Abstract
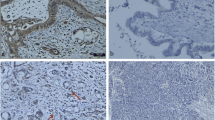
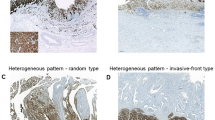
We investigated the expression of claudin 5 in 88 ductal adenocarcinomas of the pancreas. The results were correlated with patient prognosis, with claudin 5 expression in blood vessels, with the expression level of bcl2 and bax and with apoptosis. Claudin 5 expression was detected in 24 (38 %) cases. It was not associated with tumour size or spread, but strong claudin 5 expression correlated with a worse survival (p = 0.005). Claudin 5 also associated with a higher extent of apoptosis and greater expression of bax protein. In the tumour vasculature, some vessels displayed a loss of claudin 5 expression. The presence of this loss was associated with tumour grade and the presence of nodal metastases (p = 0.02, p = 0.022, respectively). These results indicate that claudin 5 is upregulated in a proportion of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas. The association of strong claudin 5 expression with a worse survival is in line with some earlier reports indicating that this protein is involved with increased locomotion and more aggressive spread of carcinomas. The association of claudin 5 with apoptosis and bax might be due to stronger cellular kinetics found in such tumours. The loss of claudin 5 expression in the tumour vasculature points to a leaky vessel type; this might also ease the access of tumours to vessels and be reflected in its association with the presence of nodal metastases.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krause G, Winkler L, Mueller SL, Haseloff RF, Piontek J, Blasig IE. Structure and function of claudins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1778:631–45.
Sawada N, Murata M, Kikuchi K, Osanai M, Tobioka H, Kojima T, et al. Tight junctions and human diseases. Med Electron Microsc. 2003;36:147–56.
Mineta K, Yamamoto Y, Yamazaki Y, Tanaka H, Tada Y, Saito K, et al. Predicted expansion of the claudin multigene family. FEBS Lett. 2011;585:606–12.
Evans MJ, von Hahn T, Tscherne DM, Syder AJ, Panis M, Wölk B, et al. Claudin-1 is a hepatitis C virus co-receptor required for a late step in entry. Nature. 2007;446:801–5.
Morita K, Sasaki H, Furuse M, Tsukita S. Endothelial claudin: claudin-5/TMVCF constitutes tight junction strands in endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1999;147:185–94.
Morrow CM, Tyagi G, Simon L, Carnes K, Murphy KM, Cooke PS, et al. Claudin 5 expression in mouse seminiferous epithelium is dependent upon the transcription factor ets variant 5 and contributes to blood-testis barrier function. Biol Reprod. 2009;81:871–9.
Nitta T, Hata M, Gotoh S, Seo Y, Sasaki H, Hashimoto N, et al. Size-selective loosening of the blood–brain barrier in claudin-5-deficient mice. J Cell Biol. 2003;161:653–60.
Soini Y. Expression of claudins 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 7 in various types of tumours. Histopathology. 2005;46:551–60.
Turunen M, Talvensaari-Mattila A, Soini Y, Santala M. Claudin-5 overexpression correlates with aggressive behavior in serous ovarian adenocarcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2009;29:5185–9.
Escudero-Esparza A, Jiang WG, Martin TA. Claudin-5 is involved in breast cancer cell motility through the N-WASP and ROCK signalling pathways. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2012;31:43.
Rahner C, Mitic LL, Anderson JM. Heterogeneity in expression and subcellular localization of claudins 2, 3, 4, and 5 in the rat liver, pancreas, and gut. Gastroenterology. 2001;120:411–22.
Comper F, Antonello D, Beghelli S, Gobbo S, Montagna L, Pederzoli P, et al. Expression pattern of claudins 5 and 7 distinguishes solid-pseudopapillary from pancreatoblastoma, acinar cell and endocrine tumors of the pancreas. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009;33:768–74.
Karanjawala ZE, Illei PB, Ashfaq R, Infante JR, Murphy K, Pandey A, et al. New markers of pancreatic cancer identified through differential gene expression analyses: claudin 18 and annexin A8. Am J Surg Pathol. 2008;32:188–96.
Tsukahara M, Nagai H, Kamiakito T, Kawata H, Takayashiki N, Saito K, et al. Distinct expression patterns of claudin-1 and claudin-4 in intraductal papillary-mucinous tumors of the pancreas. Pathol Int. 2005;55:63–9.
Bosman FT, Carneiro F, Hruban RH, Theise ND. WHO classification of tumours of the digestive system. Lyon: IARC; 2009.
Szasz AM, Tokes AM, Micsinai M, Krenacs T, Jakab C, Lukacs L, et al. Prognostic significance of claudin expression changes in breast cancer with regional lymph node metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2011;28:55–63.
Korompay A, Borka K, Lotz G, Somorácz A, Törzsök P, Erdélyi-Belle B, et al. Tricellulin expression in normal and neoplastic human pancreas. Histopathology. 2012;60:E76–86.
Liu T, Sun B, Zhao X, Gu Q, Dong X, Yao Z, et al. HER2/neu expression correlates with vasculogenic mimicry in invasive breast carcinoma. J Cell Mol Med. 2013;17:116–22.
Taddei A, Giampietro C, Conti A, Orsenigo F, Breviario F, Pirazzoli V, et al. Endothelial adherens junctions control tight junctions by VE-cadherin-mediated upregulation of claudin-5. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10:923–34.
Ping YF, Bian XW. Concise review: contribution of cancer stem cells to neovascularization. Stem Cells. 2011;29:888–94.
Jouppila-Mättö A, Närkiö-Mäkelä M, Soini Y, Pukkila M, Sironen R, Tuhkanen H, et al. Twist and snai1 expression in pharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma stroma is related to cancer progression. BMC Cancer. 2011;11:350.
Kokudo T, Suzuki Y, Yoshimatsu Y, Yamazaki T, Watabe T, Miyazono K. Snail is required for TGF beta-induced endothelial-mesenchymal transition of embryonic stem cell-derived endothelial cells. J Cell Sci. 2008;121:3317–24.
Soini Y, Tommola S, Helin H, Martikainen P. Claudins 1, 3, 4 and 5 in gastric carcinoma, loss of claudin expression associates with the diffuse subtype. Virchows Arch. 2006;448:52–8.
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the support of the Finnish Anti-Tuberculosis Association and the Finnish Cancer Society.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soini, Y., Eskelinen, M., Juvonen, P. et al. Strong claudin 5 expression is a poor prognostic sign in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Tumor Biol. 35, 3803–3808 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-1503-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-1503-7