Abstract
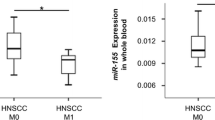
The aim of the study is to investigate the alteration of plasma miRNA in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Altered microRNAs (miRNAs) expression has been found in many cancers, including lung cancer, breast cancer, prostate cancer, bladder cancer and colorectal cancer. Many recent studies have demonstrated that aberrant plasma miRNAs were also found in various types of cancers. However the alteration of plasma expression in HNSCC remains unclear. In this present study, the expression profiles of ten miRNAs, let-7a, miR-21, miR26b, miR-34c, miR-99a, miR-133a, miR-137, miR-184, miR-194a, and miR-375, in plasma from 50 patients and 36 healthy subjects were evaluated using real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Our results demonstrated that the expression level of miR-21 was significantly up-regulated in plasma samples obtained from HNSCC patients (p < 0.01) than those from healthy subjects, which were in consistent with our finding in HNSCC tissues. A 7.7-fold increase of miR-21 in cancerous parts when compared to their non-cancerous counterparts (p < 0.0001) was observed in HNSCC tissues. In addition, the expression levels of miR-21 and miR-26b were both reduced in post-operative HNSCC patients with good prognosis. In contrast, the concentration of plasma miR-21 and miR-26b stayed high after tumor removal in the expired cases. Our study suggests that detecting circulating miR-21 and miR-26b pre- and post-operatively might provide a novel tumor marker for HNSCC.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Smigal C, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2006. CA Cancer J Clin. 2006;56:106–30.
Boring CC, Squires TS, Tong T. Cancer statistics, 1991. Bol Asoc Med P R. 1991;83:225–42.
Jemal A, Murray T, Ward E, Samuels A, Tiwari RC, Ghafoor A, Feuer EJ, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2005. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:10–30.
Department of Health EY, Taiwan, R.O.C. Cancer Registry Annual Report in Taiwan Area, 2005; 2006.
Massano J, Regateiro FS, Januario G, Ferreira A. Oral squamous cell carcinoma: review of prognostic and predictive factors. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006;102:67–76. doi:10.1016/j.tripleo.2005.07.038.
Cunningham D, Sirohi B, Pluzanska A, Utracka-Hutka B, Zaluski J, Glynne-Jones R, Koralewski P, Bridgewater J, Mainwaring P, Wasan H, Wang JY, Szczylik C, Clingan P, Chan RT, Tabah-Fisch I, Cassidy J. Two different first-line 5-fluorouracil regimens with or without oxaliplatin in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol. 2009;20:244–50. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdn638.
Calin GA, Pekarsky Y, Croce CM. The role of microRNA and other non-coding RNA in the pathogenesis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2007;20:425–37. doi:10.1016/j.beha.2007.02.003.
Liu N, Chen NY, Cui RX, Li WF, Li Y, Wei RR, Zhang MY, Sun Y, Huang BJ, Chen M, He QM, Jiang N, Chen L, Cho WC, Yun JP, Zeng J, Liu LZ, Li L, Guo Y, Wang HY, Ma J. Prognostic value of a microRNA signature in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a microRNA expression analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:633–41. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(12)70102-X.
Eder M, Scherr M. MicroRNA and lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:2446–8. doi:10.1056/NEJMcibr051201.
Gao W, Lu X, Liu L, Xu J, Feng D, Shu Y. MiRNA-21: a biomarker predictive for platinum-based adjuvant chemotherapy response in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 2012;13. doi:19073 [pii]
Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J, Weinberg RA. Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast cancer. Nature. 2007;449:682–8. doi:10.1038/nature06174.
Khoshnaw SM, Green AR, Powe DG, Ellis IO. MicroRNA involvement in the pathogenesis and management of breast cancer. J Clin Pathol. 2009;62:422–8. doi:10.1136/jcp.2008.060681.
Rokhlin OW, Scheinker VS, Taghiyev AF, Bumcrot D, Glover RA, Cohen MB. MicroRNA-34 mediates AR-dependent p53-induced apoptosis in prostate cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 2008;7:1288–96.
Gade S, Porzelius C, Faelth M, Brase JC, Wuttig D, Kuner R, Binder H, Sueltmann H, Beissbarth T. Graph based fusion of miRNA and mRNA expression data improves clinical outcome prediction in prostate cancer. BMC Bioinf. 2011;12:488. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-12-488.
Lin T, Dong W, Huang J, Pan Q, Fan X, Zhang C, Huang L. MicroRNA-143 as a tumor suppressor for bladder cancer. J Urol. 2009;181:1372–80. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2008.10.149.
Enkelmann A, Heinzelmann J, von Eggeling F, Walter M, Berndt A, Wunderlich H, Junker K. Specific protein and miRNA patterns characterise tumour-associated fibroblasts in bladder cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2011;137:751–9. doi:10.1007/s00432-010-0932-6.
Oberg AL, French AJ, Sarver AL, Subramanian S, Morlan BW, Riska SM, Borralho PM, Cunningham JM, Boardman LA, Wang L, Smyrk TC, Asmann Y, Steer CJ, Thibodeau SN. miRNA expression in colon polyps provides evidence for a multihit model of colon cancer. PLoS One. 2011;6:e20465. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0020465PONE-D-11-04534.
Agirre X, Martinez-Climent JA, Odero MD, Prosper F. Epigenetic regulation of miRNA genes in acute leukemia. Leukemia. 2012;26:395–403. doi:10.1038/leu.2011.344leu2011344.
Takamizawa J, Konishi H, Yanagisawa K, Tomida S, Osada H, Endoh H, Harano T, Yatabe Y, Nagino M, Nimura Y, Mitsudomi T, Takahashi T. Reduced expression of the let-7 microRNAs in human lung cancers in association with shortened postoperative survival. Cancer Res. 2004;64:3753–6. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-063764/11/3753.
Taft RJ, Pang KC, Mercer TR, Dinger M, Mattick JS. Non-coding RNAs: regulators of disease. J Pathol. 2010;220:126–39. doi:10.1002/path.2638.
Gilad S, Meiri E, Yogev Y, Benjamin S, Lebanony D, Yerushalmi N, Benjamin H, Kushnir M, Cholakh H, Melamed N, Bentwich Z, Hod M, Goren Y, Chajut A. Serum microRNAs are promising novel biomarkers. PLoS One. 2008;3:e3148. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0003148.
Ranade AR, Cherba D, Sridhar S, Richardson P, Webb C, Paripati A, Bowles B, Weiss GJ. MicroRNA 92a-2*: a biomarker predictive for chemoresistance and prognostic for survival in patients with small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2010;5:1273–8. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181dea6be.
Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:857–66. doi:10.1038/nrc1997.
Rosenfeld N, Aharonov R, Meiri E, Rosenwald S, Spector Y, Zepeniuk M, Benjamin H, Shabes N, Tabak S, Levy A, Lebanony D, Goren Y, Silberschein E, Targan N, Ben-Ari A, Gilad S, Sion-Vardy N, Tobar A, Feinmesser M, Kharenko O, Nativ O, Nass D, Perelman M, Yosepovich A, Shalmon B, Polak-Charcon S, Fridman E, Avniel A, Bentwich I, Bentwich Z, Cohen D, Chajut A, Barshack I. MicroRNAs accurately identify cancer tissue origin. Nat Biotechnol. 2008;26:462–9. doi:10.1038/nbt1392.
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR, Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, Peterson A, Noteboom J, O'Briant KC, Allen A, Lin DW, Urban N, Drescher CW, Knudsen BS, Stirewalt DL, Gentleman R, Vessella RL, Nelson PS, Martin DB, Tewari M. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:10513–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.0804549105.
Taylor DD, Gercel-Taylor C. MicroRNA signatures of tumor-derived exosomes as diagnostic biomarkers of ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2008;110:13–21. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2008.04.033.
Albulescu R, Neagu M, Albulescu L, Tanase C. Tissular and soluble miRNAs for diagnostic and therapy improvement in digestive tract cancers. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2011;11:101–20. doi:10.1586/erm.10.106.
Cho WC. Circulating MicroRNAs as minimally invasive biomarkers for cancer theragnosis and prognosis. Front Genet. 2011;2:7. doi:10.3389/fgene.2011.00007.
Chim SS, Shing TK, Hung EC, Leung TY, Lau TK, Chiu RW, Lo YM. Detection and characterization of placental microRNAs in maternal plasma. Clin Chem. 2008;54:482–90. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2007.097972.
Kroh EM, Parkin RK, Mitchell PS, Tewari M. Analysis of circulating microRNA biomarkers in plasma and serum using quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR). Methods. 2010;50:298–301. doi:10.1016/j.ymeth.2010.01.032.
Shen J, Liu Z, Todd NW, Zhang H, Liao J, Yu L, Guarnera MA, Li R, Cai L, Zhan M, Jiang F. Diagnosis of lung cancer in individuals with solitary pulmonary nodules by plasma microRNA biomarkers. BMC Cancer. 2011;11:374. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-11-374.
Komatsu S, Ichikawa D, Takeshita H, Tsujiura M, Morimura R, Nagata H, Kosuga T, Iitaka D, Konishi H, Shiozaki A, Fujiwara H, Okamoto K, Otsuji E. Circulating microRNAs in plasma of patients with oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2011;105:104–11. doi:10.1038/bjc.2011.198bjc2011198.
Tsujiura M, Ichikawa D, Komatsu S, Shiozaki A, Takeshita H, Kosuga T, Konishi H, Morimura R, Deguchi K, Fujiwara H, Okamoto K, Otsuji E. Circulating microRNAs in plasma of patients with gastric cancers. Br J Cancer. 2010;102:1174–9. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6605608.
Cheng H, Zhang L, Cogdell DE, Zheng H, Schetter AJ, Nykter M, Harris CC, Chen K, Hamilton SR, Zhang W. Circulating plasma MiR-141 is a novel biomarker for metastatic colon cancer and predicts poor prognosis. PLoS One. 2011;6:e17745. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0017745.
Liu X, Chen Z, Yu J, Xia J, Zhou X. MicroRNA profiling and head and neck cancer. Comp Funct Genomics. 2009:837514. doi:10.1155/2009/837514
Chang SS, Jiang WW, Smith I, Poeta LM, Begum S, Glazer C, Shan S, Westra W, Sidransky D, Califano JA. MicroRNA alterations in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2008;123:2791–7. doi:10.1002/ijc.23831.
Wong TS, Liu XB, Wong BY, Ng RW, Yuen AP, Wei WI. Mature miR-184 as potential oncogenic microRNA of squamous cell carcinoma of tongue. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:2588–92. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0666.
Li J, Huang H, Sun L, Yang M, Pan C, Chen W, Wu D, Lin Z, Zeng C, Yao Y, Zhang P, Song E. MiR-21 indicates poor prognosis in tongue squamous cell carcinomas as an apoptosis inhibitor. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:3998–4008. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-3053.
Hui AB, Lenarduzzi M, Krushel T, Waldron L, Pintilie M, Shi W, Perez-Ordonez B, Jurisica I, O'Sullivan B, Waldron J, Gullane P, Cummings B, Liu FF. Comprehensive microRNA profiling for head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16:1129–39. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2166.
Long XB, Sun GB, Hu S, Liang GT, Wang N, Zhang XH, Cao PP, Zhen HT, Cui YH, Liu Z. Let-7a microRNA functions as a potential tumor suppressor in human laryngeal cancer. Oncol Rep. 2009;22:1189–95.
Corney DC, Flesken-Nikitin A, Godwin AK, Wang W, Nikitin AY. MicroRNA-34b and MicroRNA-34c are targets of p53 and cooperate in control of cell proliferation and adhesion-independent growth. Cancer Res. 2007;67:8433–8. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1585.
Yu S, Liu Y, Wang J, Guo Z, Zhang Q, Yu F, Zhang Y, Huang K, Li Y, Song E, Zheng XL, Xiao H. Circulating microRNA profiles as potential biomarkers for diagnosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012. doi:jc.2011–3059 [pii] 10.1210/jc.2011-3059.
Bihrer V, Waidmann O, Friedrich-Rust M, Forestier N, Susser S, Haupenthal J, Welker M, Shi Y, Peveling-Oberhag J, Polta A, von Wagner M, Radeke HH, Sarrazin C, Trojan J, Zeuzem S, Kronenberger B, Piiper A. Serum microRNA-21 as marker for necroinflammation in hepatitis C patients with and without hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 2011;6:e26971. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0026971PONE-D-11-08476.
Iliopoulos D, Jaeger SA, Hirsch HA, Bulyk ML, Struhl K. STAT3 activation of miR-21 and miR-181b-1 via PTEN and CYLD are part of the epigenetic switch linking inflammation to cancer. Mol Cell. 2010;39:493–506. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2010.07.023.
Si ML, Zhu S, Wu H, Lu Z, Wu F, Mo YY. miR-21-mediated tumor growth. Oncogene. 2007;26:2799–803. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210083.
Sayed D, Rane S, Lypowy J, He M, Chen IY, Vashistha H, Yan L, Malhotra A, Vatner D, Abdellatif M. MicroRNA-21 targets Sprouty2 and promotes cellular outgrowths. Mol Biol Cell. 2008;19:3272–82. doi:10.1091/mbc.E08-02-0159.
Komatsu S, Ichikawa D, Takeshita H, Konishi H, Nagata H, Hirajima S, Kawaguchi T, Arita T, Shiozaki A, Fujiwara H, Okamoto K, Otsuji E. Prognostic impact of circulating miR-21 and miR-375 in plasma of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2012;12 Suppl 1:S53–9. doi:10.1517/14712598.2012.681373.
Zhang HL, Yang LF, Zhu Y, Yao XD, Zhang SL, Dai B, Zhu YP, Shen YJ, Shi GH, Ye DW. Serum miRNA-21: elevated levels in patients with metastatic hormone-refractory prostate cancer and potential predictive factor for the efficacy of docetaxel-based chemotherapy. Prostate. 2011;71:326–31. doi:10.1002/pros.21246.
Asaga S, Kuo C, Nguyen T, Terpenning M, Giuliano AE, Hoon DS. Direct serum assay for microRNA-21 concentrations in early and advanced breast cancer. Clin Chem. 2011;57:84–91. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2010.151845.
Xu J, Wu C, Che X, Wang L, Yu D, Zhang T, Huang L, Li H, Tan W, Wang C, Lin D. Circulating MicroRNAs, miR-21, miR-122, and miR-223, in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma or chronic hepatitis. Mol Carcinog. 2011;50(2):136–42. doi:10.1002/mc.20712.
Tomimaru Y, Eguchi H, Nagano H, Wada H, Kobayashi S, Marubashi S, Tanemura M, Tomokuni A, Takemasa I, Umeshita K, Kanto T, Doki Y, Mori M. Circulating microRNA-21 as a novel biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2012;56:167–75. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2011.04.026.
Cho WC. MicroRNAs: potential biomarkers for cancer diagnosis, prognosis and targets for therapy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010;42:1273–81. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2009.12.014.
Cho WC. Molecular diagnostics for monitoring and predicting therapeutic effect in cancer. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2011;11:9–12. doi:10.1586/erm.10.111.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsu, CM., Lin, PM., Wang, YM. et al. Circulating miRNA is a novel marker for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 33, 1933–1942 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-012-0454-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-012-0454-8