Abstract
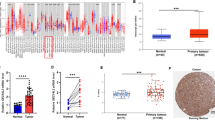
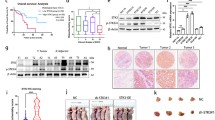
MicroRNA-613 (miR-613) plays important roles in tumorigenesis and cancer progression. We aimed to evaluate its expression level and potential for diagnosis and prognosis in esophageal squamous cell cancer (ESCC). We examined miR-613 expression in 60 pairs of ESCC cancerous and matched paracancerous tissues, serum samples from 75 ESCC patients and 75 healthy volunteers, and 105 formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue samples using quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis, Kaplan-Meier method, and Cox regression were applied to analyze its diagnostic and prognostic value. MiR-613 was significantly decreased in ESCC tissue compared with paracancerous tissue (P < 0.001). Moreover, the expression level of miR-613 was significantly reduced with increased T stage of ESCC. Statistically significant difference between ESCC patients and healthy controls in expression level of miR-613 (0.89 ± 0.73 vs. 1.71 ± 1.03, P < 0.001) was found. The area under the ROC curve (AUC) based on serum miR-613 was 0.767 ± 0.040. We also performed analysis on early-stage patients and revealed that the AUC value was 0.728 ± 0.052 (P < 0.001). The Kaplan-Meier curve revealed that the downregulation of miR-613 was related to worse overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) of ESCC patients (P = 0.018 and P = 0.035, respectively). Furthermore, the multivariate analysis identified miR-613 to be an independent prognostic factor for OS and PFS (P = 0.031 and P = 0.006, respectively) In conclusion, miR-613 is significantly reduced in cancerous tissue and serum samples of ESCC patients. It can serve as an ideal indicator for the diagnosis and prognosis of ESCC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Napier KJ, Scheerer M, Misra S. Esophageal cancer: a review of epidemiology, pathogenesis, staging workup and treatment modalities. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2014;6(5):112–20. doi:10.4251/wjgo.v6.i5.112.
Pennathur A, Gibson MK, Jobe BA, Luketich JD. Oesophageal carcinoma. Lancet. 2013;381(9864):400–12. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60643-6.
Feng JF, Huang Y, Lu WS, Chen QX. Preoperative platelet count in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: is it a prognostic factor? Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2013;398(8):1115–22. doi:10.1007/s00423-013-1111-4.
Feng JF, Huang Y, Zhao Q. Tumor length in elderly patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: is it a prognostic factor? Ups J Med Sci. 2013;118(3):145–52. doi:10.3109/03009734.2013.792887.
Yu G, Chen G, Huang B, Shao W, Zeng G. Effect of early enteral nutrition on postoperative nutritional status and immune function in elderly patients with esophageal cancer or cardiac cancer. Chin J Cancer Res. 2013;25(3):299–305. doi:10.3978/j.issn.1000-9604.2013.06.01.
Ren P, Yu ZT, Xiu L, Wang M, Liu HM. Elevated serum levels of human relaxin-2 in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19(15):2412–8. doi:10.3748/wjg.v19.i15.2412.
Wang Q, Ma C, Kemmner W. Wdr66 is a novel marker for risk stratification and involved in epithelial-mesenchymal transition of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2013;13:137. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-13-137.
Ren P, Zhang JG, Xiu L, Yu ZT. Clinical significance of phospholipase A2 group IIA (PLA2G2A) expression in primary resected esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2013;17(6):752–7.
Reddy KB. MicroRNA (miRNA) in cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2015;15:38. doi:10.1186/s12935-015-0185-1.
Garzon R, Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu Rev Med. 2009;60:167–79. doi:10.1146/annurev.med.59.053006.104707.
Komatsu S, Ichikawa D, Hirajima S, Kawaguchi T, Miyamae M, Okajima W, et al. Plasma microRNA profiles: identification of miR-25 as a novel diagnostic and monitoring biomarker in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2014;111(8):1614–24. doi:10.1038/bjc.2014.451.
Wu C, Li M, Hu C, Duan H. Clinical significance of serum miR-223, miR-25 and miR-375 in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Biol Rep. 2014;41(3):1257–66. doi:10.1007/s11033-013-2970-z.
Tanaka K, Miyata H, Yamasaki M, Sugimura K, Takahashi T, Kurokawa Y, et al. Circulating miR-200c levels significantly predict response to chemotherapy and prognosis of patients undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy for esophageal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20 Suppl 3:S607–15. doi:10.1245/s10434-013-3093-4.
Dong W, Li B, Wang Z, Zhang Z, Wang J. Clinical significance of microRNA-24 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Neoplasma. 2015;62(2):250–8. doi:10.4149/neo_2015_030.
Yang Z, Yuan Z, Fan Y, Deng X, Zheng Q. Integrated analyses of microRNA and mRNA expression profiles in aggressive papillary thyroid carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 2013;8(5):1353–8. doi:10.3892/mmr.2013.1699.
Shah AA, Leidinger P, Backes C, Keller A, Karpinski P, Sasiadek MM, et al. A set of specific miRNAs is connected with murine and human gastric cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2013;52(3):237–49. doi:10.1002/gcc.22024.
Cho WC. OncomiRs: the discovery and progress of microRNAs in cancers. Mol Cancer. 2007;6:60. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-6-60.
Meng H, Wang K, Chen X, Guan X, Hu L, Xiong G, et al. MicroRNA-330-3p functions as an oncogene in human esophageal cancer by targeting programmed cell death 4. Am J Cancer Res. 2015;5(3):1062–75.
Ide S, Toiyama Y, Shimura T, Kawamura M, Yasuda H, Saigusa S, et al. MicroRNA-503 promotes tumor progression and acts as a novel biomarker for prognosis in oesophageal cancer. Anticancer Res. 2015;35(3):1447–51.
Jiang L, Wang Y, Rong Y, Xu L, Chu Y, Zhang Y, et al. miR-1179 promotes cell invasion through SLIT2/ROBO1 axis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(1):319–27.
Li M, He XY, Zhang ZM, Li S, Ren LH, Cao RS, et al. MicroRNA-1290 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell proliferation and metastasis. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21(11):3245–55. doi:10.3748/wjg.v21.i11.3245.
Qi Y, Li X, Zhao S. miR-29b inhibits the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting MMP-2. Neoplasma. 2015;62(3):384–90. doi:10.4149/neo_2015_046.
Nie J, Ge X, Geng Y, Cao H, Zhu W, Jiao Y, et al. miR-34a inhibits the migration and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting Yin Yang-1. Oncol Rep. 2015. doi:10.3892/or.2015.3962.
Yang JS, Li BJ, Lu HW, Chen Y, Lu C, Zhu RX, et al. Serum miR-152, miR-148a, miR-148b, and miR-21 as novel biomarkers in non-small cell lung cancer screening. Tumour Biol. 2015;36(4):3035–42. doi:10.1007/s13277-014-2938-1.
Chen J, Wang W, Zhang Y, Chen Y, Hu T. Predicting distant metastasis and chemoresistance using plasma miRNAs. Med Oncol. 2014;31(1):799. doi:10.1007/s12032-013-0799-x.
Ouyang M, Li Y, Ye S, Ma J, Lu L, Lv W, et al. MicroRNA profiling implies new markers of chemoresistance of triple-negative breast cancer. PLoS One. 2014;9(5):e96228. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0096228.
Mar-Aguilar F, Mendoza-Ramirez JA, Malagon-Santiago I, Espino-Silva PK, Santuario-Facio SK, Ruiz-Flores P, et al. Serum circulating microRNA profiling for identification of potential breast cancer biomarkers. Dis Markers. 2013;34(3):163–9. doi:10.3233/DMA-120957.
Hezova R, Kovarikova A, Srovnal J, Zemanova M, Harustiak T, Ehrmann J, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic potential of miR-21, miR-29c, miR-148 and miR-203 in adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of esophagus. Diagn Pathol. 2015;10(1):42. doi:10.1186/s13000-015-0280-6.
Sun N, Ye L, Chang T, Li X, Li X. microRNA-195-Cdc42 axis acts as a prognostic factor of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7(10):6871–9.
Wang TY, Liu SG, Zhao BS, Qi B, Qin XG, Yao WJ. Implications of microRNA-197 downregulated expression in esophageal cancer with poor prognosis. Genet Mol Res. 2014;13(3):5574–81. doi:10.4238/2014.July.25.12.
Zhang BJ, Gong HY, Zheng F, Liu DJ, Liu HX. Up-regulation of miR-335 predicts a favorable prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7(9):6213–8.
Qi B, Liu SG, Qin XG, Yao WJ, Lu JG, Guo L, et al. Overregulation of microRNA-212 in the poor prognosis of esophageal cancer patients. Genet Mol Res. 2014;13(3):7800–7. doi:10.4238/2014.September.26.18.
Wang C, Guan S, Chen X, Liu B, Liu F, Han L, et al. Clinical potential of miR-3651 as a novel prognostic biomarker for esophageal squamous cell cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;465(1):30–4. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.07.109.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Science and Technology Development Planning Project of Shandong Province (2014GSF118058).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, S., Wang, C., Chen, X. et al. MiR-613: a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 37, 4383–4391 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4271-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4271-8