Abstract
Background
The ark shell (Scapharca broughtonii) is one of the most economically important mollusks in the Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea of China. In recent years, ark shells from the Korean population were introduced to China for seed propagation and culture.
Objective
To explore the impact of the introduction of Korean ark shell on the genetic diversity of native population in China.
Methods
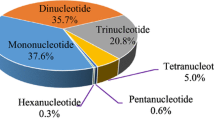
Simple sequence repeat (SSR) is effective and widely used tool for genetic analysis. In this study, 180 EST-SSRs were selected and verified by polymerase chain reaction and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Subsequently, five polymorphic EST-SSRs were screened and their primers were modified by fluorescein for use in the genetic analysis of four populations.
Results
Genetic analysis showed that 361 alleles amplified by five SSR loci were detected in the four populations. The number of alleles for the five SSRs ranged from 8 to 30, with a mean of 18.05 (standard deviation, SD = 6.492). The effective number of alleles varied from 2.253 to 22.222, with a mean of 10.596 (SD = 4.713). Observed heterozygosity and expected heterozygosity were 0.167–0.833 and 0.566–0.971, with average values of 0.520 (SD = 0.177) and 0.891 (SD = 0.062), respectively. Polymorphic information content ranged from 0.521 to 0.953, with a mean of 0.865 (SD = 0.070). The pairwise genetic differentiation coefficient (FST) of the four populations ranged from 0.0267 to 0.0477, showing low genetic differentiation. The phylogenetic tree constructed by neighbor-joining method showed that the genetic distance between the Chinese Dalian native population and three Korean populations was relatively more far than that among those Korean populations.
Conclusion
The results indicated that the genetic structure of the Dalian wild population was less affected by the introduced Korean wild populations.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
An HY, Park JY (2005) Ten new highly polymorphic microsatellite loci in the blood clam Scapharca broughtonii. Mol Ecol Notes 5(4):896–898
Cai Q, Aitken KS, Fan YH et al (2005) A preliminary assessment of the genetic relationship between Erianthus rockii and the “Saccharum complex” using microsatellite (SSR) and AFLP markers. Plant Sci 169(5):976–984
Cai Z, Zheng Y, Ren L et al (2016) Growth and survival of the first hybrid generation of Chinese and Korean populations of Scapharca broughtonii. Prog Fish Sci 37(6):81–86
Cho YG, Ishii T, Temnykh S et al (2000) Diversity of microsatellites derived from genomic libraries and GenBank sequences in rice (Oryza sativa L.). TAG Theor Appl Genet 100(5):713–722
Cho E, Jung C, Sohn S et al (2007) Population genetic structure of the ark shell Scapharca broughtonii schrenck from Korea, China, and Russia based on COI gene sequences. Mar Biotechnol 9(2):203–216
Guo XL (2016) A comparative study on physiological metabolism and growth characteristics of Scapharca broughtonii from China and south Korea [dissertation]. Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai
Hu Y, Zhao P, Zhang Q et al (2015) De novo assembly and characterization of transcriptome using Illumina sequencing and development of twenty five microsatellite markers for an endemic tree Juglans hopeiensis Hu in China. Biochem Syst Ecol 63:201–211
Jee YJ, Kim WJ, Kim BH et al (2012) Genetic variation of wild and hatchery populations of the Korean ark shell, Scapharca broughtonii assessed by microsatellite markers. Korean J Malacol 28(3):269–274
Jurgen T, Dan G (1988) Nei's Modified Genetic Identity and Distance Measures and Their Sampling Variances. Systematic Zoology 37(2):156
Laurent V, Devaux P, Thiel T et al (2007) Comparative effectiveness of sugar beet microsatellite markers isolated from genomic libraries and GenBank ESTs to map the sugar beet genome. Theor Appl Genet 115(6):793–805
Li J, Li Q (2008) Isolation and characterization of twelve novel microsatellite loci in the ark shell Scapharca broughtonii. Conserv Genet 9(4):1055–1057
Li Q, Park C, Kijima A (2002) Isolation and characterization of microsatellite loci in the Pacific abalone, Haliotis discus hannai. Shellfish Res 21:811–815
Li L, Guo X, Zhang G (2009) Inheritance of 15 microsatellites in the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas: segregation and null allele identification for linkage analysis. Chin J Oceanol Lirrmol 27(1):74–79
Li M, Zhu L, Zhou C et al (2012) Development and characterization of EST-SSR markers from Scapharca broughtonii and their transferability in Scapharca subcrenata and Tegillarca granosa. Molecules 17:10716–10723
Li R, Li Q, Wang C (2013) Sibship reconstruction and effective population size estimation in mass spawning ark shell, Scapharca broughtonii based on microsatellite analysis. Genes Genom 35(6):703–708
Li N, Li Q, Kong L et al (2016) Development of three multiplex PCR primer sets for ark shell (Scapharca broughtonii) and their validation in parentage assignment. Ocean Univ China 15:311–317
Liu H, Wu B, Liu Z et al (2017) Genetic diversity and geographic population structures of Scapharca broughtonii. Prog Fish Sci 38(6):92–99
Lönneborg A, Sharma P, Stougaard P (1995) Construction of subtractive cDNA library using magnetic beads and PCR. Pcr Methods Appl 4(4):S168
Lu X, Wang H, Dai P et al (2011) Characterization of EST-SSR and genomic-SSR markers in the clam, Meretrix meretrix. Conserv Genet Resour 3(4):655–658
Pan T, Zhang Y, Gao T et al (2014) Genetic diversity of Pleuronectes yokohamae population revealed by fluorescence microsatellite labeled. Biochem Syst Ecol 55:118–124
Parthiban S, Govindaraj P, Senthilkumar S (2018) Comparison of relative efficiency of genomic SSR and EST-SSR markers in estimating genetic diversity in sugarcane. 3 Biotech 8(3):144–155
Sándor N, Péter P et al (2012) PICcalc: an online program to calculate polymorphic information content for molecular genetic studies. Biochem Genet 50:670-672**
Santos CA, Rossini BC, Marques CG et al (2012) Characterization and genomic annotation of polymorphic EST-SSR loci in Litopenaeus vannamei shrimp. Aquac Res 43(10):1567–1570
Schuelke M (2000) An economic method for the fluorescent labeling of PCR fragments. Nat Biotechnol 18(2):233–234
Sekino M, Kurokawa T, Sasaki K (2010) Multiplex PCR panels of novel microsatellites for the ark shell Scapharca broughtonii (Pteriomorphia, Arcoida). Conserv Genet Resour 2(S1):39–42
Sudhir K, Glen S, Michael L et al (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35(6):1547–1549
Sun X, Li D, Liu Z et al (2017) De novo assembly of pen shell (Atrina pectinata) transcriptome and screening of its genic microsatellites. Ocean Univ China 16(5):882–888
Tanaka T, Aranishi F (2016) Comparative genetic characterization of ark shell Scapharca broughtoniiin northeast Asia. Shellfish Res 35(2):421–427
Tian J, Liu Z, Zhou L et al (2012) Isolation and characterization of 48 polymorphic microsatellite markers for the blood clam Scapharca broughtonii (Arcidae). Genet Mol Res 11(4):4501–4507
Tian J, Liu Z, Yang A et al (2013) Microsatellite analysis of genetic diversity in four geographic populations of Scapharca broughtonii. Prog Fish Sci 34(06):59–67
Varshney RK, Chabane K, Hendre PS et al (2007) Comparative assessment of EST-SSR, EST-SNP and AFLP markers for evaluation of genetic diversity and conservation of genetic resources using wild, cultivated and elite barleys. Plant Sci 173(6):638–649
Wang Y, Wang X, Wang A et al (2010) A 16-microsatellite multiplex assay for parentage assignment in the eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica Gmelin). Aquaculture 308(2010):S28–S33
Wang Z, Li J, Hao R et al (2019a) Characterization and development of SSR markers of Pinctada maxima by RNA-Seq approach. Aquac Rep 15:100230
Wang Z, Liang F, Huang R et al (2019b) Identification of the differentially expressed genes of Pinctada maxima individuals with different sizes through transcriptome analysis. Reg Stud Mar Sci 26:100512
Wu B, Liang C, Yang A et al (2012) Genetic variation in different populations of Scapharca broughtonii schrenck inferred from microsatellite data. Oceanol Limnol Sin 43(04):863–869
Xue S, Wang J, Li J et al (2019) Effects of temperature on energy metabolism and antioxidant enzyme activities of Scapharca broughtonii. Fish China 43(03):573–583
Yu H, Gao S, Chen A et al (2015) Genetic diversity and population structure of the ark shell Scapharca broughtonii along the coast of China based on microsatellites. Biochem Syst Ecol 58:235–241
Zhang Y, Lin Z, Xia Q et al (2008) Characteristics and analysis of simple sequence repeats in the cotton genome based on a linkage map constructed from a BC1 population between Gossypium hirsutum and G. barbadense. Genome 51(7):534–546
Zhu C, Pan Z, Wang H et al (2017) Development of 34 polynucleotide repeat microsatellites for Chinese lake gudgeon (Sarcocheilichthys sinensis Bleeker, 1871) by transcriptome sequencing. Appl Ichthyol 33(3):566–571
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the financial grants from Key R & D project of Shandong Province (2018GHY115030, 2019JZZY020706), National Key R&D Pro-gram of China (2018YFD0900304) and Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund (HY2019-JC02, 20603022019003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human subjects performed by any of the above authors. The research was conducted in the absence of any ethical issue on animal research.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Wu, B., Liu, Z. et al. Development of EST-SSRs from the ark shell (Scapharca broughtonii) transcriptome and their application in genetic analysis of four populations. Genes Genom 43, 669–677 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-021-01090-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-021-01090-3