Abstract
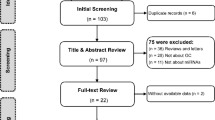
Dysregulated microRNAs (miRNAs) have been reported to be associated with pancreatic cancer (PaC), suggesting that they may serve as useful novel diagnostic biomarkers for PaC. Various studies have been performed to investigate the diagnostic value of miRNAs for PaC but have obtained conflicting results. Therefore, this meta-analysis aims to comprehensively and quantitatively evaluate the potential diagnostic value of miRNAs for PaC. We systematically searched PubMed, Embase, Google Scholar, Cochrane Library, and Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure for publications concerning the diagnostic value of miRNAs for PaC without language restriction. The quality of each study was scored using the revised Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies (QUADAS-2). The summary receiver operator characteristic curve and other parameters were applied to check the overall test performance. Heterogeneity was tested with the I 2 test and publication bias was tested with the Deek’s funnel plot asymmetry test. This meta-analysis included 18 articles with a total of 2,036 patients and 1,444 controls. The pooled sensitivity was 82 % (95 % CI, 78–86 %); the specificity was 77 % (95 % CI, 73–81 %); the PLR was 3.6 (95 % CI, 3.0–4.4); the NLR was 0.23 (95 % CI, 0.18–0.29); the DOR was 16 (95 % CI, 10–24); and the AUC was 0.86 (95 % CI, 0.83–0.89). Subgroups analyses were also performed and revealed that there were significant differences between some subgroups: the multiple-miRNAs profiling-based assays, non-blood-based assays, and healthy control-based studies all showed higher accuracies in diagnosing PaC than that of their counterparts. This meta-analysis suggests that the use of miRNAs has potential diagnostic value with a relatively high sensitivity and specificity for PaC, particularly the use of multiple miRNAs for discriminating PaC patients from healthy individuals. More prospective studies on the diagnostic value of miRNAs for PaC are needed in the future.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9–29.
Mann DV, Edwards R, Ho S, Lau WY, Glazer G. Elevated tumour marker CA19-9: clinical interpretation and influence of obstructive jaundice. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2000;26:474–9.
Schmidt C. Early detection tools for pancreatic cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012;104:1117–8.
Locker GY, Hamilton S, Harris J, Jessup JM, Kemeny N, Macdonald JS, et al. ASCO 2006 update of recommendations for the use of tumor markers in gastrointestinal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:5313–27.
Poruk KE, Gay DZ, Brown K, Mulvihill JD, Boucher KM, Scaife CL, et al. The clinical utility of CA 19-9 in pancreatic adenocarcinoma: diagnostic and prognostic updates. Curr Mol Med. 2013;13:340–51.
Flynt AS, Lai EC. Biological principles of microRNA-mediated regulation: shared themes amid diversity. Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:831–42.
Ouimet M, Moore KJ. A big role for small RNAs in HDL homeostasis. J Lipid Res. 2013;54:1161–7.
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R, Zupo S, Noch E, et al. Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99:15524–9.
Navon R, Wang H, Steinfeld I, Tsalenko A, Ben-Dor A, Yakhini Z. Novel rank-based statistical methods reveal microRNAs with differential expression in multiple cancer types. PLoS One. 2009;4:e8003.
Weber JA, Baxter DH, Zhang S, Huang DY, Huang KH, Lee MJ, et al. The microRNA spectrum in 12 body fluids. Clin Chem. 2010;56:1733–41.
Zhao H, Shen J, Medico L, Wang D, Ambrosone CB, Liu S. A pilot study of circulating miRNAs as potential biomarkers of early stage breast cancer. PLoS One. 2010;5:e13735.
Ryu JK, Matthaei H, Dal Molin M, Hong SM, Canto MI, Schulick RD, et al. Elevated microRNA miR-21 levels in pancreatic cyst fluid are predictive of mucinous precursor lesions of ductal adenocarcinoma. Pancreatology. 2011;11:343–50.
Munding JB, Adai AT, Maghnouj A, Urbanik A, Zollner H, Liffers ST, et al. Global microRNA expression profiling of microdissected tissues identifies miR-135b as a novel biomarker for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2012;131:E86–95.
Schultz NA, Werner J, Willenbrock H, Roslind A, Giese N, Horn T, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles associated with pancreatic adenocarcinoma and ampullary adenocarcinoma. Mod Pathol. 2012;25:1609–22.
Wang J, Chen J, Chang P, LeBlanc A, Li D, Abbruzzesse JL, et al. MicroRNAs in plasma of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients as novel blood-based biomarkers of disease. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2009;2:807–13.
Liu JQ, Gao J, Ren Y, Wang XW, Wang WW, Lu H. Diagnostic value of plasma miR-21 in pancreatic cancer. World Chinese Journal of Digestology. 2011;19:860–3.
Zhang J, Zhao CY, Zhang SH, Yu DH, Chen Y, Liu QH, et al. Upregulation of miR-194 contributes to tumor growth and progression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2014;31:1157–64.
Ganepola GA, Rutledge JR, Suman P, Yiengpruksawan A, Chang DH. Novel blood-based microRNA biomarker panel for early diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2014;6:22–33.
Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME, Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, et al. QUADAS-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med. 2011;155:529–36.
Reitsma JB, Glas AS, Rutjes AW, Scholten RJ, Bossuyt PM, Zwinderman AH. Bivariate analysis of sensitivity and specificity produces informative summary measures in diagnostic reviews. J Clin Epidemiol. 2005;58:982–90.
Deeks JJ. Systematic reviews in health care: systematic reviews of evaluations of diagnostic and screening tests. BMJ. 2001;323:157–62.
Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 2002;21:1539–58.
Dillhoff M, Liu J, Frankel W, Croce C, Bloomston M. MicroRNA-21 is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer and a potential predictor of survival. J Gastrointest Surg. 2008;12:2171–6.
Habbe N, Koorstra JB, Mendell JT, Offerhaus GJ, Ryu JK, Feldmann G, et al. MicroRNA miR-155 is a biomarker of early pancreatic neoplasia. Cancer Biol Ther. 2009;8:340–6.
Morimura R, Komatsu S, Ichikawa D, Takeshita H, Tsujiura M, Nagata H, et al. Novel diagnostic value of circulating miR-18a in plasma of patients with pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer. 2011;105:1733–40.
Bauer AS, Keller A, Costello E, Greenhalf W, Bier M, Borries A, et al. Diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and chronic pancreatitis by measurement of microRNA abundance in blood and tissue. PLoS One. 2012;7:e34151.
Liu J, Gao J, Du Y, Li Z, Ren Y, Gu J, et al. Combination of plasma microRNAs with serum CA19-9 for early detection of pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer. 2012;131:683–91.
Liu R, Chen X, Du Y, Yao W, Shen L, Wang C, et al. Serum microRNA expression profile as a biomarker in the diagnosis and prognosis of pancreatic cancer. Clin Chem. 2012;58:610–8.
Ren Y, Gao J, Liu JQ, Wang XW, Gu JJ, Huang HJ, et al. Differential signature of fecal microRNAs in patients with pancreatic cancer. Mol Med Rep. 2012;6:201–9.
Li A, Yu J, Kim H, Wolfgang CL, Canto MI, Hruban RH, et al. MicroRNA array analysis finds elevated serum miR-1290 accurately distinguishes patients with low-stage pancreatic cancer from healthy and disease controls. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19:3600–10.
Wang WS, Liu LX, Li GP, Chen Y, Li CY, Jin DY, et al. Combined serum CA19-9 and miR-27a-3p in peripheral blood mononuclear cells to diagnose pancreatic cancer. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2013;6:331–8.
Zhao C, Zhang J, Zhang S, Yu D, Chen Y, Liu Q, et al. Diagnostic and biological significance of microRNA-192 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2013;30:276–84.
Schultz NA, Dehlendorff C, Jensen BV, Bjerregaard JK, Nielsen KR, Bojesen SE, et al. MicroRNA biomarkers in whole blood for detection of pancreatic cancer. JAMA. 2014;311:392–404.
Yeo CJ, Abrams RA, Grochow LB, Sohn TA, Ord SE, Hruban RH, et al. Pancreaticoduodenectomy for pancreatic adenocarcinoma: postoperative adjuvant chemoradiation improves survival. A prospective, single-institution experience. Ann Surg. 1997;225:621–33.
Real FX. A “catastrophic hypothesis” for pancreas cancer progression. Gastroenterology. 2003;124:1958–64.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, Z., Wu, H., Zhang, J. et al. MicroRNAs as novel biomarkers for pancreatic cancer diagnosis: a meta-analysis based on 18 articles. Tumor Biol. 35, 8837–8848 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2133-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2133-4