Abstract
Backgrounds
Lipid metabolism dysregulation is an important characteristic of tumor cells. Increased lipid metabolism provides a vital material and energy source for tumor growth, thereby promoting tumor invasion and metastasis.
Objectives
In the current work, we carried out a series of in vivo and in vitro studies to explore the relationship between miR-29 and lung cancer.
Results
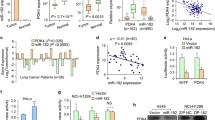
The results showed that miR-29 was down-regulated in lung cancer, and overexpression of miR-29 inhibited the proliferation and migration of lung cancer cells (in vitro). Anti-lung cancer effect of miR-29 in vivo was evaluated, and results indicated that transfection of miR-29b/c markedly inhibited lung tumor growth (in vivo). We further explored the potential mechanism by which miR-29 could inhibit the cell proliferation of lung cancer. It is well known that lipid metabolism dysregulation is an important characteristic of tumor cells. Increased lipid metabolism provides a vital material and energy source for tumor growth, thereby promoting tumor invasion and metastasis, and sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP) is involved in liposome metabolism. Therefore, we analyzed the interaction between miR-29C and SREBP-1 in lung cancer cells. Bioinformatics analysis showed that the miR-29 has the potential binding site on SCAP and SREBP mRNA, and Luciferase reporter gene assays revealed the interaction between 3′UTR of SREBP-1 mRNA and miR-29c. Further study showed that miR-29 suppressed (SREBP-1) expression by interacting with 3′UTR of SREBP-1. Further work indicated that miR-29 transfection strongly inhibited lung cancer cell proliferation, which was rescued by the overexpression of SREBP-1.
Conclusion
These findings demonstrate that transfection of miR-29 suppressed lung cancer proliferation via inhibiting SREBP-1 expression. The current study provides a basis for exploring the targeted agents against lung cancer.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheng C et al (2015) Glucose-mediated n-glycosylation of scap is essential for srebp-1 activation and tumor growth. Cancer Cell 28(5):569–581
Cheng X, Li J et al (2018) Scap/srebps are central players in lipid metabolism and novel meta-bolic targets in cancer therapy. Curr Top Med Chem. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568026618666180523104541
Cong MA et al (2009) Micrornas-powerful repression comes from small Rnas. China C Life 52(004):323–330
Fabbri M et al (2007) Microrna-29 family reverts aberrant methylation in lung cancer by targeting dna methyltransferases 3a and 3b. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104(40):15805–15810
Guo D et al (2009) Egfr signaling through an akt-srebp-1–dependent, rapamycin-resistant pathway sensitizes glioblastomas to antilipogenic therapy. Sci Signal 2(101):ra82
Guo D et al (2014) Targeting SREBP-1-driven lipid metabolism to treat cancer. Curr Pharm Des 20(15):2619–2626
Guy AT et al (2021) Lipids as new players in axon guidance and circuit development. Curr Opin Neurobiol 66:22–29
Kaoru et al (2001) Is the determination of serum lipoprotein lipase useful for the analysis of diseases with abnormal lipid metabolism? Jpn J Clin Chem 30(2):86–90
Li X et al (2012) Abstract 4728: fatostatin, a novel SREBP inhibitor, suppresses cell growth and induces apoptosis in prostate cancer. Can Res 72:4728–4728
Menendez JA et al (2007) Fatty acid synthase and the lipogenic phenotype in cancer pathog enesis. NatRev Cancer 7(10):763–777. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2222
Miranda B et al (2015) Clinical potential of gene mutations in lung cancer. Clin Transl Med 4(1):1–2
Morton JD et al (1999) Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins. Curr Opin Lipidol 10(2):143–150
Okubo M et al (2006) Renal diseases and abnormal lipid metabolism. J Rural Med. https://doi.org/10.2185/jrm.1.2_13
Ru P et al (2016) Feedback loop regulation of SCAP/SREBP-1 by mir-29 modulates EGFR signaling-driven glioblastoma growth. Cell Rep. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.07.017
Saito T et al (1997) Abnormal lipid metabolism and renal disorders. Tohoku J Exp Al Med 181(3):321–337
Sun Y et al (2015) SREBP1 regulates tumorigenesis and prognosis of pancreatic cancer through targeting lipid metabolism. Tumour Biol 36(6):4133–4141
Sundqvist A et al (2005) Control of lipid metabolism by phosphorylation-dependent degradation of the SREBP family of transcription factors by scf(fbw7). Cell Metab 1(6):379–391
Swierczynski J et al (2014) Role of abnormal lipid metabolism in development, progression, diagnosis and therapy of pancreatic cancer. World J Gastroenterol. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i9.2279
Wang T et al (2017) Aspirin suppresses the abnormal lipid metabolism in liver cancer cells via disrupting a nf kappa b-acsl1 signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 486(3):827–832
Wong RH et al (2010) Insulin signaling in fatty acid and fat synthesis: a transcriptional perspective. Curr Opin Pharmacol 10(6):684–691
Wu X et al (2017) Lncrna-PAGBC acts as a Microrna sponge and promotes gallbladder tumorigenesis. EMBO Rep 18(10):e201744147
Yamada N et al (1999) Abnormal lipid metabolism in tangier disease. Nippon rinsho. Jpn J Clin Med 41(8):1817–1823
Yang L et al (2015) Relationship between genetic polymorphisms in mcp-1, ccr-2, and non-small-cell lung cancer in the han nationality of northern china. Genet Mol Res. https://doi.org/10.4238/2015.April.22.2
Acknowledgements
The author thanks Dr. Zhao for his help in FACS and CLSM analysis.
Funding
This research was supported by the first affiliated hospital of Harbin Medical University (Grant 20200506).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LL and WZ designed the study. YB, MT, QR, and WZ designed and performed the experiments. LL wrote the manuscript. YB, MT, QR, and LL revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Lin Lin, Yongxia Bao, Miao Tian, Qiu Ren, and Wei Zhang declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All animal procedures were conducted according to Regulations for the Administration of Affairs Concerning Experimental Animals (The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China, 1988).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, L., Bao, Y., Tian, M. et al. miR-29 family inhibited the proliferation and migration of lung cancer cells by targeting SREBP-1. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 18, 165–175 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-021-00180-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-021-00180-3