976) Principal component analysis of taxonomic data with multi-state discrete characters. Taxon. International Association for Plant Taxonomy (IAPT) 25:249–255
Holm S (1979) A simple sequentially rejective multiple test procedure. Scand J Stat 6:65–70
Hothorn T, Hornik K, Zeileis A (2006) Unbiased recursive partitioning: a conditional inference framework. J Computat and Graph Stat 15(3):651–674
Kaplan JE, Osame M, Kubota H, Igata A, Nishitani H, Maeda Y, Khabbaz RF, Janssen RS (1990) The risk of development of HTLV-I-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis among persons infected with HTLV-I. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 3(11):1096–1101
Kiers HAL (1991) Simple structure in component analysis techniques for mixtures of qualitative and quantitative variables. Psychometrika 56:197–212
Kurtzke JF (1983) Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: an expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology 33(11):1444–1452
MacCallum RC, Widaman KF, Preacher KJ, Hong S (2001) Sample size in factor analysis: the role of model error. Multivar Behav Res 36:611–637
Maechler M, Rousseeuw P, Struyf A, Hubert M, Hornik K (2016) cluster: cluster analysis basics and extensions. R package version 2.0.4
Mearin F, Lacy BE, Chang L, Chey WD, Lembo AJ, Simren M, Spiller R (2016) Bowel disorders. Gastroenterology S0016-5085(16):00222–00225. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2016.02.031
Medical Research Council of the United Kingdom (1978) Aids to examination of the peripheral nervous system: memorandum, no.45. Palo Alto, California: Pedragon House
Miyazaki M, Sakakima H, Goto T, Kiyama R, Matsuzaki T, Ijiri K, Yoshida Y (2011) Isokinetic trunk and knee muscle strengths and gait performance in walking patients with T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1-associated myelopathy/ tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP). J Jpn Phys Ther Assoc 14(1):19–26. https://doi.org/10.1298/jjpta.Vol14_003
Murphy EL, Fridey J, Smith JW, Engstrom J, Sacher RA, Miller K, Gibble J, Stevens J, Thomson R, Hansma D, Kaplan J, Khabbaz R, Nemo G (1997) HTLV-associated myelopathy in a cohort of HTLV-I and HTLV-II-infected blood donors. The REDS investigators. Neurology 48(2):315–320
Poetker SK, Porto AF, Giozza SP, Muniz AL, Caskey MF, Carvalho EM, Glesby MJ (2011) Clinical manifestations in individuals with recent diagnosis of HTLV type I infection. J Clin Virol 51(1):54–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcv.2011.02.004
R Core Team (2016) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. In: R Foundation for statistical computing. Austria. URL, Vienna https://www.R-project.org/
Sebastien L, Josse J, Husson F (2008) FactoMineR: an R package for multivariate analysis. J Stat Softw 25(1):1–18
Shoeibi A, Etemadi M, Moghaddam Ahmadi A, Amini M, Boostani R (2013) “HTLV-I infection” twenty-year research in Neurology Department of Mashhad University of Medical Sciences. Iran J Basic Med Sci 16(3):202–207
Slater CM, Ribeiro LC, Puccioni-Sohler M (2012) Difficulties in HAM/TSP diagnosis. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 70(9):686–690
Tanajura D, Castro N, Oliveira P, Neto A, Muniz A, Carvalho NB, Orge G, Santos S, Glesby MJ, Carvalho EM (2015) Neurological manifestations in human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1)-infected individuals without HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis: a longitudinal cohort study. Clin Infect Dis 61(1):49–56. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/civ229
Tinetti ME (1986) Performance-oriented assessment of mobility problems in elderly patients. J Am Geriatr Soc 34(2):119–126
Verdonck K, González E, Van Dooren S, Vandamme AM, Vanham G, Gotuzzo E (2007) Human T-lymphotropic virus 1: recent knowledge about an ancient infection. Lancet Infect Dis 7(4):266–281
World Health Organization. Regional Office for the Western Pacific. (1988). Scientific group on HTLV-I infections and associated diseases, Kagoshima, Japan 10–15 December 1988 : report. Manila: WHO Regional Office for Western Pacific
Funding
This work was supported by the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq number 457393/2014-9).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The local human research ethics committee approved the present study, and all participants signed a statement of informed consent.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koyama, R.V.L., Yoshikawa, G.T., Fujihara, S. et al. Incomplete myelopathy and human T cell lymphotropic virus type-1 (HTLV-1). J. Neurovirol. 25, 1–8 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13365-018-0677-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13365-018-0677-6