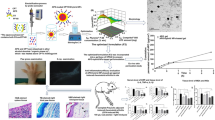
Abstract
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a common immune disease characterized mainly by erosive arthritis with extensive clinical sequelae. Resveratrol (Res) has pharmacological effects in the treatment of RA, but it has not been widely used in the clinic due to its poor water solubility and low bioavailability. In this study, a drug delivery system (Res-NC MNs) of dissolved microneedles (MNs) loaded with Res nanocrystals (NC) was designed for the treatment of RA. Res-NC MNs can improve the drawbacks of long-term oral drug delivery with toxic side effects and low compliance associated with intra-articular drug delivery. In this study, Res-NC was prepared by media milling and loaded into soluble microneedles prepared from hyaluronic acid (HA) by vacuum casting for the treatment of RA. HA has high mechanical strength and can penetrate the cuticle layer of the skin for effective drug delivery. In in vivo pharmacodynamic experiments, Res-NC MNs achieved better therapeutic efficacy in the treatment of RA compared with oral Res. These findings suggest that Res-NC MNs may be an effective and promising drug delivery strategy for the treatment of RA.
Graphical Abstract

Schematic diagram of resveratrol nanocrystals microneedles for rheumatoid arthritis







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Neither the entire paper nor any part of its content has been published or has been accepted elsewhere. It is not being submitted to any other journal. Hope this study can be suitable for the journal.
References
Alivernini S, Firestein GS, McInnes IB. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Immunity. 2022;55:2255–70.
Zaiss MM, Joyce Wu H-J, Mauro D, Schett G, Ciccia F. The gut–joint axis in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021;17:224–37.
Scherer HU, Häupl T, Burmester GR. The etiology of rheumatoid arthritis. J Autoimmun. 2020;110:102400.
Adawi M, Watad A, Bragazzi NL, Amital H, Saaida G, Sirchan R, Blum A. Endothelial function in rheumatoid arthritis. QJM: Int J Med. 2018;111:243–7.
Brock J, Basu N, Schlachetzki JCM, Schett G, McInnes IB, Cavanagh J. Immune mechanisms of depression in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2023;19:790–804.
van Delft MA, Huizinga TW. An overview of autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. J Autoimmun. 2020;110:102392.
Weyand CM, Goronzy JJ. The immunology of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Immunol. 2021;22:10–8.
McInnes IB, Schett G. Pathogenetic insights from the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2017;389:2328–37.
Wang J, Zeng J, Liu Z, Zhou Q, Wang X, Zhao F, Zhang Y, Wang J, Liu M, Du R. Promising strategies for Transdermal Delivery of Arthritis drugs. Microneedle Systems; 2022. p. 14.
Chen K, Zhao Y, Zhao W, Mao X, Li D, Wang Y, Shang S, Zhang H. Lubricating Microneedles System with Multistage Sustained Drug Delivery for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis, Small, (2024) e2307281.
Wang Q, Yang X, Gu X, Wei F, Cao W, Zheng L, Li Y, Ma T, Wu C, Wang Q. Celecoxib Nanocrystal-loaded dissolving microneedles with highly efficient for osteoarthritis treatment. Int J Pharm. 2022;625:122108.
Cao J, Su J, An M, Yang Y, Zhang Y, Zuo J, Zhang N, Zhao Y. Novel DEK-Targeting Aptamer delivered by a Hydrogel Microneedle attenuates Collagen-Induced Arthritis. Mol Pharm. 2021;18:305–16.
Yu K, Yu X, Cao S, Wang Y, Zhai Y, Yang F, Yang X, Lu Y, Wu C, Xu Y. Layered dissolving microneedles as a need-based delivery system to simultaneously alleviate skin and joint lesions in psoriatic arthritis. Acta Pharm Sinica B. 2021;11:505–19.
Rajendran K, Pahal S, Badnikar K, Nayak MM, Subramanyam DN, Vemula PK, Krishnan UM. Methotrexate delivering microneedle patches for improved therapeutic efficacy in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Pharm. 2023;642:123184.
Xie J, Zhu X, Wang M, Liu C, Ling G, Zhang P. Dissolving microneedle-mediated transdermal delivery of flurbiprofen axetil-loaded pH-responsive liposomes for arthritis treatment. Chem Eng J. 2024;482:148840.
Du G, He P, Zhao J, He C, Jiang M, Zhang Z, Zhang Z, Sun X. Polymeric microneedle-mediated transdermal delivery of melittin for rheumatoid arthritis treatment. J Controlled Release. 2021;336:537–48.
Oh WY, Shahidi F. Lipophilization of Resveratrol and effects on antioxidant activities. J Agric Food Chem. 2017;65:8617–25.
Pang Q, Wang C, Li B, Zhang S, Li J, Gu S, Shi X. Resveratrol-loaded copolymer nanoparticles with anti-neurological impairment, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities against cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury. Arab J Chem. 2024;17:105393.
Hu LF, Lan HR, Li XM, Jin KT. A Systematic Review of the Potential Chemoprotective Effects of Resveratrol on Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity: Focus on the Antioxidant, Antiapoptotic, and Anti-Inflammatory Activities, Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2021 (2021) 2951697.
Li W, Yuan H, Liu Y, Wang B, Xu X, Xu X, Hussain D, Ma L, Chen D. Current analytical strategies for the determination of resveratrol in foods. Food Chem. 2024;431:137182.
Zhang X, Li Z, Gao J, Wang Z, Gao X, Liu N, Li M, Zhang H, Zheng A. Preparation of nanocrystals for Insoluble drugs by top-down nanotechnology with improved solubility and bioavailability. Molecules; 2020. p. 25.
Zheng Y, Wang Y, Xia M, Gao Y, Zhang L, Song Y, Zhang C. The combination of nanotechnology and traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) inspires the modernization of TCM: review on nanotechnology in TCM-based drug delivery systems. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2022;12:1306–25.
Colombo M, Staufenbiel S, Rühl E, Bodmeier R. In situ determination of the saturation solubility of nanocrystals of poorly soluble drugs for dermal application. Int J Pharm. 2017;521:156–66.
Pang Z, Zhang J, Cao W, Kong X, Peng X. Partitioning surface ligands on nanocrystals for maximal solubility. Nat Commun. 2019;10:2454.
Funding
All authors acknowledge financial support from Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No. ZR2019ZD24, ZR2019YQ30); Taishan Scholar Foundation of Shandong Province (No. qnts20161035); Graduate Innovation Foundation of Yantai University, GIFYTU.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ningning Diao: Contributed to the conception of the study, experimented. Yan Liu: Revised the manuscript. Wenxin Wang and Min Cao: Visualization, Data curation. Xiaowei Liu and Weili Yang: Visualization, Data curation. Tianying Sun and Huijie Pei: Performed the data analyses and wrote the manuscript. Chunjing Guo: Helped perform the analysis with constructive discussions. Daquan Chen: Conceptualization, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing-review & editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All experiments were conducted by the ARRIVE Guidelines and were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Yantai University (Ethical Annotation License Number: YTU20220923). Male Sprague-Dawley rats (180 ∼ 200 g) were purchased from Jinan Pengyue Experimental Animal Breeding Co., Ltd. (Shandong, China). All animals have free access to food and water and are housed at a temperature of 22 ± 1℃, relative humidity of 50 ± 1%, and a light/dark cycle of 12/12 h. Before administration, the rats were anesthetized with intra-peritoneal injection of anesthetics (80 mg/kg ketamine and 4.5 mg/kg xylazine) while monitoring body temperature with a feedback-conditioned heating pad. Rats were euthanized by intraperitoneal injection of excessive pentobarbital sodium. The study does not involve human subjects.
Consent for publication
All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Competing interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Diao, N., Liu, Y., Wang, W. et al. Resveratrol nanocrystals based dissolving microneedles with highly efficient for rheumatoid arthritis. Drug Deliv. and Transl. Res. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-024-01581-2
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-024-01581-2