Abstract
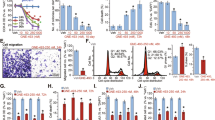
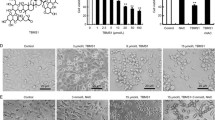
GW501516 is a selective and high-affinity synthetic agonist of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor β/δ (PPARβ/δ). This molecule promoted the inhibition of proliferation and apoptosis in few cancer cell lines, but its anticancer action has never been investigated in bladder tumor cells. Thus, this study was undertaken to determine whether GW501516 had antiproliferative and/or apoptotic effects on RT4 and T24 urothelial cancer cells and to explore the molecular mechanisms involved. Our results indicated that, in RT4 cells (derived from a low-grade papillary tumor), GW501516 did not induce cell death. On the other hand, in T24 cells (derived from an undifferentiated high-grade carcinoma), this PPARβ/δ agonist induced cytotoxic effects including cell morphological changes, a decrease of cell viability, a G2/M cell cycle arrest, and the cell death as evidenced by the increase of the sub-G1 cell population. Furthermore, GW501516 triggered T24 cell apoptosis in a caspase-dependent manner including both extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic pathways through Bid cleavage. In addition, the drug led to an increase of the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio, a mitochondrial dysfunction associated with the dissipation of ΔΨm, and the release of cytochrome c from the mitochondria to the cytosol. GW501516 induced also ROS generation which was not responsible for T24 cell death since NAC did not rescue cells upon PPARβ/δ agonist exposure. For the first time, our data highlight the capacity of GW501516 to induce apoptosis in invasive bladder cancer cells. This molecule could be relevant as a therapeutic drug for high-grade urothelial cancers.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee R, Droller MJ. The natural history of bladder cancer. Implications for therapy. Urol Clin North Am. 2000;27:1–13.
Epstein JI, Amin MB, Reuter VR, Mostofi FK. The World Health Organization/International Society of Urological Pathology consensus classification of urothelial (transitional cell) neoplasms of the urinary bladder. Bladder Consensus Conference Committee. Am J Surg Pathol. 1998;22:1435–48.
Kliewer SA, Umesono K, Noonan DJ, Heyman RA, Evans RM. Convergence of 9-cis retinoic acid and peroxisome proliferator signalling pathways through heterodimer formation of their receptors. Nature. 1992;358:771–4.
Peters JM, Gonzalez FJ. Sorting out the functional role(s) of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor beta/delta (PPARbeta/delta) in cell proliferation and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1796:230–41.
Peters JM, Gonzalez FJ, Müller R. Establishing the role of PPARβ/δ in carcinogenesis. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2015;26:595–607.
Hwang JS, Eun SY, Ham SA, Yoo T, Lee WJ, Paek KS, Do JT, Lim DS, Seo HG. PPARδ modulates oxLDL-induced apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells through a TGF-β/FAK signaling axis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015;62:54–61.
Zhu D, Wang J, Sun X, Chen J, Duan Y, Pan J, Xu T, Qin Y, He X, Huang C. Septin4_i1 regulates apoptosis in hepatic stellate cells through peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ/Akt/B-cell lymphoma 2 pathway. J Histochem Cytochem. 2015;63:163–9.
Yang Y, Tong Y, Gong M, Lu Y, Wang C, Zhou M, Yang Q, Mao T, Tong N. Activation of PPARβ/δ protects pancreatic β cells from palmitate-induced apoptosis by upregulating the expression of GLP-1 receptor. Cell Signal. 2014;26:268–78.
Wang D, Ning W, Xie D, Guo L, DuBois RN. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor δ confers resistance to peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ-induced apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells. Oncogene. 2012;31:1013–23.
Tong Q, Wu L, Gao Q, Ou Z, Zhu D, Zhang Y. PPARβ/δ agonist provides neuroprotection by suppression of IRE1α-caspase-12-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway in the rotenone rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Mol Neurobiol. 2015. doi:10.1007/s12035-015-9309-9.
Ma JJ, Monsivais D, Dyson MT, Coon JS, Malpani S, Ono M, Zhao H, Xin H, Pavone ME, Kim JJ, Chakravarti D, Bulun SE. Ligand-activated peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor β/δ modulates human endometrial cancer cell survival. Horm Cancer. 2013;4:358–70.
Foreman JE, Sharma AK, Amin S, Gonzalez FJ, Peters JM. Ligand activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-beta/delta (PPARbeta/delta) inhibits cell growth in a mouse mammary gland cancer cell line. Cancer Lett. 2010;288:219–25.
Nicolier M, Decrion-Barthod AZ, Launay S, Prétet JL, Mougin C. Spatiotemporal activation of caspase-dependent and -independent pathways in staurosporine-induced apoptosis of p53wt and p53mt human cervical carcinoma cells. Biol Cell. 2009;101:455–67.
Plissonnier ML, Fauconnet S, Bittard H, Lascombe I. The antidiabetic drug ciglitazone induces high grade bladder cancer cells apoptosis through the up-regulation of TRAIL. PLoS One. 2011;6:e28354.
Liou GY, Storz P. Reactive oxygen species in cancer. Free Radic Res. 2010;44:479–96.
Leliveld AM, Bastiaannet E, Doornweerd BH, Schaapveld M, de Jong IJ. High risk bladder cancer: current management and survival. Int Braz J Urol. 2011;37:203–10.
Sprecher DL, Massien C, Pearce G, Billin AN, Perlstein I, Willson TM, Hassall DG, Ancellin N, Patterson SD, Lobe DC, Johnson TG. Triglyceride: high-density lipoprotein cholesterol effects in healthy subjects administered a peroxisome proliferator activated receptor delta agonist. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007;27:359–65.
Risérus U, Sprecher D, Johnson T, Olson E, Hirschberg S, Liu A, Fang Z, Hegde P, Richards D, Sarov-Blat L, Strum JC, Basu S, Cheeseman J, Fielding BA, Humphreys SM, Danoff T, Moore NR, Murgatroyd P, O’Rahilly S, Sutton P, Willson T, Hassall D, Frayn KN, Karpe F. Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)delta promotes reversal of multiple metabolic abnormalities, reduces oxidative stress, and increases fatty acid oxidation in moderately obese men. Diabetes. 2008;57:332–9.
Ooi EM, Watts GF, Sprecher DL, Chan DC, Barrett PH. Mechanism of action of a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-delta agonist on lipoprotein metabolism in dyslipidemic subjects with central obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96:1568–76.
Olson EJ, Pearce GL, Jones NP, Sprecher DL. Lipid effects of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta agonist GW501516 in subjects with low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol: characteristics of metabolic syndrome. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012;32:2289–94.
Boulaire J, Fotedar A, Fotedar R. The functions of the cdk-cyclin kinase inhibitor p21WAF1. Pathol Biol (Paris). 2000;48:190–202.
el-Deiry WS, Tokino T, Velculescu VE, Levy DB, Parsons R, Trent JM, Lin D, Mercer WE, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell. 1993;75:817–25.
Gartel AL, Tyner AL. Transcriptional regulation of the p21((WAF1/CIP1)) gene. Exp Cell Res. 1999;246:280–9.
Zhu HB, Yang K, Xie YQ, Lin YW, Mao QQ, Xie LP. Silencing of mutant p53 by siRNA induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human bladder cancer cells. World J Surg Oncol. 2013;11:–22.
Jesenberger V, Jentsch S. Deadly encounter: ubiquitin meets apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3:112–21.
Wang J, Zhao Q, Qi Q, Gu HY, Rong JJ, Mu R, Zou MJ, Tao L, You QD, Guo QL. Gambogic acid-induced degradation of mutant p53 is mediated by proteasome and related to CHIP. J Cell Biochem. 2011;112:509–19.
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Brenner C. Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization in cell death. Physiol Rev. 2007;87:99–163.
Wei MC, Zong WX, Cheng EH, Lindsten T, Panoutsakopoulou V, Ross AJ, Roth KA, MacGregor GR, Thompson CB, Korsmeyer SJ. Proapoptotic BAX and BAK: a requisite gateway to mitochondrial dysfunction and death. Science. 2001;292:727–30.
Maillet A, Yadav S, Loo YL, Sachaphibulkij K, Pervaiz S. A novel osmium-based compound targets the mitochondria and triggers ROS-dependent apoptosis in colon carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4:e653.
Afanas’ev I. Reactive oxygen species signaling in cancer: comparison with aging. Aging Dis. 2011;2:219–30.
Yoo T, Ham SA, Hwang JS, Lee WJ, Paek KS, Oh JW, Kim JH, Do JT, Han CW, Kim JH, Seo HG. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor δ inhibits Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide-induced activation of matrix metalloproteinase-2 by downregulating NADPH oxidase 4 in human gingival fibroblasts. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2015. doi:10.1111/omi.12137.
Lee H, Ham SA, Kim MY, Kim JH, Paek KS, Kang ES, Kim HJ, Hwang JS, Yoo T, Park C, Kim JH, Lim DS, Han CW, Seo HG. Activation of PPARδ counteracts angiotensin II-induced ROS generation by inhibiting rac1 translocation in vascular smooth muscle cells. Free Radic Res. 2012;46:912–9.
Ham SA, Hwang JS, Yoo T, Lee H, Kang ES, Park C, Oh JW, Lee HT, Min G, Kim JH, Seo HG. Ligand-activated PPARδ inhibits UVB-induced senescence of human keratinocytes via PTEN-mediated inhibition of superoxide production. Biochem J. 2012;444:27–38.
Kim HJ, Ham SA, Paek KS, Hwang JS, Jung SY, Kim MY, Jin H, Kang ES, Woo IS, Kim HJ, Lee JH, Chang KC, Han CW, Seo HG. Transcriptional up-regulation of antioxidant genes by PPARδ inhibits angiotensin II-induced premature senescence in vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;406:564–9.
Carnero A, Blanco-Aparicio C, Renner O, Link W, Leal JF. The PTEN/PI3K/AKT signalling pathway in cancer, therapeutic implications. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2008;8:187–98.
Rajesh K, Krishnamoorthy J, Kazimierczak U, Tenkerian C, Papadakis AI, Wang S, Huang S, Koromilas AE. Phosphorylation of the translation initiation factor eIF2α at serine 51 determines the cell fate decisions of Akt in response to oxidative stress. Cell Death Dis. 2015;6:e1591.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by research grants from the Ligue Nationale Contre le Cancer (CCIR-GE) and the LabEx LipSTIC. We thank Julie Frejaville for technical assistance and Virginie Mougey for her help for the flow cytometry analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Additional information
Adeline Péchery and Sylvie Fauconnet contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Péchery, A., Fauconnet, S., Bittard, H. et al. Apoptotic effect of the selective PPARβ/δ agonist GW501516 in invasive bladder cancer cells. Tumor Biol. 37, 14789–14802 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5305-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5305-6