Abstract
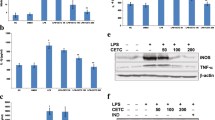
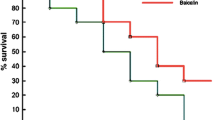
Antibiotics and immunotherapies possess unavoidable adverse effects that hinder sepsis management. Herbal drugs have demonstrated potential immunomodulatory properties vital for sepsis treatment. We hypothesized in the present study that the use of Carica papaya leaves extract had the potential to improve survival and modulate immune cytokine release during sepsis. Animals were subjected to cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) to induce sepsis. Septic rats divided into 10 groups received ethanol extract of C. papaya leaves (50 and 100 mg/kg), imipenem (120 mg/kg) and cyclophosphamide (CP, 10 mg/kg). To investigate the immunomodulatory potentials of EE, cytokine levels like interleukin (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α), and IL-10 along with hematological and biochemical parameters were analyzed. Our results exhibited improved survival rates concerning ethanol extract treatment alone and in combination with imipenem and CP (100%) as compared to the CLP group (33.3%) on day 7 post-surgery. The combination treatment of ethanol extract with imipenem and CP significantly (P < 0.001) ameliorated cytokine levels and hematological and biochemical parameters in septic rats. A histopathological examination suggested improved liver and kidney tissue condition after combination treatment as compared to the CLP group. Therefore, it was concluded that combination therapy of extract with imipenem and CP improved survival rates and marked immunomodulatory potential in septic rats compared to monotherapy. The findings suggested the use of a mixture of these drugs in clinical settings to treat sepsis.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Available upon request.
References
Ahn HK, Koo KC, Chung BH, Lee KS (2018) Comparison of the delta neutrophil index with procalcitonin, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and C-reactive protein as predictors of sepsis in patients with acute prostatitis. Prostate Int 6:157–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PRNIL.2018.05.001
Aird WC (2003) The hematologic system as a marker of organ dysfunction in sepsis. Mayo Clin Proc 78:869–881. https://doi.org/10.4065/78.7.869
Ajiboye AE, Olawoyin RA (2020) Antibacterial activities and phytochemical screening of crude extract of Carica papaya leaf against selected pathogens. Glob J Pure Appl Sci 26:165–170. https://doi.org/10.4314/gjpas.v26i2.8
Ansari MN, Bhandari U, Pillai KK (2016) Protective role of curcumin in myocardial oxidative damage induced by isoproterenol in rats. 26:933–938. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327107085835
Ansari MN, Saeedan AS, Bajaj S, Singh L (2021) Evaluation of antidiabetic and hypolipidemic activity of Barleria cristata Linn. leaves in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. 3 Biotech 114:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13205-021-02728-5
Arulkumaran N, Sixma ML, Pollen S, et al (2018) P2X 7 receptor antagonism ameliorates renal dysfunction in a rat model of sepsis. Physiol Rep 6:e13622. https://doi.org/10.14814/PHY2.13622
Barati M, Alinejad F, Bahar MA et al (2008) Comparison of WBC, ESR, CRP and PCT serum levels in septic and non-septic burn cases. Burns 34:770–774. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BURNS.2008.01.014
Bone RC (1991) A critical evaluation of new agents for the treatment of sepsis. JAMA J Am Med Assoc 266:1686–1691. https://doi.org/10.1001/JAMA.1991.03470120088038
Bone RC (1992) Modulators of coagulation: a critical appraisal of their role in sepsis. Arch Intern Med 152(7):3
Bone RC (1992) Modulators of coagulation: a critical appraisal of their role in sepsis. Arch Intern Med 152(7):1
Brown I, Bellevue O, Shawo A et al (2015) Low dose cyclophosphamide improves survival in a murine treatment model of sepsis. Shock 43:92. https://doi.org/10.1097/SHK.0000000000000263
Bryda O, Stadnytska N (2021) Extraction methods of extractive substances from medicinal plant raw materials: advantages and limitations. Ann Rom Soc Cell Biol 25:1737–1751
Calandra T, Glauser MP, Schellekens J, Verhoef J (1988) Treatment of gram-negative septic shock with human IgG antibody to Escherichia coli J5: a prospective, double-blind, randomized trial. J Infect Dis 158:312–319. https://doi.org/10.1093/INFDIS/158.2.312
Carbonell LF, Nadal JA, Llanos MC et al (2000) Depletion of liver glutathione potentiates the oxidative stress and decreases nitric oxide synthesis in a rat endotoxin shock model. Crit Care Med 28:2002–2006. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003246-200006000-00054
Christaki E, Anyfanti P, Opal SM (2011) Immunomodulatory therapy for sepsis: an update. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 9:1013–1033
Cirioni O, Ghiselli R, Tomasinsig L et al (2008) Efficacy of LL-37 and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in a neutropenic murine sepsis due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Shock 30:443–448. https://doi.org/10.1097/SHK.0B013E31816D2269
Coopersmith CM, Amiot DM, Stromberg PE et al (2003) Antibiotics improve survival and alter the inflammatory profile in a murine model of sepsis from Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia. Shock 19:408–414. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.SHK.0000054370.24363.EE
Coskun AK, Yigiter M, Oral A et al (2011) The effects of montelukast on antioxidant enzymes and proinflammatory cytokines on the heart, liver, lungs, and kidneys in a rat model of cecal ligation and puncture-induced sepsis. Sci World J 11:1341–1356. https://doi.org/10.1100/TSW.2011.122
D’Agostino P, La Rosa M, Barbera C et al (1998) Doxycycline reduces mortality to lethal endotoxemia by reducing nitric oxide synthesis via an interleukin-10-independent mechanism. J Infect Dis 177:489–492. https://doi.org/10.1086/517383
Dewitte A, Lepreux S, Villeneuve J et al (2017) Blood platelets and sepsis pathophysiology: a new therapeutic prospect in critical ill patients? Ann Intensive Care 71(7):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1186/S13613-017-0337-7
Esmon CT (2005) The interactions between inflammation and coagulation. Br J Haematol 131:417–430. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1365-2141.2005.05753.X
Faix JD (2013) Biomarkers of sepsis. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 50:23–36. https://doi.org/10.3109/10408363.2013.764490
Fourrier F, Chopin C, Goudemand J et al (1992) Septic shock, multiple organ failure, and disseminated intravascular coagulation. Compared patterns of antithrombin III, protein C, and protein S deficiencies. Chest 101:816–823. https://doi.org/10.1378/CHEST.101.3.816
Gaieski DF, Edwards JM, Kallan MJ, Carr BG (2013) Benchmarking the incidence and mortality of severe sepsis in the united states. Crit Care Med 41:1167–1174. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0B013E31827C09F8
Guclu E, Durmaz Y, Karabay O (2013) Effect of severe sepsis on platelet count and their indices. Afr Health Sci 13:333–338. https://doi.org/10.4314/AHS.V13I2.19
Guo P, Zhang SW, Zhang J et al (2018) Effects of imipenem combined with low-dose cyclophosphamide on the intestinal barrier in septic rats. Exp Ther Med 16:1919. https://doi.org/10.3892/ETM.2018.6373
Hasimun P, Suwendar EGI (2014) Analgetic activity of papaya (Carica papaya L.) leaves extract. Procedia Chem 13:147–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PROCHE.2014.12.019
Hassaan PS, Mehanna RA, Dief AE (2015) The potential role of hemopexin and heme oxygenase-1 inducer in a model of sepsis. Physiol J 2015:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/208485
Herwald HEA (2011) Sepsis-pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory responses. Contrib Microbiol. Basel; Karger: 1–11
Hotchkiss RS, Opal S (2010) Immunotherapy for sepsis–a new approach against an ancient foe. N Engl J Med 363:87–89. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMCIBR1004371
Huang M, Cai S, Su J (2019) The pathogenesis of sepsis and potential therapeutic targets. Int J Mol Sci 20:5376. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJMS20215376
Iba T, Umemura Y, Wada H, Levy JH (2021) Roles of coagulation abnormalities and microthrombosis in sepsis: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Arch Med Res 52:788–797. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ARCMED.2021.07.003
Ita SO, Akpanyung EO, Robert AS et al (2016) Evaluation of some inflammatory biomarkers in male albino wistar rats following ingestion of crude oil and the role of bee honey, vitamins C and E. Mod Res Inflamm 05:55–62. https://doi.org/10.4236/MRI.2016.53006
Jantan I, Ahmad W, Science SB-F in P, 2018 U (2018) Corrigendum: Plant-derived immunomodulators: An insight on their preclinical evaluation and clinical trials. frontiersin.org 9:1178:
Jung SM, Kim YJ, Ryoo SM, Kim WY (2019) Relationship between low hemoglobin levels and mortality in patients with septic shock. Acute Crit Care 34:141–147. https://doi.org/10.4266/ACC.2019.00465
Kalechman Y, Gafter U, Gal R et al (2002) Anti-IL-10 therapeutic strategy using the immunomodulator AS101 in protecting mice from sepsis-induced death: dependence on timing of immunomodulating intervention. J Immunol 169:384–392. https://doi.org/10.4049/JIMMUNOL.169.1.384
Lee IC, Bae JS (2019) Pelargonidin protects against renal injury in a mouse model of sepsis. J Med Food 22:57–61. https://doi.org/10.1089/JMF.2018.4230
Lee W, Lee Y, Jeong GS et al (2017) Cudratricusxanthone A attenuates renal injury in septic mice. Food Chem Toxicol 106:404–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FCT.2017.06.009
Lin SR, Chang CH, Hsu CF et al (2020) Natural compounds as potential adjuvants to cancer therapy: preclinical evidence. Br J Pharmacol 177:1409–1423. https://doi.org/10.1111/BPH.14816
Lupu F, Kinasewitz G, Dormer K (2020) The role of endothelial shear stress on haemodynamics, inflammation, coagulation and glycocalyx during sepsis. J Cell Mol Med 24:12258–12271. https://doi.org/10.1111/JCMM.15895
Mannaa FA, Abdel-Wahhab KG, Abdel-Wahhab MA (2014) Prevention of cardiotoxicity of aflatoxin B1 via dietary supplementation of papaya fruit extracts in rats. Cytotechnology 66:327–334. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10616-013-9579-X/TABLES/2
Mukherjee PK, Nema NK, Bhadra S et al (2014) Immunomodulatory leads from medicinal plants. Indian J Tradit Knowl 13:235–256
Nnaemeka UM, Ugwu, Ukamaka IA, et al (2023) Comparative study of aqueous, methanol and petroleum ether extracts of unripe Carica papaya seed on liver and kidney function in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. GSC Biol Pharm Sci 22:038–047. https://doi.org/10.30574/gscbps.2023.22.1.0488
Patel A, Joseph J, Periasamy H, Mokale S (2018) Azithromycin in combination with ceftriaxone reduces systemic inflammation and provides survival benefit in a murine model of polymicrobial sepsis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00752-18
Patil US, Jaydeokar AV, Bandawane DD (2012) Immunomodulators: a pharmacological review. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 4:30–36
Pereira RS, Bertoncheli CM, Adefegha SA et al (2017) Sepsis induced by cecal ligation and perforation (CLP) alters nucleotidase activities in platelets of rats. Microb Pathog 111:345–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MICPATH.2017.08.047
Peter JK, Kumar Y, Pandey P et al. (2014) Antibacterial activity of seed and leaf extract of Carica Papaya var. Pusa dwarf Linn. Sci J pharm Biol 9(2):29–37
Petronilho F, Florentino D, Danielski LG et al (2016) Alpha-lipoic acid attenuates oxidative damage in organs after sepsis. Inflammation 39:357–365. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10753-015-0256-4
Rahmani AH, Aldebasi YH (2016) Potential role of carica papaya and their active constituents in the prevention and treatment of diseases Implication of PTEN, akt and bcl2 expressions and its co-relation with apoptotic pathways in oral squamous cell carcinoma View project Natural product. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 8:11–15
Remick DG, Bolgos GR, Siddiqui J et al (2002) Six at six: interleukin-6 measured 6 h after the initiation of sepsis predicts mortality over 3 days. Shock 17:463–467. https://doi.org/10.1097/00024382-200206000-00004
Resim S, Kurutas EB, Gul AB et al (2015) The levels of oxidative stress biomarkers in rats as a response to different techniques of testicular biopsy. Indian J Surg 77:310–313. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12262-013-0808-5
Rhodes A, Evans LE, Alhazzani W et al (2017) Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock: 2016. Intensive Care Med 433(43):304–377. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00134-017-4683-6
Ritter C, Andrades M, Frota MLC et al (2003) Oxidative parameters and mortality in sepsis induced by cecal ligation and perforation. Intensive Care Med 29:1782–1789. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00134-003-1789-9
Ross D (1988) Glutathione, free radicals and chemotherapeutic agents. Mechanisms of free-radical induced toxicity and glutathione-dependent protection. Pharmacol Ther 37:231–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/0163-7258(88)90027-7
Sapin F, Biston P, Piagnerelli M (2017) Predictive value of C-reactive protein in critically ill patients after abdominal surgery. Clinics
Satran R, Almog Y (2003) The coagulopathy of sepsis: pathophysiology and management. Isr Med Assoc J 5:516–520
Scartezzini P, Speroni E (2000) Review on some plants of Indian traditional medicine with antioxidant activity. J Ethnopharmacol 71:23–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-8741(00)00213-0
Shapira L, Aubrey Soskolne W, Houri Y et al (1996) Protection against endotoxic shock and lipopolysaccharide-induced local inflammation by tetracycline: correlation with inhibition of cytokine secretion. Infect Immun 64:825–828. https://doi.org/10.1128/iai.64.3.825-828.1996
Sinha H, Maitra S, Anand RK et al (2021) Epidemiology and prognostic utility of cellular components of hematological system in sepsis. Indian J Crit Care Med 25:660. https://doi.org/10.5005/JP-JOURNALS-10071-23874
Somayaji YT, Vidya V, Rao S et al (2016) Modulatory effects of Carica papaya ( Linn.) on electron beam radiation induced hematological suppression and biochemical alterations in swiss albino mice. J Biochem Technol 7:1044–1050
Upadhyay G, Tiwari N, Maurya H, et al (2021) In vivo wound-healing and antioxidant activity of aqueous extract of Roylea elegans leaves against physically induced burn model in Wistar albino rats. 3 Biotech 1110(11):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13205-021-02993-4
Usmani J, Khan T, Ahmad R, Sharma M (2021) Potential role of herbal medicines as a novel approach in sepsis treatment. Biomed Pharmacother 144:112337
Vyas D, Javadi P, Di Pasco PJ, et al (2005) Early antibiotic administration but not antibody therapy directed against IL-6 improves survival in septic mice predicted to die on basis of high IL-6 levels. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1152/AJPREGU.00312.2005
Wang D, Yin Y, Yao Y (2014) Advances in sepsis-associated liver dysfunction. Burn Trauma 2:97–105. https://doi.org/10.4103/2321-3868.132689
Watanabe E, Thampy LK, Hotchkiss RS (2018) Immunoadjuvant therapy in sepsis: novel strategies for immunosuppressive sepsis coming down the pike. Acute Med Surg 5:309–315. https://doi.org/10.1002/AMS2.363
Weighardt H, Heidecke CD, Emmanuilidis K et al (2000) Sepsis after major visceral surgery is associated with sustained and interferon-gamma-resistant defects of monocyte cytokine production. Surgery 127:309–315. https://doi.org/10.1067/MSY.2000.104118
Yang J, Zhang S, Wu J et al (2018) Imipenem and normal saline with cyclophosphamide have positive effects on the intestinal barrier in rats with sepsis. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub 162:90–98. https://doi.org/10.5507/BP.2018.032
Zeni F, Freeman B, Natanson C (1997) Anti-inflammatory therapies to treat sepsis and septic shock: a reassessment. Crit Care Med 25:1095–1100. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003246-199707000-00001
Zilahi G, McMahon MA, Povoa P, Martin-Loeches I (2016) Duration of antibiotic therapy in the intensive care unit. J Thorac Dis 8:3774. https://doi.org/10.21037/JTD.2016.12.89
Funding
This research received no funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, JU, RA; Data curation, JU; Formal analysis, JU, MW, RA; Investigation, JU, MW, MH, RA; Methodology, JU, RA; Project administration, JU, RA; Resources, JU, MNA, MH, MJ, RA; Supervision, MNA, MH, MJ, RA; Validation, RA; Visualization, JU, RA; Writing—original draft, JU, MW, MNA, MJ, RA; Writing—review and editing, JU, MW, MNA, MH, MJ, RA.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors of the present study declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Usmani, J., Wasim, M., Ansari, M.N. et al. Potential therapeutic effect of Carica papaya leaves extract on immune response, biochemical and hematological mechanisms on cecal ligation and puncture model of sepsis in rats: an in vivo study. 3 Biotech 13, 151 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03567-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03567-2