Abstract
The utilization of minimally invasive distal pancreatectomy (MIDP) is increasing, yet debate remains regarding its oncologic safety in the setting of pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Herein we present our institutional experience with robotic (RDP), laparoscopic (LDP), and open distal pancreatectomy (ODP) in the setting of PDAC.
Retrospective review of a prospectively collected single institutional database of patients undergoing consecutive ODP, LDP, and RDP for left-sided PDAC between January 2008 and December 2019 at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center (UPMC) was done. Perioperative and postoperative outcomes were compared using non-parametric testing and Fischer exact or chi-squared testing. Kaplan–Meier survival curves for disease-free survival and overall survival were compared by Log-Rank sum test. Backward Cox-proportional hazard regression analysis was used to determine if the operative approach was an independent predictor of recurrence and overall survival.
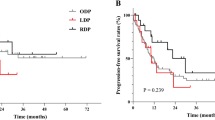
Over 12 years, 146 consecutive distal pancreatectomies for PDAC were performed, of which 28.1% ODP, 60.3% RDP, and 11.6% LDP. There were no statistical differences in patients’ baseline characteristics, including gender, comorbidities, prior abdominal surgeries, and AJCC8th stage (p > 0.05). Postoperatively, there was no difference in the frequency of major complications (p = 0.414), CR-POPF (p = 0.563), or DGE (p = 0.179). The median overall survival was 28.4 months for ODP, 34.6 months for RDP, and 32.5 months for LDP (Log Rank p = 0.914). On multivariate Cox proportional hazard analysis, the surgical approach was not associated with overall survival. This comparative analysis suggests a non-inferiority of RDP platforms, compared to LDP and classic ODP. The merits of MIS pancreatic surgery in the setting of PDAC should be evaluated in future prospective studies with care to analyze RDP outcomes separately from LDP.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Melvin WS, Needleman BJ, Krause KR, Ellison EC (2003) Robotic resection of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech 13:33–36
Giulianotti PC et al (2003) Robotics in general surgery: personal experience in a large community hospital. Arch Surg-chicago 138:777
Shakir M et al (2015) The learning curve for robotic distal pancreatectomy: an analysis of outcomes of the first 100 consecutive cases at a high-volume pancreatic centre. HPB (Oxford) 17:580–586
Nassour I et al (2020) Long-term oncologic outcomes of robotic and open pancreatectomy in a national cohort of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Surg Oncol 122:234–242
van Hilst J et al (2019a) Minimally invasive versus open distal pancreatectomy for Ductal Adenocarcinoma (DIPLOMA). Ann Surg 269:10–17
Guerrini GP et al (2017) Robotic versus laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy: an up-to-date meta-analysis. Bmc Surg 17:105
Gavriilidis P, Roberts KJ, Sutcliffe RP (2019) Comparison of robotic vs laparoscopic vs open distal pancreatectomy. A systematic review and network meta-analysis. HPB (Oxford) 21:1268–1276
Alfieri S et al (2019) Full robotic distal pancreatectomy: safety and feasibility analysis of a multicenter cohort of 236 patients. Surg Innov 27:11–18
van Hilst J et al (2019b) Oncologic outcomes of minimally invasive versus open distal pancreatectomy for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Surg Oncol 45:719–727
Pericleous S, Middleton N, McKay SC, Bowers KA, Hutchins RR (2012) Systematic review and meta-analysis of case-matched studies comparing open and laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy: is it a safe procedure? Pancreas 41:993–1000
Zhou J et al (2020) Up-to-date comparison of robotic-assisted versus open distal pancreatectomy: a PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis. Medicine 99:e20435
Chun YS, Pawlik TM, Vauthey J-N (2017) 8th Edition of the AJCC cancer staging manual: pancreas and hepatobiliary cancers. Ann Surg Oncol 25:845–847
van Hilst J et al (2019c) Costs and quality of life in a randomized trial comparing minimally invasive and open distal pancreatectomy (LEOPARD trial). Bjs 106:910–921
de Rooij T et al (2019) Minimally invasive versus open distal pancreatectomy (LEOPARD). Ann Surg 269:2–9
Daouadi M et al (2013) Robot-assisted minimally invasive distal pancreatectomy is superior to the laparoscopic technique. Ann Surg 257:128–132
Magge D et al (2013) Comparative effectiveness of minimally invasive and open distal pancreatectomy for ductal adenocarcinoma. JAMA surgery 148:525–527
Magge DR et al (2018) Comprehensive comparative analysis of cost-effectiveness and perioperative outcomes between open, laparoscopic, and robotic distal pancreatectomy. Hpb 20:1172–1180
Nassour I et al (2017) Conversion of minimally invasive distal pancreatectomy: predictors and outcomes. Ann Surg Oncol 24:3725–3731
Klompmaker S et al (2019) Outcomes and risk score for distal pancreatectomy with celiac axis resection (DP-CAR): an international multicenter analysis. Ann Surg Oncol 26:772–781
Ocuin LM et al (2016) Robotic and open distal pancreatectomy with celiac axis resection for locally advanced pancreatic body tumors: a single institutional assessment of perioperative outcomes and survival. Hpb 18:835–842
Greer J, Zureikat AH (2017) Robotic distal pancreatectomy combined with celiac axis resection. J Vis Surg 3:145–145
Lof S et al (2019) Impact of neoadjuvant therapy in resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreatic body or tail on surgical and oncological outcome: a propensity-score matched multicenter study. Ann Surg Oncol 57:1–11
Wu W et al (2014) The impact of postoperative complications on the administration of adjuvant therapy following pancreaticoduodenectomy for adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 21:2873–2881
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally to the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human rights
Retrospective chart reviews qualify for “exempt” status under human subjects regulations.
Informed consent
Consent requirement was waived as this was a retrospective chart review study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chopra, A., Nassour, I., Zureikat, A. et al. Perioperative and oncologic outcomes of open, laparoscopic, and robotic distal pancreatectomy for pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Updates Surg 73, 947–953 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13304-020-00927-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13304-020-00927-y