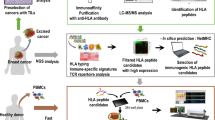
Abstract
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is an aggressive, metastatic/invasive sub-class of breast cancer (BCa). Cell surface protein-derived multi-epitope vaccine-mediated targeting of TNBC cells could be a better strategy against the disease. Literature-based identified potential cell surface markers for TNBC cells were subjected to expression pattern and survival analysis in BCa patient sample using TCGA database. The cytotoxic and helper T-lymphocytes antigenic epitopes in the test proteins were identified, selected and fused together with the appropriate linkers and an adjuvant, to construct the multi-epitope vaccine (MEV). The immune profile, physiochemical property (PP) and world population coverage of the MEV was studied. Immune simulation, cloning in a suitable vector, molecular docking (against Toll-like receptors, MHC (I/II) molecules), and molecular dynamics simulations of the MEV was performed. Cell surface markers were differentially expressed in TNBC samples and showed poor survival in TNBC patients. Satisfactory PP and WPC (up to 89 and 99%) was observed. MEV significant stable binding with the immune molecules and induced the immune cells in silico. The designed vaccine has capability to elicit immune response which could be utilized to target TNBC alone/combination with other therapy. The experimental studies are required to check the efficacy of the vaccine.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Latif M, Youness RA (2020) Why natural killer cells in triple negative breast cancer? World J Clin Oncol 11:464–476. https://doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v11.i7.464
Bussi G, Donadio D, Parrinello M (2007) Canonical sampling through velocity rescaling. J Chem Phys 126:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2408420
Chandrashekar DS, Bashel B, Balasubramanya SAH, Creighton CJ, Ponce-Rodriguez I, Chakravarthi BVSK, Varambally S (2017) UALCAN: a portal for facilitating tumor subgroup gene expression and survival analyses. Neoplasia 19:649–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neo.2017.05.002
Cîmpean AM, Ribatti D, Raica M (2017) Triple negative breast cancer: the kiss of death. Oncotarget 8:46652–46662. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.16938
Cubas R, Zhang S, Li M, Chen C, Yao Q (2011) Chimeric Trop2 virus-like particles: a potential immunotherapeutic approach against pancreatic cancer. J Immunother 34:251–263. https://doi.org/10.1097/CJI.0b013e318209ee72
Drabner B, Guzmán CA (2001) Elicitation of predictable immune responses by using live bacterial vectors. Biomol Eng 17:75–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1389-0344(00)00072-1
Folcik VA, An GC, Orosz CG (2007) The basic immune simulator: an agent-based model to study the interactions between innate and adaptive immunity. Theor Biol Med Model 4:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-4682-4-39
Forero A, Li Y, Chen D, Grizzle WE, Updike KL, Merz ND, Downs-Kelly E, Burwell TC, Vaklavas C, Buchsbaum DJ, Myers RM, LoBuglio AF, Varley KE (2016) Expression of the MHC class II pathway in triple-negative breast cancer tumor cells is associated with a good prognosis and infiltrating lymphocytes. Cancer Immunol Res 4:390–399. https://doi.org/10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-15-0243
Gupta S, Singh AK, Kushwaha PP, Prajapati KS, Shuaib M, Senapati S, Kumar S (2020) Identification of potential natural inhibitors of SARS-CoV2 main protease by molecular docking and simulation studies. J Biomol Struct Dyn 2020:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2020.1776157
Hassan R, Thomas A, Alewine C, Le DT, Jaffee EM, Pastan I (2016) Mesothelin immunotherapy for cancer: ready for prime time? J Clin Oncol 34:4171–4189. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2016.68.3672
Hess B, Bekker H, Berendsen HJ, Fraaije JG (1997) LINCS: a linear constraint solver for molecular simulations. J Comput Chem 18:1463–1472
Jiang T, Shi T, Zhang H, Hu J, Song Y, Wei J, Ren S, Zhou C (2019) Tumor neoantigens: from basic research to clinical applications. J Hematol Oncol 12:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-019-0787-5
Jorgovanovic D, Song M, Wang L, Zhang Y (2020) Roles of IFN-γ in tumor progression and regression: a review. Biomark Res 8:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40364-020-00228-x
Kardani K, Bolhassani A, Namvar A (2020) An overview of in silico vaccine design against different pathogens and cancer. Expert Rev Vaccines 19(8):699–726. https://doi.org/10.1080/14760584.2020.1794832
Kushwaha PP, Singh AK, Prajapati KS, Shuaib M, Gupta S, Kumar S (2021) Phytochemicals present in Indian ginseng possess potential to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 virulence: a molecular docking and MD simulation study. Microb Pathog 157:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2021.104954
Kwon J, Eom KY, Koo TR, Kim BH, Kang E, Kim SW, Kim YJ, Park SY, Kim IA (2017) A prognostic model for patients with triple-negative breast cancer: importance of the modified Nottingham prognostic index and age. J Breast Cancer 20:65–73. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2015.61
Lemkul J (2019) From proteins to perturbed Hamiltonians: a suite of tutorials for the GROMACS-2018 molecular simulation package. LiveCoMS 1:1–53
Lindahl A, Hess VDS, van der Spoel D (2020) GROMACS 2020.2 Source code 2020
Ling B, Watt K, Banerjee S, Newsted D, Truesdell P, Adams J, Sidhu SS, Craig AWB (2017) A novel immunotherapy targeting MMP-14 limits hypoxia, immune suppression and metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer models. Oncotarget 8:58372–58385. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.17702
Mrabet M, Cabaud O, Josselin E, Finetti P, Castellano R, Farina A, Agavnian-Couquiaud E, Saviane G, Collette Y, Viens P, Gonçalves A, Ginestier C, Charafe-Jauffret E, Birnbaum D, Olive D, Bertucci F, Lopez M (2017) Nectin-4: a new prognostic biomarker for efficient therapeutic targeting of primary and metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Ann Oncol 28:769–776. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdw678
Nagy Á, Munkácsy G, Győrffy B (2021) Pancancer survival analysis of cancer hallmark genes. Sci Rep 11:6047–6057. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-84787-5
Parrinello M, Rahman A (1981) Polymorphic transitions in single crystals: a new molecular dynamics method. J Appl Phys 52:7182–7190. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9dt02916h
Quintero M, Adamoski D, Reis LMD, Ascenção CFR, Oliveira KRS, Gonçalves KA, Dias MM, Carazzolle MF, Dias SMG (2017) Guanylate-binding protein-1 is a potential new therapeutic target for triple-negative breast cancer. BMC Cancer 17:727–733. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-017-3726-2
Rapin N, Lund O, Bernaschi M, Castiglione F (2010) Computational immunology meets bioinformatics: the use of prediction tools for molecular binding in the simulation of the immune system. PLoS ONE 5:9862–9876. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0009862
Riggio AI, Varley KE, Welm AL (2021) The lingering mysteries of metastatic recurrence in breast cancer. Br J Cancer 24:13–26. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-020-01161-4
Sanchez-Trincado JL, Gomez-Perosanz M, Reche PA (2017) Fundamentals and methods for T- and B-cell epitope prediction. J Immunol Res 2017:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2680160
Sharma N, Patiyal S, Dhall A, Pande A, Arora C, Raghava GPS (2020) AlgPred 2.0: an improved method for predicting allergenic proteins and mapping of IgE epitopes. Brief Bioinform 17:294–306. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbaa294
Shi S, Xu C, Fang X, Zhang Y, Li H, Wen W, Yang G (2020) Expression profile of Toll-like receptors in human breast cancer. Mol Med Rep 21:786–794. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2019.10853
Singh AK, Kushwaha PP, Prajapati KS, Shuaib M, Gupta S, Kumar S (2021) Identification of FDA approved drugs and nucleoside analogues as potential SARS-CoV-2 A1 pp domain inhibitor: an in silico study. Comp Biol Med 130:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2020.104185
Song Y, DiMaio F, Wang RY, Kim D, Miles C, Brunette T, Thompson J, Baker D (2013) High-resolution comparative modeling with RosettaCM. Structure 21:1735–1742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2013.08.005
Tuomela J, Sandholm J, Karihtala P, Ilvesaro J, Vuopala KS, Kauppila JH, Kauppila S, Chen D, Pressey C, Härkönen P, Harris KW, Graves D, Auvinen PK, Soini Y, Jukkola-Vuorinen A, Selander KS (2012) Low TLR9 expression defines an aggressive subtype of triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 135:481–493. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-012-2181-7
Turdo F, Bianchi F, Gasparini P, Sandri M, Sasso M, De Cecco L, Forte L, Casalini P, Aiello P, Sfondrini L, Agresti R, Carcangiu ML, Plantamura I, Sozzi G, Tagliabue E, Campiglio M (2016) CDCP1 is a novel marker of the most aggressive human triple-negative breast cancers. Oncotarget 7:69649–69665. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.11935
Tursynbay Y, Zhang J, Li Z, Tokay T, Zhumadilov Z, Wu D, Xie Y (2016) Pim-1 kinase as cancer drug target: An update. Biomed Rep 4:140–146. https://doi.org/10.3892/br.2015.561
Wan Q, Qu J, Li L, Gao F (2021) Guanylate-binding protein 1 correlates with advanced tumor features, and serves as a prognostic biomarker for worse survival in lung adenocarcinoma patients. J Clin Lab Anal 35:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcla.23610
Wilkins MR, Gasteiger E, Bairoch A, Sanchez JC, Williams KL, Appel RD, Hochstrasser DF (1999) Protein identification and analysis tools in the ExPASy server. Methods Mol Biol 112:531–552. https://doi.org/10.1385/1-59259-584-7:531
Zhang L (2018) Multi-epitope vaccines: a promising strategy against tumors and viral infections. Cell Mol Immunol 15(2):182–184. https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2017.92
Acknowledgements
SK acknowledges Indian Council of Medical Research, India and Department of Science and Technology, India for providing financial support in the form Ad-hoc Project [No. 5/13/15/2020/NCD-III] and DST-SERB Grant [EEQ/2016/000350], respectively. SK also acknowledges DST-India for providing Departmental grant to the Department of Biochemistry, Central University of Punjab, Bathinda, India in the form of DST-FIST grant. KSP acknowledge Department of Biotechnology, India for providing DBT-Senior Research Fellowship. MS acknowledges Indian Council of Medical Research, India for providing ICMR-Senior Research fellowship [File No. 5/3/8/80/ITR-F/2020-ITR]. AKS acknowledges CSIR, India for providing CSIR-Senior Research Fellowship. SS and PC acknowledge Central Computing Facility, Indian Institute of Information Technology-Allahabad, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SK conceptualized, supervised, the study and wrote the original draft of the manuscript; KSP, MS, and AKS curated the data and analyzed them. PC and SS generated MD simulation data and AKS analyzed it. SG critically read the manuscript and provided his valuable suggestions.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, S., Shuaib, M., Prajapati, K.S. et al. A candidate triple-negative breast cancer vaccine design by targeting clinically relevant cell surface markers: an integrated immuno and bio-informatics approach. 3 Biotech 12, 72 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-022-03140-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-022-03140-3