Abstract
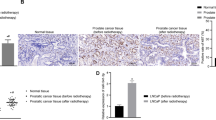
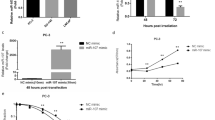
miR-449a, a novel tumor suppressor, is deregulated in various malignancies, including prostate cancer. Overexpression of miR-449a induces cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, and senescence, but its role in response to ionizing radiation and underlying molecular mechanism are still unknown. Here, we report that miR-449a enhances radiation-induced G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis through modulating pRb/E2F1 and sensitizes prostate cancer cells to X-ray radiation. In wild-type Rb PC-3 cells, overexpression of miR-449a enhances radiation-induced G2/M arrest and apoptosis and promotes the sensitivity to X-ray radiation. While mutant Rb DU-145 cells are resistant to the X-ray radiation despite in the presence of miR-449a. The cell cycle distribution of DU-145 cells is not significantly altered by miR-449a in the response to ionizing radiation. Furthermore, elevated miR-449a downregulates cell cycle regulator CDC25A and oncogene HDAC1. By targeting genes involved in controlling pRb/E2F1 activity, miR-449a regulates cell cycle progression and apoptosis and consequently enhances the radiosensitivity of PC-3 cells. Thus, miR-449a, as a miRNA component of the Rb pathway, promotes the radiosensitivity of PC-3 cells through regulating pRb/E2F1.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(1):5–29. doi:10.3322/caac.21254.
Palacios DA, Miyake M, Rosser CJ. Radiosensitization in prostate cancer: mechanisms and targets. BMC Urol. 2013;13:4. doi:10.1186/1471-2490-13-4.
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell. 2009;136(2):215–33. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.002.
Friedman RC, Farh KK-H, Burge CB, Bartel DP. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res. 2009;19(1):92–105. doi:10.1101/gr.082701.108.
Halimi M, Asghari SM, Sariri R, Moslemi D, Parsian H. Cellular response to ionizing radiation: a microRNA story. Int J Mol Cell Med. 2012;1(4):178–84.
Mao A, Liu Y, Zhang H, Di C, Sun C. microRNA expression and biogenesis in cellular response to ionizing radiation. DNA Cell Biol. 2014;33(10):667–79. doi:10.1089/dna.2014.2401.
Zhao L, Bode AM, Cao Y, Dong Z. Regulatory mechanisms and clinical perspectives of miRNA in tumor radiosensitivity. Carcinogenesis. 2012;33(11):2220–7. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgs235.
Carleton M, Cleary MA, Linsley PS. MicroRNAs and cell cycle regulation. Cell Cycle. 2014;6(17):2127–32. doi:10.4161/cc.6.17.4641.
Lizé M, Klimke A, Dobbelstein M. MicroRNA-449 in cell fate determination. Cell Cycle. 2014;10(17):2874–82. doi:10.4161/cc.10.17.17181.
Gallinas SC, Lizé M. MIR449A (microRNA 449a). Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol. 2013(3). doi:10.4267/2042/48759.
Luo W, Huang B, Li Z, Li H, Sun L, Zhang Q, et al. MicroRNA-449a is downregulated in non-small cell lung cancer and inhibits migration and invasion by targeting c-Met. PLoS One. 2013;8(5), e64759. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0064759.
Ren XS, Yin MH, Zhang X, Wang Z, Feng SP, Wang GX, et al. Tumor-suppressive microRNA-449a induces growth arrest and senescence by targeting E2F3 in human lung cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2014;344(2):195–203. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2013.10.031.
Noonan EJ, Place RF, Pookot D, Basak S, Whitson JM, Hirata H, et al. miR-449a targets HDAC-1 and induces growth arrest in prostate cancer. Oncogene. 2009;28(14):1714–24. doi:10.1038/onc.2009.19.
Li X, Li H, Zhang R, Liu J. MicroRNA-449a inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis by directly repressing E2F3 in gastric cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;35(5):2033–42. doi:10.1159/000374010.
Yao Y, Ma J, Xue Y, Wang P, Li Z, Hu Y, et al. MiR-449a exerts tumor-suppressive functions in human glioblastoma by targeting Myc-associated zinc-finger protein. Mol Oncol. 2015;9(3):640–56. doi:10.1016/j.molonc.2014.11.003.
Zhao Z, Ma X, Sung D, Li M, Kosti A, Lin G, et al. microRNA-449a functions as a tumor suppressor in neuroblastoma through inducing cell differentiation and cell cycle arrest. RNA Biol. 2015;12(5):538–54. doi:10.1080/15476286.2015.1023495.
Yang G, Lu X, Wang L, Bian Y, Fu H, Wei M, et al. E2F1 and RNA binding protein QKI comprise a negative feedback in the cell cycle regulation. Cell Cycle. 2014;10(16):2703–13. doi:10.4161/cc.10.16.15928.
Johson DG, Schwarz JK, Cress WD, Nevins JR. Expression of transcription factor E2F induces quiescent cells to S phase. Nature. 1993;365:349–52.
Sage J, Miller AL, Perez-Mancera PA, Wysocki JM, Jacks T. Acute mutation of retinoblastoma gene function is sufficient for cell cycle re-entry. Nature. 2003;424(6945):223–8.
Mayhew CN, Bosco E, Fox SR, Okaya T, Tarapore P, Schwemberger SJ, et al. Liver-specific pRB loss results in ectopic cell cycle entry and aberrant ploidy. Cancer Res. 2005;65(11):4568–77.
Chang CN, Feng MJ, Chen YL, Yuan RH, Jeng YM. p15(PAF) is an Rb/E2F-regulated S-phase protein essential for DNA synthesis and cell cycle progression. PLoS One. 2013;8(4), e61196. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0061196.
Jackson MW, Agarwal MK, Yang J, Bruss P, Uchiumi T, Agarwal ML, et al. p130/p107/p105Rb-dependent transcriptional repression during DNA-damage-induced cell-cycle exit at G2. J Cell Sci. 2005;118(Pt 9):1821–32. doi:10.1242/jcs.02307.
Eguchi T, Takaki T, Itadani H, Kotani H. RB silencing compromises the DNA damage-induced G2/M checkpoint and causes deregulated expression of the ECT2 oncogene. Oncogene. 2007;26(4):509–20. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209810.
Rigberg DA, Kim FS, Sebastian JL, Kazanjian KK, McFadden DW. Hypophosphorylated retinoblastoma protein is associated with G2 arrest in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Surg Res. 1999;84(1):101–5. doi:10.1006/jsre.1999.5617.
Yang X, Feng M, Jiang X, Wu Z, Li Z, Aau M, et al. miR-449a and miR-449b are direct transcriptional targets of E2F1 and negatively regulate pRb-E2F1 activity through a feedback loop by targeting CDK6 and CDC25A. Genes Dev. 2009;23(20):2388–93. doi:10.1101/gad.1819009.
Lize M, Pilarski S, Dobbelstein M. E2F1-inducible microRNA 449a/b suppresses cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2010;17(3):452–8. doi:10.1038/cdd.2009.188.
Yan F, Liu H, Hao J, Liu Z. Dynamical behaviors of Rb-E2F pathway including negative feedback loops involving miR449. PLoS One. 2012;7(9), e43908. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0043908.
Yan F, Liu H, Liu Z. Dynamic analysis of the combinatorial regulation involving transcription factors and microRNAs in cell fate decisions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1844(1 Pt B):248–57. doi:10.1016/j.bbapap.2013.06.022.
Albright N. Computer programs for the analysis of cellular survival data. Radiat Res. 1987;112(2):331–40.
Pawlik TM, Keyomarsi K. Role of cell cycle in mediating sensitivity to radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004;59(4):928–42. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2004.03.005.
Sobel RE, Sadar MD. Cell lines used in prostate cancer research: a compendium of old and new lines--part 1. J Urol. 2005;173(2):342–59. doi:10.1097/01.ju.0000141580.30910.57.
Bookstein R, Shew JY, Chen PL, Scully P, Lee WH. Suppression of tumorigenicity of human prostate carcinoma cells by replacing a mutated RB gene. Science (New York, NY). 1990;247(4943):712–5.
Tan HL, Sood A, Rahimi HA, Wang W, Gupta N, Hicks J, et al. Rb loss is characteristic of prostatic small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20(4):890–903. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-1982.
Isaacs WB, Carter BS, Ewing CM. Wild-type p53 suppresses growth of human prostate cancer cells containing mutant p53 alleles. Cancer Res. 1991;51(17):4716–20.
Gurova KV, Rokhlin OW, Budanov AV, Burdelya LG, Chumakov PM, Cohen MB, et al. Cooperation of two mutant p53 alleles contributes to Fas resistance of prostate carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2003;63(11):2905–12.
van Bokhoven A, Varella-Garcia M, Korch C, Johannes WU, Smith EE, Miller HL, et al. Molecular characterization of human prostate carcinoma cell lines. Prostate. 2003;57(3):205–25. doi:10.1002/pros.10290.
Ye W, Xue J, Zhang Q, Li F, Zhang W, Chen H, et al. MiR-449a functions as a tumor suppressor in endometrial cancer by targeting CDC25A. Oncol Rep. 2014;32(3):1193–9. doi:10.3892/or.2014.3303.
Hu J, Fang Y, Cao Y, Qin R, Chen Q. miR-449a regulates proliferation and chemosensitivity to cisplatin by targeting cyclin D1 and BCL2 in SGC7901 cells. Dig Dis Sci. 2014;59(2):336–45. doi:10.1007/s10620-013-2923-3.
Paik S, Jung HS, Lee S, Yoon DS, Park MS, Lee JW. miR-449a regulates the chondrogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells through direct targeting of lymphoid enhancer-binding factor-1. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21(18):3298–308. doi:10.1089/scd.2011.0732.
Noonan EJ, Place RF, Basak S, Pookot D, Li LC. miR-449a causes Rb-dependent cell cycle arrest and senescence in prostate cancer cells. Oncotarget. 2010;1(5):349–58.
Liu YJ, Lin YF, Chen YF, Luo EC, Sher YP, Tsai MH, et al. MicroRNA-449a enhances radiosensitivity in CL1-0 lung adenocarcinoma cells. PLoS One. 2013;8(4), e62383. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0062383.
Teyssier F, Bay JO, Dionet C, Verrelle P. Cell cycle regulation after exposure to ionizing radiation. Bull Cancer. 1999;86(4):345–57.
Kim SY, Yang ES, Lee YS, Lee J, Park JW. Sensitive to apoptosis gene protein regulates ionizing radiation-induced apoptosis. Biochimie. 2011;93(2):269–76. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2010.09.020.
Diego A. Palacions MMaCJR. Radiosensitization in prostate cancer mechanisms and targets. BMC Urol. 2013;13(4):1472490. doi:10.1186/1471-2490-13-4.
Bowen C, Spiegel S, Gelmann EP. Radiation-induced apoptosis mediated by retinoblastoma protein. Cancer Res. 1998;58(15):3275–81.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the grants from the Key program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (U1432248), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11105203 and 11405230), and the Scientific Technology Research Projects of Gansu Province (1107RJYA033).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yang Liu joint first author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mao, A., Liu, Y., Wang, Y. et al. miR-449a enhances radiosensitivity through modulating pRb/E2F1 in prostate cancer cells. Tumor Biol. 37, 4831–4840 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4336-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4336-8