Abstract
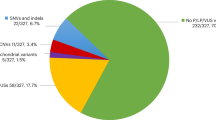
X-linked hydrocephalus, MASA syndrome, X-linked complicated Spastic Paraplegia Type I, and X-linked partial agenesis of the corpus callosum are rare diseases mainly affecting male population and broadly referred as L1 syndrome, caused by mutations in the L1CAM gene. In the present study 36 boys and a male fetus whose clinical features were consistent with L1 syndrome were analyzed by dHPLC assay and direct sequencing of L1CAM gene. Sequence analysis of the 14 different aberrant dHPLC elution profiles demonstrated that six of them were associated with already reported polymorphisms, four with previously described causative variants while the remaining four represented novel L1CAM mutations. The dHPLC method proposed identified eight (21 %) causative L1CAM mutations in our patients while direct sequencing failed to detect any variation in patients negative to dHPLC analysis. We conclude that the dHPLC assay represents a fast and efficient method for the screening of L1CAM mutations and that L1 syndrome should be considered in the differential diagnosis of intellectual disability in children, especially when other signs such as hydrocephalus or adducted thumbs are present.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adzhubei I, Jordan DM, Sunyaev SR (2013) Predicting functional effect of human missense mutations using PolyPhen-2. Curr Protoc Hum Genet 7:7–20. doi:10.1002/0471142905.hg0720s76
Coutelle O, Nyakatura G, Taudien S, Elgar G, Brenner S, Platzer M, Drescher B, Jouet M, Kenwrick S, Rosenthal A (1998) The neural cell adhesion molecule L1: genomic organisation and differential splicing is conserved between man and the pufferfish Fugu. Gene 208:7–15
Finckh U, Schröder J, Ressler B, Veske A, Gal A (2000) Spectrum and detection rate of L1CAM mutations in isolated and familial cases with clinically suspected L1-disease. Am J Med Genet 92:40–46
Fransen E, Lemmon V, Van Camp G, Vits L, Coucke P, Willems PJ (1995) CRASH syndrome: clinical spectrum of corpus callosum hypoplasia, retardation, adducted thumbs, spastic paraparesis and hydrocephalus due to mutations in one single gene, L1. Eur J Hum Genet 3:273–284
Fransen E, Van Camp G, Vits L, Willems PJ (1997) L1-associated diseases: clinical geneticists divide, molecular geneticists. Hum Mol Genet 6:1625–1632
Fransen E, Van Camp G, D’Hooge R, Vits L, Willems PJ (1998) Genotype–phenotype correlation in L1 associated diseases. J Med Genet 35:399–404
Grumet M, Edelman GM (1988) Neuron–glia cell adhesion molecule interacts with neurons and astroglia via different binding mechanisms. J Cell Biol 106:487–503
Gu SM, Orth U, Zankl M (1997) Molecular analysis of the L1CAM gene in patients with X-linked hydrocephalus demonstrates eight novel mutations and suggests non-allelic heterogeneity of the trait. Am J Med Genet 71:336–340
Haney CA, Sahenk Z, Li C (1999) Heterophilic binding of L1 on unmyelinated sensory axons mediates Schwann cell adhesion and is required for axonal survival. J Cell Biol 146:1173–1184
Hlavin ML, Lemmon V (1991) Molecular structure and functional testing of human L1CAM: an interspecies comparison. Genomics 11:416–423
Jouet M, Rosenthal A, Kenwrick S (1995) Exon 2 of the gene for neural cell adhesion molecule L1 is alternatively spliced in B cells. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 30:378–380
Kamiguchi H, Hlavin ML, Yamasaki M, Lemmon V (1998) Adhesion molecules and inherited diseases of the human nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci 21:97–125
Lemmon V, Farr KL, Lagenaur C (1989) L1-mediated axon outgrowth occurs via a homophilic binding mechanism. Neuron 2:1597–1603
Lindner J, Rathjen FG, Schachner M (1983) L1 mono-and polyclonal antibodies modify cell migration in early postnatal mouse cerebellum. Nature 305:427–430
Moos M, Tacke R, Scherer H, Teplow D, Früh K, Schachner M (1988) Neural adhesion molecule L1 as a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily with binding domains similar to fibronectin. Nature 334:701–703
Persohn E, Schachner M (1987) Immunoelectron microscopic localization of theneural cell adhesion molecules L1 and N-CAM during postnatal development of the mouse cerebellum. J Cell Biol 105:569–576
Shaw M, Yap TY, Henden L, Bahlo M, Gardner A, Kalscheuer VM, Haan E, Christie L, Hackett A, Gecz J (2015) Identical by descent L1CAM mutation in two apparently unrelated families with intellectual disability without L1 syndrome. Eur J Med Genet 58:364–368
Stumpel C, Vos YJ (2004) L1 Syndrome. In: Pagon RA, Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, Bean LJH, Bird TD, Dolan CR, Fong CT, Smith RJH, Stephens K (eds) GeneReviews® [Internet]. University of Washington, Seattle, pp 1993–2015
Vos YJ, de Walle HE, Bos KK, Stegeman JA, Ten Berge AM, Bruining M, van Maarle MC, Elting MW, den Hollander NS, Hamel B et al (2010) Genotype–phenotype correlations in L1 syndrome: a guide for genetic counselling and mutation analysis. J Med Genet 47:169–175
Wong EV, Kenwrick S, Willems P, Lemmon V (1995) Mutations in the cell adhesion molecule L1 cause mental retardation. Trends Neurosci 18:168–172
Yamasaki M, Thompson P, Lemmon V (1997) CRASH syndrome: mutations in L1CAM correlate with severity of the disease. Neuropediatrics 28:175–178
Acknowledgments
The authors thanks the patients and their family for their participation in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Mirella Vinci, Michele Falco, Lucia Castiglia, Lucia Grillo, Angela Spalletta, Maurizio Sturnio, Ornella Galesi, Michele Salemi, Angelo Gloria, Silvestra Amata, Maria Piccione, Vincenzo Antona, Girolamo Aurelio Vitello, and Marco Fichera declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consents
Informed consents were obtained from the parents of the patients in accordance with the declaration of Helsinki. The study was also approved by the local ethical review board.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vinci, M., Falco, M., Castiglia, L. et al. Identification of novel mutations in L1CAM gene by a DHPLC-based assay. Genes Genom 38, 1159–1164 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-016-0460-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-016-0460-0