Abstract
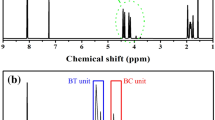
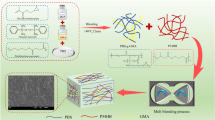
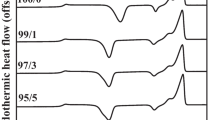
Innovative poly(butylene succinate) (PBS)/Spirulina composites were fabricated by melt blending. Maleic anhydride-grafted PBS (PBS-g-MAH) was synthesized and used as a compatibilizer in the composites. Extra amount of water was added to Spirulina to ensure that it acted as a plastic during blending with PBS. The tensile strength and Young’s modulus of the composites considerably increased after incorporation of PBS-g-MAH due to better interfacial adhesion between the components and better dispersion of Spirulina in the PBS matrix, which were verified by scanning electron microscopy. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy analysis also indicated the reaction between PBS-g-MAH and Spirulina, which resulted in improved Spirulina-PBS interaction. Differential scanning calorimetry analysis revealed that the crystallization temperature of the composites increased after addition of PBS-g-MAH, especially for the composites with higher Spirulina loading, while the PBS in compatibilized composites exhibited higher enthalpies. However, the compatibilized composites exhibited slight decreases of degradation temperature accompanied by slightly higher weight loss as indicated by thermal gravimetric analysis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Zini and M. Scandola, Polym. Compos., 32, 1905 (2011).
R. Muthuraj, M. Misra, and A. K. Mohanty, ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 3, 2767 (2015).
A. A. Shah, F. Hasan, A. Hameed, and S. Ahmed, Biotechnol. Adv., 26, 246 (2008).
J. Xu and B.-H. Guo, Biotechnol. J., 5, 1149 (2010).
Y. Du, S. Li, Y. Zhang, C. Rempel, and Q. Liu, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 133, 43351 (2016).
V. M. Hernandez-Izquierdo and J. M. Krochta, J. Food Sci., 73, 30 (2008).
A. H. Brandenburg, C. L. Weller, and R. F. Testin, J. Food Sci., 58, 1086 (1993).
Z. Zhong and X. S. Sun, Polymer, 42, 6961 (2001).
J. Zhang, L. Jiang, L. Zhu, J.-L. Jane, and P. Mungara, Biomacromolecules, 7, 1551 (2006).
F. Chen and J. Zhang, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2, 3324 (2010).
M. A. Zeller, R. Hunt, A. Jones, and S. Sharma, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 130, 3263 (2013).
H. Duan, R. Ma, X. Xu, F. Kong, S. Zhang, W. Kong, J. Hao, and L. Shang, Environ. Sci. Technol., 43, 3522 (2009).
E. W. Becker, Biotechnol. Adv., 25, 207 (2007).
C. Toro, M. Reddy, R. Navia, M. Rivas, M. Misra, and A. Mohanty, J. Polym. Environ., 21, 944 (2013).
S. Torres, R. Navia, R. Campbell Murdy, P. Cooke, M. Misra, and A. K. Mohanty, ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 3, 614 (2015).
Z. A. M. Ishak, Y. J. Phua, and W. S. Chow, eXPRESS Polym. Lett., 7, 340 (2013).
Q. Yin, F. Chen, H. Zhang, and C. Liu, Plast. Rubber Compos., 44, 362 (2015).
R. Mani, M. Bhattacharya, and J. Tang, J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem., 37, 1693 (1999).
Y. Nabar, J. M. Raquez, P. Dubois, and R. Narayan, Biomacromolecules, 6, 807 (2005).
F. Chen and J. Zhang, Polymer, 51, 1812 (2010).
M.-C. Li, X. Ge, and U. R. Cho, Macromol. Res., 21, 519 (2013).
M.-C. Li and U. R. Cho, Mater. Lett., 92, 132 (2013).
T. Mekonnen, M. Misra, and A. K. Mohanty, ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 4, 782 (2016).
R. Zhu, H. Liu, and J. Zhang, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 51, 7786 (2012).
R. R. N. Sailaja, B. G. Girija, G. Madras, and N. Balasubramanian, J. Mater. Sci., 43, 64 (2008).
X. Zhang and Y. Zhang, Carbohydr. Polym., 134, 52 (2015).
Y.-D. Li, J.-B. Zeng, W.-D. Li, K.-K. Yang, X.-L. Wang, and Y.-Z. Wang, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 48, 4817 (2009).
P. Chen, H. Tian, L. Zhang, and P. R. Chang, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 47, 9389 (2008).
G. M. MacDonald and B. A. Barry, Biochemistry, 31, 9848 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, N., Ye, M., Shi, D. et al. Reactive compatibilization of biodegradable poly(butylene succinate)/Spirulina microalgae composites. Macromol. Res. 25, 165–171 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-017-5025-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-017-5025-9