Abstract
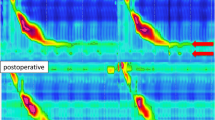
Identifying and treating patients with extra-esophageal symptoms is a challenge. When the patient is unable to control his symptoms with pharmacological therapy alone, anti-reflux surgery may be indicated. This study aims to evaluate the outcomes of total fundoplication in the resolution of extra-esophageal manifestations and verify changes in 24-h MII-pH monitoring before and after surgery. From October 2005 to October 2010, patients who reported respiratory symptoms, possibly related to GERD, have been sent to our Institute. All patients were practiced ambulatory 24-h MII-pH before and after surgery. Thirty-five patients selected for the antireflux surgery have undergone all the same surgical procedures. Data were collected prospectively at 6 and 12 months after laparoscopic fundoplication. After laparoscopic fundoplication, the total percentage of exposure time with esophageal pH < 4, and both in upright and supine position was very low. A statistically significant difference (p < 0.05) was found in the number of detected refluxes at MII and detected refluxes at MII 15-cm segment in pre and post-operative period. Symptom relief was obtained in all patients. Laparoscopic fundoplication is a safe and effective procedure to protect from refractory GERD and extra-esophageal symptoms, when evaluated with a thorough pre-operative selection.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GERD:
-
Gastro-esophageal reflux disease
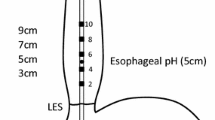
- MII-pH:
-
Combined multichannel intraluminal pH monitoring
- LES:
-
Lower esophageal sphincter
- LNRF:
-
Laparoscopic Nissen–Rossetti fundoplication
References
Watson MG (2011) Review article: laryngopharyngeal reflux—the ear, nose and throat patient. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 33(Suppl 1):53–57
Harding SM (2011) Review article: reflux and asthma—mechanisms of interaction and asthma outcomes. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 33(Suppl 1):42–47
Morice AH (2011) Review article: reflux in cough and airway disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 33(Suppl 1):48–52
Pauwels A, Blondeau K, Dupont L et al (2009) Cough and gastroesophageal reflux: from the gastroenterologist end. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 22:135–138
Patterson N, Mainie I, Rafferty G et al (2009) Nonacid reflux episodes reaching the pharynx are important factors associated with cough. J Clin Gastroenterol 43:414–419
Spechler SJ, Castell DO (2001) Classification of oesophageal motility abnormalities. Gut 49:145–151
Sifrim D, Castell D, Dent J et al (2004) Gastro-esophageal reflux monitoring: review and consensus report on detection and definitions of acid, non-acid, and gas reflux. Gut 53:1024–1031
Del Genio G, Rossetti G, Brusciano L et al (2007) Laparoscopic Nissen–Rossetti fundoplication with routine use of intraoperative endoscopy and manometry: technical aspects of a standardized technique. World J Surg 31:1099–1106
Vakil N, van Zanten S, Kahrilas P et al (2006) The Montreal Definition and Classification of Gastresophageal Reflux Disease: a global evidence-based consensus. Am J Gastroenterol 101:1900–1920
Fass R, Achem SR, Harding S et al (2004) Extra-esophageal manifestations of gastro-esophageal reflux disease and the role of night-time gastro-esophageal reflux. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 20(Suppl 9):26–38
Koufman JA (1991) The otolaryngologic manifestations of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): a clinical investigation of 225 patients using ambulatory 24-hour pH monitoring and an experimental investigation of the role of acid and pepsin in the development of laryngeal injury. Laryngoscope 101(Suppl 53):1–78
Maldonado A, Diederich L, Castell DO et al (2003) Laryngopharyngeal reflux identified using a new catheter design: defining normal values and excluding artifacts. Laryngoscope 113:349–355
Katz PO (1990) Ambulatory esophageal and hypopharyngeal pH monitoring in patients with hoarseness. Am J Gastroenterol 85:38–40
Mainie I, Tutuian R, Shay S et al (2006) Acid and non-acid reflux in patients with persistent symptoms despite acid suppressive therapy: a multicenter study using combined ambulatory impedance-pH monitoring. Gut 55:1398–1402
Williams RB, Szczesniak MM, Maclean JC et al (2004) Predictors of outcome in an open label, therapeutic trial of high-dose omeprazole in laryngitis. Am J Gastroenterol 99:777–785
El-Serag HB, Lee P, Buchner A et al (2001) Lansoprazole treatment of patients with chronic idiopathic laryngitis: a placebo-controlled trial. Am J Gastroenterol 96:979–983
DeMeester TR, Bonavina L, Iascone C et al (1990) Chronic respiratory symptoms and occult gastroesophageal reflux: a prospective clinical study and results of surgical therapy. Ann Surg 211:337–345
Chen RY, Thomas RJ (2000) Results of laparoscopic fundoplication where atypical symptoms coexist with oesophageal reflux. Aust NZ J Surg 70:840–842
Lindstrom DR, Wallace J, Loehrl TA et al (2002) Nissen fundoplication surgery for extraesophageal manifestations of gastroesophageal reflux (EER). Laryngoscope 112:1762–1765
Oelschlager BK, Eubanks TR, Oleynikov D et al (2002) Symptomatic and physiologic outcomes after operative treatment for extraesophageal reflux. Surg Endosc 16:1032–1036
del Genio G, Tolone S, del Genio F et al (2008) Prospective assessment of patient selection for antireflux surgery by combined multichannel intraluminal impedance pH monitoring. J Gastrointest Surg 12:1491–1496
del Genio G, Tolone S, del Genio F et al (2008) Total fundoplication controls acid and non acid reflux: evaluation by pre- and postoperative 24-hour pH-multichannel intraluminal impedance. Surg Endosc 22:2518–2523
del Genio G, Tolone S, Rossetti G et al (2008) Objective assessment of gastroesophageal reflux after extended Heller myotomy and total fundoplication for achalasia with the use of 24-hour combined multichannel intraluminal impedance and pH monitoring (MII-pH). Dis Esophagus 21:664–667
Mainie I, Tutuian R, Agrawal A et al (2006) Combined multichannel intraluminal impedance-pH monitoring to select patients with persistent gastro-oesophageal reflux for laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. Br J Surg 93:1483–1487
del Genio G, Tolone S, del Genio F et al (2012) Impact of total fundoplication on esophageal transit: analysis by combined multichannel intraluminal impedance and manometry. J Clin Gastroenterol 46:e1–e5
Acknowledgments
This work is independent of any funding or grant support.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tolone, S., del Genio, G., Docimo, G. et al. Objective outcomes of extra-esophageal symptoms following laparoscopic total fundoplication by means of combined multichannel intraluminal impedance pH-metry before and after surgery. Updates Surg 64, 265–271 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13304-012-0171-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13304-012-0171-2