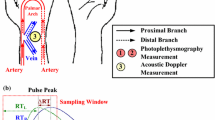
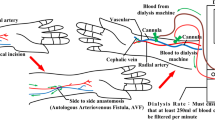
Abstract
In physical examinations, hemodialysis access stenosis leading to dysfunction occurs at the venous anastomosis site or the outflow vein. Information from the inflow stenosis, such as blood pressure, pressure drop, and flow resistance increases, allows dysfunction screening from the stage of early clots and thrombosis to the progression of outflow stenosis. Therefore, this study proposes dysfunction screening model in experimental arteriovenous grafts (AVGs) using the fractional-order extractor (FOE) and the color relation analysis (CRA). A Sprott system was designed using an FOE to quantify the differences in transverse vibration pressures between the inflow and outflow sites of an AVG. Experimental analysis revealed that the degree of stenosis (DOS) correlated with an increase in fractional-order dynamic errors (FODEs). Exponential regression was used to fit a non-linear curve and can be used to quantify the relationship between the FODEs and DOS (R 2 = 0.8064). The specific ranges were used to evaluate the stenosis degree, such as DOS: <50, 50–80, and >80%. A CRA-based screening method was derived from the hue angle-saturation-value color model, which describes perceptual color relationships for the DOS. It has a flexibility inference manner with color visualization to represent the different stenosis degrees, which has average accuracy >90% superior to the traditional methods. This in vitro experimental study demonstrated that the proposed model can be used for dysfunction screening in stenotic AVGs.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asif, Arif, Florin N. Gadalean, Donna Merrill, Gautam Cherla, Cristian D. Cipleu, David L. Epstein, and David Roth. Inflow stenosis in arteriovenous fistulas and grafts: a multicenter, prospective study. Kidney Int. 67:1986–1992, 2005.
Botti, L., K. Van Canneyt, R. Kaminsky, T. Claessens, R. N. Planken, P. Verdonck, A. Remuzzi, and L. Antiga. Numerical evaluation and experimental validation of pressure drops across a patient-specific model of vascular access for hemodialysis. Cardiovasc Eng Technol 4(4):485–499, 2013.
Chang, K.-C., and M.-F. Yeh. Grey relational analysis based approach for data clustering. IEE Proc. Vis. Image Signal Process. 152(2):165–172, 2005.
Chen, W. L., T. Chen, C. H. Lin, P. J. Chen, and C. D. Kan. Phonoangiography with a fractional order chaotic system-a novel and simple algorithm in analyzing residual arteriovenous access stenosis. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 51(9):1011–1019, 2013.
Cohn, J. Arterial compliance to stratify cardiovascular risk: more precision in therapeutic decision making. Am. J. Hypertens. 14(8):S258, 2001.
Du, Y.-C., W.-L. Chen, C.-H. Lin, C.-D. Kan, and M.-J. Wu. Residual stenosis estimation of arteriovenous graft using a dual-channel phonoangiography with fractional-order features. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inf. 19(2):590–600, 2015.
Du, Y.-C., C.-D. Kan, W.-L. Chen, and C.-H. Lin. Estimation residual stenosis for an arteriovenous shunt using a flexible fuzzy classifier. IEEE Comput. Sci. Eng. 16(6):80–91, 2014.
Gonzalez, R., and R. E. Woods. Digital Image Processing (2nd ed.). Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall Press, 2002. ISBN ISBN 0-201-18075-8.
Huynh, Thanh N., B. C. Brott, Y. Ito, C. H. Cheng, A. M. Shih, M. Allon, and A. S. Anayiotos. Turbulent flow evaluation of the venous needle during hemodialysis. J. Biomech. Eng. 127:1141–1146, 2005.
Jasti, V., E. Ivan, V. Yalamanchili, N. Wongpraparut, and M. A. Leesar. Correlations between fractional flow reserve and intravascular ultrasound in patients with an ambiguous left main coronary artery stenosis. Circulation 110(18):2831–2836, 2004.
Kashyap, V. S., R. O. Lakin, L. E. Feiten, P. D. Bishop, and T. P. Sarac. In vivo assessment of endothelial function in human lower extremity arteries. J. Vasc. Surg. 58(5):1259–1266, 2013.
Knuttel, A., and M. Boehlau-Godau. Spatially confined and temporally resolved refractive index and scattering evaluation in human performed with optical coherence tomography. J. Biomed. Opt. 5(1):83–92, 2000.
Kuo, Chao-Lin. Design of an adaptive Fuzzy sliding-mode controller for chaos synchronization. Int. J. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 8(4):631–636, 2007.
Kuo, C.-L., C.-H. Lin, H.-T. Yau, and J.-L. Chen. Using self-synchronization error dynamics formulation based controller for maximum photovoltaic power tracking in micro-grid systems. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Circuits Syst. 3(3):459–467, 2013.
Lantz, J., R. Gardhagen, and M. Karlsson. Quantifying turbulent wall shear stress in a subject specific human aorta using large eddy simulation. Med. Eng. Phys. 34:1139–1148, 2012.
Leea, S. W., P. F. Fischerb, F. Lotha, T. J. Royston, J. K. Grogan, and H. S. Bassiouny. Flow-induced vein-wall vibration in an arteriovenous graft. J. Fluids Struct. 20(6):837–852, 2005.
Lin, C.-H. Assessment of bilateral photoplethysmography for lower limb peripheral vascular occlusive disease using color relation analysis classifier. Comput. Method Progr. Biomed. 103(3):121–131, 2011.
Longest, P. W., and C. Kleinstreuer. Computational hemodynamics analysis and comparison study of arteriovenous grafts. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 24(3):102–110, 2000.
Manos, T. A., D. P. Sokolis, A. T. Giagini, C. H. Davos, J. D. Kakisis, E. P. Kritharis, N. Stergiopulos, P. E. Karayannacos, and S. Tsangaris. Local hemodynamics and intimal hyperplasia at the venous side of a porcine arteriovenous shunt. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 14(3):681–690, 2010.
Misra, Madhukar. The basics of hemodialysis equipment. Hemodial Int 9:30–36, 2005.
Moini, M., M. R. Rasouli, G. M. Williams, S. Najafizadeh, and G. Sheykholeslami. Comparison of side-to-side Brachiocephalic arteriovenous fistula with ligation of the perforating vein with end-to-side Brachiocephalic arteriovenous fistula, Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 17:7–10, 2009.
Nico, H. J., B. Van Gelder, P. Van der Voort, K. Peels, F. A. L. E. Bracke, H. J. R. M. Bonnier, and M. I. H. EI Gamal. Fractional flow reserve: a useful index to evaluate the influence of an epicardial coronary stenosis on myocardial blood flow. Circulation 92(3):183–193, 1995.
Paulson, William D., Sunanda J. Ram, Jack Work, Steven A. Conrad, and Steven A. Jones. Inflow stenosis obscures recognition of outflow stenosis by dialysis venous pressure: analysis by a mathematical model. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 23:3966–3971, 2008.
Podlubny, I. Fractional differential equations, Mathematics in Science and Engineering, Chaps 6 and 10, Vol. 198. New York: Academic Press, 1999.
Sebastian, P., Y. V. Voon, and R. Comley. Colour space effect on tracking in video surveillance. Int. J. Electr. Eng. Inform. 2(4):298–312, 2010.
Sigovan, M., V. Rayz, W. Gasper, H. F. Alley, C. D. Owens, and D. Saloner. Vascular remodeling in autogenous arterio-venous fistulas by MRI and CFD. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 41(4):657–668, 2013.
Stalder, A. F., A. Frydrychowicz, M. F. Russe, J. G. Korvink, J. Hennig, K. Li, and M. Markl. Assessment of flow instabilities in the healthy aorta using flow-sensitive MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 33:839–846, 2011.
Stanziale, R., M. Lodi, E. D’Andrea, F. Sammartino, and V. Dl Luzio. Arteriovenous fistula: end-to-end or end-to-side anastomosis? Hemodial. Int. 15(1):100–103, 2011.
Tordoir, J. H. M. Dialysis: early pre-emptive intervention might reduce AVF access loss. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 10:9–10, 2014.
Tozzi, Piergiorgio, Antonio Corno, and Daniel Hayoz. Definition of arterial compliance. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 278(4):H1407, 2000.
Van Tricht, I., D. De Wachter, J. Tordoir, and P. Verdonck. Hemodynamics in a compliant hydraulic in vitro model of straight versus tapered PTFE aeterivenous graft. J. Surg. Res. 116(2):297–304, 2004.
Wei, C.-C. Analysis of blood pressure wave based on the viewpoint of resonance and coherence, PhD Thesis, College of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science: National Chiao Tung University, 2006.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported in part by the research grant of National Cheng Kung University, under contract number: NCKUH-103-05001, duration: January 1, 2014 ~ December 31, 2014 and the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan, under contract number: MOST 103-2221-E-244-001, duration: August 1 2014 ~ July 31 2015.
Conflict of Interest
The author(s) declare(s) that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this article.
Ethical Approval
Not applicable, the study doesn’t involve human subjects, animal subjects, human embryonic stem cell, and use of cells or tissues obtained by commercial sale.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Associate Editor Ajit P. Yoganathan oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, MJ., Chen, WL., Kan, CD. et al. Dysfunction Screening in Experimental Arteriovenous Grafts for Hemodialysis Using Fractional-Order Extractor and Color Relation Analysis. Cardiovasc Eng Tech 6, 463–473 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13239-015-0239-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13239-015-0239-5