Abstract
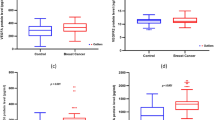
Breast cancer is the most common malignancy predominantly affecting women. To date, numerous numbers of studies were reported novel genetic contributors with diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic potential for the breast carcinogenesis. However, the role of urotensin-II in breast carcinogenesis has not been elucidated yet. Urotensin-II is a somatostatin-like cyclic tiny peptide identified by its potent vasoconstrictor activity. Soon after its discovery, its involvement in many disease states as well as its expression in various tissues including the tumors have been demonstrated. Moreover, there is strong evidence that suggest urotensin-II as the significant contributor of angiogenesis as well as cell proliferation and tumor biology. In this study, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis were used to evaluate plasma levels of urotensin-II and Thr21Met and Ser89Asn polymorphisms of UTS2 gene in breast cancer patients. In the present case-control study, we noticed a significant decrease in the levels of urotensin-II protein in the plasma of the breast cancer patients (p < 0.05). Also, Thr21Met polymorphism in the UTS2 gene was associated with the risk of developing breast cancer (p < 0.0001), whereas the genotype frequency of Ser89Asn was found to be similar in patients and controls (p > 0.05). In addition, we demonstrated the gradual decreasing of urotensin-II protein levels from TT and TM to MM genotypes. In conclusion, these results strongly suggest that urotensin-II could contribute to breast carcinogenesis and Thr21Met polymorphism can be an important risk factor in developing breast tumors.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miki Y, Swensen J, Shattuckeidens D, Futreal PA, Harshman K, Tavtigian S, et al. A strong candidate for the breast and ovarian-cancer susceptibility gene brca1. Science. 1994;266:66–71.
Christodoulatos GS, Dalamaga M. Micro-RNAs as clinical biomarkers and therapeutic targets in breast cancer: Quo vadis? World J Clin Oncol. 2014;5:71–81.
van de Vijver MJ. Molecular tests as prognostic factors in breast cancer. Virchows Arch. 2014;464:283–91.
Weigelt B, Peterse JL, van’t Veer LJ. Breast cancer metastasis: markers and models. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:591–602.
Ames RS, Sarau HM, Chambers JK, Willette RN, Alyar NV, Romanic AM, et al. Human urotensin-ii is a potent vasoconstrictor and agonist for the orphan receptor gpr14. Nature. 1999;401:282.
Okumus S, Igci YZ, Taskin T, Oztuzcu S, Gurler B, Eslik Z, et al. Association between thr21met and ser89asn polymorphisms of the urotensin-ii (uts2) gene, diabetes mellitus, and diabetic retinopathy. Curr Eye Res. 2012;37:921–9.
Ong KL, Lam KS, Cheung BM. Urotensin ii: its function in health and its role in disease. Cardiovascular drugs and therapy/sponsored by the. Int Soc Cardiovasc Pharmacother. 2005;19:65–75.
McDonald J, Batuwangala M, Lambert DG. Role of urotensin ii and its receptor in health and disease. J Anesth. 2007;21:378–89.
Takahashi K, Totsune K, Murakami O, Arihara Z, Noshiro T, Hayashi Y, et al. Expression of urotensin ii and its receptor in adrenal tumors and stimulation of proliferation of cultured tumor cells by urotensin ii. Peptides. 2003;24:301–6.
Pehlivan Y, Gogebakan B, Oztuzcu S, Ozgen M, Cetin GY, Bayraktar R, et al. Association between thr21met and ser89asn polymorphisms of the urotensin ii gene and systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol. 2012;39:106–11.
Oztuzcu S, Ulasli M, Pehlivan Y, Cevik MO, Cengiz B, Gogebakan B, et al. Thr21met (t21m) but not ser89asn (s89n) polymorphisms of the urotensin-ii (uts-ii) gene are associated with Behcet’s disease (bd). Peptides. 2013;42:97–100.
Wenyi Z, Suzuki S, Hirai M, Hinokio Y, Tanizawa Y, Matsutani A, et al. Role of urotensin ii gene in genetic susceptibility to type 2 diabetes mellitus in Japanese subjects. Diabetologia. 2003;46:972–6.
Suzuki S, Wenyi Z, Hirai M, Hinokio Y, Suzuki C, Yamada T, et al. Genetic variations at urotensin ii and urotensin ii receptor genes and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Japanese. Peptides. 2004;25:1803–8.
Spinazzi R, Albertin G, Nico B, Guidolin D, Di Liddo R, Rossi GP, et al. Urotensin-ii and its receptor (ut-r) are expressed in rat brain endothelial cells, and urotensin-ii via ut-r stimulates angiogenesis in vivo and in vitro. Int J Mol Med. 2006;18:1107.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a project from the Scientific Research Projects Management Unit of Adiyaman University.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yumrutas, O., Oztuzcu, S., Büyükhatipoglu, H. et al. The role of the UTS2 gene polymorphisms and plasma Urotensin-II levels in breast cancer. Tumor Biol. 36, 4427–4432 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3082-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3082-2