Abstract
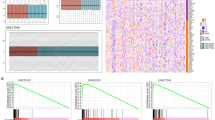
The purpose of this study was to identify biomarkers and construct a diagnostic prediction model for multiple sclerosis (MS). Microarray datasets in the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) were downloaded. Weighted gene coexpression analysis (WGCNA) was used to search for hub modules and biomarkers related to MS. Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analyses were used to roughly define their biological functions and pathways. Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression and multivariate logistic regression analysis were used to identify the diagnostic biomarkers and construct a nomogram. The calibration curve and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve were used to judge the diagnostic predictive ability. In addition, cell-type identification by estimating relative subsets of RNA transcripts (CIBERSORT) algorithm was used to calculate the proportion of 22 kinds of immune cells. GSE41850 was used as the training set, and GSE17048 was used as the test set. WGCNA revealed one hub module containing 165 hub genes. Most of their biological functions and pathways are related to cell metabolism and immune cell activation. The diagnostic nomogram contained ARPC5, ROD1, UBQLN2, ZNF281, ABCA1 and FAS. The ROC curve and the calibration curve of the training set and test set confirmed that the nomogram had great prediction ability. In addition, monocytes and M0 macrophages were significantly different between MS patients and healthy people. The expression of ARPC5, ZNF281 and ABCA1 is correlated with M0 macrophages. The nomogram provides new insights and contributes to the accurate diagnosis of MS.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad U, Frederiksen JL (2020) Fibrinogen: a potential biomarker for predicting disease severity in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler Relat Disord 46:102509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msard.2020.102509
Balendra R, Isaacs AM (2018) C9orf72-mediated ALS and FTD: multiple pathways to disease. Nat Rev Neurol 14:544–558. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41582-018-0047-2
Bogie JFJ, Grajchen E, Wouters E et al (2020) Stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 impairs the reparative properties of macrophages and microglia in the brain. J Exp Med 217:e20191660. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20191660
Chen H, Chen C, Yuan X, Xu W, Yang MQ, Li Q, Shen Z, Yin L (2020a) Identification of immune cell landscape and construction of a novel diagnostic nomogram for Crohn’s disease. Front Genet 11:423. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2020.00423
Chen X, Li Y, Xiao J, Zhang H, Yang C, Wei Z, Chen W, Du X, Liu J (2020b) Modulating neuro-immune-induced macrophage polarization with topiramate attenuates experimental abdominal aortic aneurysm. Front Pharmacol 11:565461. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.565461
Choi JE, Lee JJ, Kang W, Kim HJ, Cho JH, Han PL, Lee KJ (2018) Proteomic analysis of hippocampus in a mouse model of depression reveals neuroprotective function of ubiquitin c-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCH-L1) via stress-induced cysteine oxidative modifications. Mol Cell Proteom 17:1803–1823. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.RA118.000835
Chow ML, Winn ME, Li HR, April C, Wynshaw-Boris A, Fan JB, Fu XD, Courchesne E, Schork NJ (2012) Preprocessing and quality control strategies for illumina DASL assay-based brain gene expression studies with semi-degraded samples. Front Genet 3:11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2012.00011
de Oliveira GLV, Ferreira AF, Gasparotto EPL et al (2017) Defective expression of apoptosis-related molecules in multiple sclerosis patients is normalized early after autologous haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Clin Exp Immunol 187:383–398. https://doi.org/10.1111/cei.12895
Eskandarian Z, Fliegauf M, Bulashevska A, Proietti M, Hague R, Smulski CR, Schubert D, Warnatz K, Grimbacher B (2019) Corrigendum: assessing the functional relevance of variants in the IKAROS family zinc finger protein 1 (IKZF1) in a cohort of patients with primary immunodeficiency. Front Immunol 10:1490. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01490
Gandhi KS, McKay FC, Cox M et al (2010) The multiple sclerosis whole blood mRNA transcriptome and genetic associations indicate dysregulation of specific T cell pathways in pathogenesis. Hum Mol Genet 19:2134–2143. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddq090
Hagman S, Raunio M, Rossi M, Dastidar P, Elovaara I (2011) Disease-associated inflammatory biomarker profiles in blood in different subtypes of multiple sclerosis: prospective clinical and MRI follow-up study. J Neuroimmunol 234:141–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2011.02.009
Høglund RA, Lossius A, Johansen JN, Homan J, Benth JŠ, Robins H, Bogen B, Bremel RD, Holmøy T (2017) In silico prediction analysis of idiotope-driven T-B cell collaboration in multiple sclerosis. Front Immunol 8:1255. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.01255
Jha NK, Kar R, Niranjan R (2019) ABC transporters in neurological disorders: an important gateway for botanical compounds mediated neuro-therapeutics. Curr Top Med Chem 19:795–811. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568026619666190412121811
Kouchaki E, Namdari M, Khajeali N, Etesam F, Asgarian FS (2020) Prevalence of suicidal ideation in multiple sclerosis patients: meta-analysis of international studies. Soc Work Public Health. https://doi.org/10.1080/19371918.2020.1810839
Labib DA, Ashmawy I, Elmazny A, Helmy H, Ismail RS (2020) Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 expression on peripheral blood lymphocytes and neutrophils of Egyptian multiple sclerosis patients. Int J Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207454.2020.1812601
Langfelder P, Horvath S (2008) WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform 9:559. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-9-559
Lavon I, Heli C, Brill L, Charbit H, Vaknin-Dembinsky A (2019) Blood levels of co-inhibitory-receptors: a biomarker of disease prognosis in multiple sclerosis. Front Immunol 10:835. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.00835
Liao Y, Wang Y, Cheng M, Huang C, Fan X (2020a) Weighted gene coexpression network analysis of features that control cancer stem cells reveals prognostic biomarkers in lung adenocarcinoma. Front Genet 11:311. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2020.00311
Liao Y, Xiao H, Cheng M, Fan X (2020b) Bioinformatics analysis reveals biomarkers with cancer stem cell characteristics in lung squamous cell carcinoma. Front Genet 11:427. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2020.00427
Ludolph AC, Brettschneider J, Weishaupt JH (2012) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Curr Opin Neurol 25:530–535. https://doi.org/10.1097/wco.0b013e328356d328
Ma X, Zhang L, Huang D, Lyu J, Fang M, Hu J, Zang Y, Zhang D, Shao H, Ma L, Tian J, Dong D, Lou X (2019) Quantitative radiomic biomarkers for discrimination between neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder and multiple sclerosis. J Magn Reson Imaging 49(4):1113–1121. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.26287
Manouchehrinia A, Zhu F, Piani-Meier D, Lange M, Silva DG, Carruthers R, Glaser A, Kingwell E, Tremlett H, Hillert J (2019) Predicting risk of secondary progression in multiple sclerosis: a nomogram. Multiple Scler 25(8):1102–1112. https://doi.org/10.1177/1352458518783667
Millard TH, Behrendt B, Launay S, Fütterer K, Machesky LM (2003) Identification and characterisation of a novel human isoform of Arp2/3 complex subunit p16-ARC/ARPC5. Cell Motil Cytoskelet 54(1):81–90. https://doi.org/10.1002/cm.10104
Mohammadzadeh A, Pourfathollah AA, Sahraian MA, Behmanesh M, Daneshmandi S, Moeinfar Z, Heidari M (2012) Evaluation of apoptosis-related genes; Fas (CD94), FasL (CD178) and TRAIL polymorphisms in Iranian multiple sclerosis patients. J Neurol Sci 312:166–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2011.07.037
Moriya Y, Nohata N, Kinoshita T, Mutallip M, Okamoto T, Yoshida S, Suzuki M, Yoshino I, Seki N (2011) Tumor suppressive microRNA-133a regulates novel molecular networks in lung squamous cell carcinoma. J Hum Genet 57:38–45. https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2011.126
Newman AM, Liu CL, Green MR, Gentles AJ, Feng W, Xu Y, Hoang CD, Diehn M, Alizadeh AA (2015) Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat Methods 12:453–457. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3337
Nickles D, Chen HP, Li MM, Khankhanian P, Madireddy L, Caillier SJ, Santaniello A, Cree BAC, Pelletier D, Hauser SL, Oksenberg JR, Baranzini SE (2013) Blood RNA profiling in a large cohort of multiple sclerosis patients and healthy controls. Hum Mol Genet 22:4194–4205. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddt267
Picher-Martel V, Valdmanis PN, Gould PV, Julien JP, Dupré N (2016) From animal models to human disease: a genetic approach for personalized medicine in ALS. Acta Neuropathol Commun 4:70. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-016-0340-5
Pieraccioli M, Nicolai S, Antonov A, Somers J, Malewicz M, Melino G, Raschellà G (2015) ZNF281 contributes to the DNA damage response by controlling the expression of XRCC2 and XRCC4. Oncogene 35:2592–2601. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.320
Polman CH, Reingold SC, Banwell B et al (2011) Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2010 revisions to the McDonald criteria. Ann Neurol 69:292–302. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.22366
Ribatti D, Tamma R, Annese T (2020) Mast cells and angiogenesis in multiple sclerosis. Inflamm Res 69:1103–1110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-020-01394-2
Riveros C, Mellor D, Gandhi KS et al (2010) A transcription factor map as revealed by a genome-wide gene expression analysis of whole-blood mRNA transcriptome in multiple sclerosis. PLoS ONE 5:e14176. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0014176
Sol N, Leurs CE, Veld SGIT, Strijbis EM, Vancura A, Schweiger MW, Teunissen CE, Mateen FJ, Tannous BA, Best MG, Würdinger T, Killestein J (2020) Blood platelet RNA enables the detection of multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler J Exp Transl Clin 6:2055217320946784. https://doi.org/10.1177/2055217320946784
Spirin NN, Kasatkin DS, Stepanov IO, Shipova EG, Baranova NS, Vinogradova TV, Molchanova SS, Kiselev DV, Shadrichev VA, Spirina NN, Kachura DA (2020) Dinamika osnovnykh epidemiologicheskikh pokazatelei rasseyannogo skleroza po rezul'tatam sravneniya registrov patsientov 1999 i 2019 gg. v Yaroslavle [Registry-based comparison of multiple sclerosis epidemiology trend data in 1999 and 2019: the case of Yaroslavl]. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova 120:48–53. https://doi.org/10.17116/jnevro202012007248
Tian Z, Song Y, Yao Y, Guo J, Gong Z, Wang Z (2020) Genetic etiology shared by multiple sclerosis and ischemic stroke. Front Genet 11:646. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2020.00646
Truong SN, Shin S, Byeon SD, Song J, Mo HS, Min KS (2015) Comparative study on statistical-variation tolerance between complementary crossbar and twin crossbar of binary nano-scale memristors for pattern recognition. Nanoscale Res Lett 10:405. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-015-1106-x
Vasquez MM, Hu C, Roe DJ, Chen Z, Halonen M, Guerra S (2016) Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator type methods for the identification of serum biomarkers of overweight and obesity: simulation and application. BMC Med Res Methodol 16:154. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-016-0254-8
Vengoechea J, David MP, Yaghi SR, Carpenter L, Rudnicki SA (2013) Clinical variability and female penetrance in X-linked familial FTD/ALS caused by a P506S mutation in UBQLN2. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Front Degener 14:615–619. https://doi.org/10.3109/21678421.2013.824001
Vogel DYS, Heijnen PDAM, Breur M, de Vries HE, Tool ATJ, Amor S, Dijkstra CD (2014) Macrophages migrate in an activation-dependent manner to chemokines involved in neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflammation 11:23. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-11-23
Volpe E, Sambucci M, Battistini L, Borsellino G (2016) Fas-fas ligand: checkpoint of T cell functions in multiple sclerosis. Front Immunol 7:382. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2016.00382
Yamamoto H, Tsukahara K, Kanaoka Y, Jinno S, Okayama H (1999) Isolation of a mammalian homologue of a fission yeast differentiation regulator. Mol Cell Biol 19:3829–3841. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.19.5.3829
Zhao AG, Li T, You SF, Zhao HL, Gu Y, Tang LD, Yang JK (2008) Effects of Wei Chang An on expression of multiple genes in human gastric cancer grafted onto nude mice. World J Gastroenterol 14:693–700. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.693
Zheng W, Chen Y, Chen H, Xiao W, Liang Y, Wang N, Jiang X, Wen S (2018) Identification of key target genes and biological pathways in multiple sclerosis brains using microarray data obtained from the Gene Expression Omnibus database. Neurol Res 40:883–891. https://doi.org/10.1080/01616412.2018.1497253
Zheng M, Tian SZ, Capurso D et al (2019) Multiplex chromatin interactions with single-molecule precision. Nature 566:558–562. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-0949-1
Zhou Y, Zou H, Wu E, Huang L, Yin R, Mei Y, Zhu X (2018) Overexpression of ROD1 inhibits invasion of breast cancer cells by suppressing the translocation of β-catenin into the nucleus. Oncol Lett 16:2645–2653. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.8917
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HL conceived and designed the study, acquired and analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. YS and RC contributed to data analysis and manuscript preparation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The researcher claims no conflicts of interests.
Availability of data and material
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. The datasets (GSE41850 and GSE17048) provided by Gene Expression Omnibus can be found here: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Sun, Y. & Chen, R. Constructing and validating a diagnostic nomogram for multiple sclerosis via bioinformatic analysis. 3 Biotech 11, 127 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02675-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02675-1