Abstract
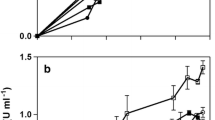
Recombinant Escherichia coli / pAD26 cells were optimally immobilized on cotton to obtain plasmid stability. An experimental design that monitored two major responses, namely stability and reusability, was applied for screening the factors affecting the immobilization of the strain (cylodextrin, sucrose, shape support, mass of cotton matrices, mass of initial biomass, age of biomass, ethylenediamine, glutaraldehyde, and incubation time) and the optimization of the most significant variables. The optimal values recorded for the two criteria were obtained with high glutaraldehyde concentration (0.15 %) and early inoculum age (2 h) in the presence of 0.2 mM cylodextrin. With those optimum conditions, cyclodextrin glucanotransferase production yields were enhanced, reaching up to 39.77 U/mL. The stability and reusability of the immobilized strain were two fold and three fold higher, respectively, than those of the control after three cycles.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bandaru VVR, Somalanka SR, Menduc DR, Madicherla NR, Chityala A (2006) Optimization of fermentation conditions for the production of ethanol from sago starch by co-immobilized amyloglucosidase and cells of Zymomonas mobilis using response surface methodology. Enzym Microb Technol 38:209–214
Bankar SB, Bule MV, Singhal RS, Ananthanarayan L (2009) Optimization of Aspergillus niger Fermentation for the Production of Glucose Oxidase. Food Bioproc Technol 2:344–352
Ben Ali M, Mhiri S, Mezghani M, Bejar S (2001) Purification and sequence analysis of the atypical maltohexaose-forming α-amylase of the B. stearothermophilus US100. Enzym Microb Technol 28:537–542
Bisht D, Yadav SK, Darmwal NS (2013) Optimization of immobilization conditions by conventional and statistical strategies for alkaline lipase production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutant cells: scale-up at bench-scale bioreactor level. Turk J Biol 37:392–404
Chandel AK, Narasu ML, Chandrasekhar G, Manikyam A, Venkateswar Rao L (2009) Use of Saccharum spontaneum (wild sugarcane) as biomaterial for cell immobilization and modulated ethanol production by thermotolerant Saccharomyces cerevisiae VS3. Bioresour Technol 100:2404–2410
Chu YF, Hsu CH, Soma PK, Lo YM (2009) Immobilization of bioluminescent Escherichia coli cells using natural and artificial fibers treated with polyethyleneimine. Bioresour Technol 100:3167–3174
Couto SR (2009) Dye removal by immobilized fungi: a review. Biotechnol Adv 27:227–235
Hajji M, Rebai A, Gharsallah N, Nasri M (2008) Optimization of alkaline protease production by Aspergillus clavatus ES1 in Mirabilis jalapa tuber powder using statistical experimental design. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79:915–923
Hu Y, Tang T, Yang W, Zhou H (2009) Bioconversion of phenylpyruvic acid to L-phenylalanine by mixed-gel immobilization of Escherichia coli EP8-10. Process Biochem 44:142–145
Jemli S, Ben Messaoud E, Ayedi ZD, Naili B, Khemakhem B, Bejar S (2007) A β-cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase from a newly isolated Paenibacillus pabuli US132 strain: Purification, properties and potential use in bread-making. Biochem Eng J 3:44–50
Jemli S, Ben Messaoud E, Ben Mabrouk S, Bejar S (2008) The cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase of Paenibacillus pabuli US132 strain: molecular characterization and overproduction of the recombinant enzyme. J Biomed Biotechnol 10, Article No. 692573
Kammoun R, Naili B, Bejar S (2008) Application of a statistical design to the optimization of parameters and culture medium for α-amylase production by Aspergillus oryzae CBS 819.72 grown on gruel (wheat grinding by-product). Bioresour Technol 99:5602–5609
Kapoor M, Nair LM, Kuhad RC (2008) Cost-effective xylanase production from free and immobilized Bacillus pumilus strain MK001 and its application in saccharification of Prosopis juliflora. Biochem Eng J 38:88–97
Kilonzo PM, Margaritis A, Bergougnou MA (2008) Effects of medium composition on glucoamylase production during batch fermentation of recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiaae. J Inst Brew 114:83–95
Kilonzo P, Margaritis A, Bergougnou M (2009) Airlift-driven fibrous-bed bioreactor for continuous production of glucoamylase using immobilized recombinant yeast cells. J Biotechnol 143:60–68
Krastanov A (1997) Continuous sucrose hydrolysis by yeast cells immobilized to wool. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 47:476–481
Kriaa M, Zouari Ayadi D, Jemli S, Sahnoun M, Bejar S, Kammoun R (2012) Improvement of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase (CGTase) production by recombinant Escherichia coli pAD26 immobilized on the cotton. Biologia 67:1049–1055
Leemhuis H, Kelly RM, Dijkhuizen L (2010) Engineering of cyclodextrine glucanotransferases and the impact for biotechnological applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85:823–835
Mazzer C, Ferreira LR, Rodella JRT, Moriwaki C, Matioli G (2008) Cyclodextrin production by Bacillus firmus strain 37 immobilized on inorganic matrices and alginate gel. Biochem Eng J 41:79–86
Meleigy SA, Khalaf MA (2009) Biosynthesis of gibberellic acid from milk permeate in repeated batch operation by a mutant Fusarium moniliforme cells immobilized on loofa sponge. Bioresour Technol 100:374–379
Moriwaki C, Pelissari FM, Gonçalves RAC, Gonçalves JE, Matioli G (2007) Immobilization of Bacillus firmus strain 37 in inorganic matrix for cyclodextrin production. J Mol Catal B Enzym 49:1–7
Mussatto SI, Aguilar CN, Rodrigues LR, Teixeira JA (2009) Colonization of Aspergillus japonicus on synthetic materials and application to the production of fructooligosaccharides. Carbohydr Res 344:795–800
Nguyen DN, Ton NMN, Le VVM (2009) Optimization of Saccharomyces cerevisiae immobilization in bacterial cellulose by ‘adsorption- incubation’ method. Int Food Res J 16:59–64
Pazzetto R, Delani TCO, Fenelon VC, Matioli G (2011) Cyclodextrin production by Bacillus firmus strain 37 cells immobilized on loofa sponge. Process Biochem 46:46–51
Saudagar PS, Shaligram NS, Singhal RS (2008) Immobilization of Streptomyces clavuligerus on loofa sponge for the production of clavulanic acid. Bioresour Technol 99:2250–2253
Vassileva A, Beschkov V, Ivanova V, Tonkova A (2003) Cyclodextrin glucanotransferase production by free and agar gel immobilized cells of Bacillus circulans ATCC 21783. Process Biochem 38:1585–1591
Wu J, Wang JL, Li MH, Lin JP, Wei DZ (2010) Optimization of immobilization for selective oxidation of benzyl alcohol by Gluconobacter oxydans using response surface methodology. Bioresour Technol 101:8936–8941
Yu J, Zhang X, Tan T (2007) An novel immobilization method of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to sorghum bagasse for ethanol production. J Biotechnol 129:415–420
Yu J, Zhang X, Tan T (2009) Optimization of media conditions for the production of ethanol from sweet sorghum juice by immobilized Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biomass Bioenergy 33:521–526
Zouari AD, Kammoun R, Jemli S, Chouayekh H, Bejar S (2011) Secretion of cyclodextrin glucanotransferase in E. coli using Bacillus subtilis lipase signal peptide and optimization of the culture medium. Indian J Exp Biol 50:72–79
Zulfikri AR, Rosli MI, Nor MM, Osman H (2008) Experimental design to optimization of beta cyclodextrine production from ungelatinized sago starch. Eur Food Res Technol 226:1421–1427
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Tunisian Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research and Technology (contract program LMB-CBS, grant no. RL02CBS01). The authors would like to express their sincere gratitude to Mr. Anouar Smaoui and Mrs. Hanen Ben Salem from the English Language Unit at the Faculty of Science of Sfax for their constructive language editing and proofreading services.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kriaa, M., Ayadi-Zouari, D., Sahnoun, M. et al. Improved stability and reusability of cotton-immobilized recombinant Escherichia coli producing US132 Cyclodextrin Glucanotransferase. Ann Microbiol 65, 383–391 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-014-0870-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-014-0870-7