Abstract
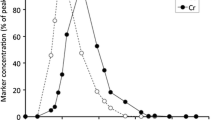
The time it takes for ingested seeds to pass through the gut of animals is an important aspect of endozoochorous seed dispersal because it influences seed dispersal distance. Variations in the physical characteristics of seeds, such as their weight, volume, and specific gravity, can affect their movement through the gastrointestinal system of a given animal. We conducted feeding experiments with captive Japanese martens, Martes melampus (n = 4), at Toyama Municipal Family Park Zoo, central Japan to examine the effects of the physical characteristics of seeds on their passage times. The mean (±SD) transit time, mean retention time, and time of last appearance of four different types of commercial seeds were 2.6 ± 0.3 h (range 0.6–5.4), 9.7 ± 1.1 h (3.8–17.3), and 23.8 ± 3.1 h (12.2–51.8), respectively. All of these values are greater than those found during previous experiments conducted with mustelids. Similar to previous studies, however, none of these passage time variables was correlated with the physical characteristics of seeds. Our results thus indicate that martens disperse seeds of different plant species, whose size, volume, and specific gravity all fall within the range of those used in the present study, from parent plants at similar distances.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arai S, Adachi T, Kuwahara Y, Yoshida K (2003) Food habit of the Japanese marten (Martes melampus) at Kuju Highland in Kyushu, Japan. Honyurui Kagaku 43:19–28 [In Japanese with English summary]
Garber PA (1986) The ecology of seed dispersal in two species of Callitrichidae primates (Saguinus mystax and Saguinus fuscicollis). Am J Primatol 10:155–170
Graae BJ, Pagh S, Bruun HH (2004) An experimental evaluation of the arctic fox (Alopex lagopus) as a seed disperser. Arct Antarct Alpine Res 36:468–473
Hickey JR, Flynn RW, Buskirk SW, Gerow KG, Willson MF (1999) An evaluation of a mammalian predator, Martes americana, as a disperser of seeds. Oikos 87:499–508
Julliot C (1996) Seed dispersal by red howling monkeys (Alouatta seniculus) in the tropical rain forest of French Guiana. Int J Primatol 17:239–258
Kawauchi N, Yamamoto Y, Imai K (2003) Annual changes in testicular size, plasma testosterone concentration, home range and active time in wild male marten, Martes melampus melampus. Honyurui Kagaku 43:93–98 [In Japanese with English summary]
Koike S, Masaki T (2008) Frugivory of carnivora in central and southern part of Japan analyzed by literature search. Nihon Shinrin Gakkaishi 90:26–35 [In Japanese with English summary]
Koike S, Morimoto H, Goto Y, Kozakai C, Yamazaki K (2008) Frugivory of carnivores and seed dispersal of fleshy fruits in cool-temperate deciduous forests. J For Res 13:215–222
Kusui H, Kusui Y (1998) Food habits of the Japanese marten, Martes melampus (Wagner, 1840) in Mt. Yamato-Katsuragi (2) studies of year to year variation. Kii Hantou No Yasei Doubutsu 4:13–19 [In Japanese]
Lambert JE (2002) Digestive retention times in forest guenons (Cercopithecus spp.) with reference to chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes). Int J Primatol 23:1169–1185
Leavy DJ, Grajal A (1991) Evolutionary implications of fruit-processing limitation in cedar wax wings. Am Nat 138:171–189
Okumura T, Kitahara M (2006) Food habits and home range of sympatric red fox and martens in north foot of Mt. Fuji: a preliminary report. Wildl Forum 10:99–100 [In Japanese]
Otani T (2002) Seed dispersal by Japanese marten Martes melampus in the subalpine shrubland of northern Japan. Eco1ogical Research 17:29–38
Pollux BJA, Ouborg NJ, van Groenendael JM, Klaassen M (2007) Consequences of intraspecific seed-size variation in Sparganium emersum for dispersal by fish. Funct Ecol 21:1084–1091
R Development Core Team (2009) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Version 2.9.1. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Rosalino LM, Santos-Reis M (2009) Fruit consumption by carnivores in Mediterranean Europe. Mamm Rev 39:67–78
Rosalino LM, Rosa S, Santos-Reis M (2010) The role of carnivores as Mediterranean seed dispersers. Ann Zoologici Fennici 47:195–205
Schaumann F, Heinken T (2002) Endozoochorous seed dispersal by martens (Martes foina, M. martes) in two woodland habitats. Flora 197:370–378
Traveset A (1998) Effect of seed passage through vertebrate frugivores' guts on germination: a review. Perspectives in plant ecology. Evol Syst 1(2):151–190
Tsuji Y, Morimoto M, Matsubayashi K (2010) Effects of the physical characteristics of seeds on gastrointestinal passage time in captive Japanese macaques. J Zool 280:171–176
Tsuji Y, Tatewaki T, Kanda E (2011) Endozoochorous seed dispersal by sympatric mustelids, Martes melampus and Mustela itatsi, in western Tokyo, central Japan. Mammalian Biology (in press)
Varela O, Bucher EH (2006) Passage time, viability, and germination of seeds ingested by foxes. J Arid Environ 67:566–578
Wilson MF (1989) Gut retention times of experimental pseudoseeds by emus. Biotropica 21:210–213
Zalewski A, Jedrzejewski W, Jedrzejewska B (2004) Mobility and home range use by pine martens (Martes martes) in a Polish primeval forest. Ecoscience 11:113–122
Zalewski A, Jedrzejewski W (2006) Spatial organization and dynamics of the pine marten Martes martes population in Białowieża Forest (E Polen) compared with other European woodlands. Ecography 29:31–43
Zhou YB, Slade E, Newman C, Wang XM, Zhang SY (2008a) Frugivory and seed dispersal by the yellow-throated marten, Martes flavigula, in a subtropical forest of China. J Trop Ecol 24:219–223
Zhou YB, Zhang L, Kaneko Y, Newman C, Wang X (2008b) Frugivory and seed dispersal by a small carnivore, the Chinese ferret-badger, Melogale moschata, in a fragmented subtropical forest of central China. For Ecol Manage 255:1595–1603
Acknowledgements
We thank all staff at the Toyama Municipal Family Park Zoo, especially H. Murai, M. Horiuchi, and Y. Ishihara, for their cooperation in our feeding experiments. We are grateful to M.A. Huffman and A.J.J. McIntosh and three anonymous reviewers for proofreading and generally improving this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: Jan M. Wójcik
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsuji, Y., Shiraishi, T. & Miura, S. Gastrointestinal passage time of seeds ingested by captive Japanese martens Martes melampus . Acta Theriol 56, 353–357 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13364-011-0034-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13364-011-0034-0